
A uniform wire of resistance $ 24\Omega $ is used to form a regular hexagon $ ABCDEFA $ . The equivalent resistance of the loop between $ A $ and $ B $ is $ ..........\Omega $
$ \left( A \right){\text{ 4}}{\text{.8}}\Omega $
$ \left( B \right){\text{ 3}}{\text{.3}}\Omega $
$ \left( C \right){\text{ 48}}\Omega $
$ \left( D \right){\text{ 33}}\Omega $
Answer
555k+ views
Hint: Since we have a regular hexagonal structure so between $ A $ and $ B $ it will be in parallel resistance. So by using the parallel formula for the resistance, we will be able to solve this question and get to the exact answer.
Formula used
When resistance is in parallel, then
$ \dfrac{1}{{{R_T}}} = \dfrac{1}{{{R_1}}} + \dfrac{1}{{{R_2}}} + \dfrac{1}{{{R_3}}} + ... $
Here, $ {R_T} $ will be the equivalent resistance
And $ {R_1},{R_2},{R_3} $ will be the resistance connected to it in parallel.
Complete step by step solution
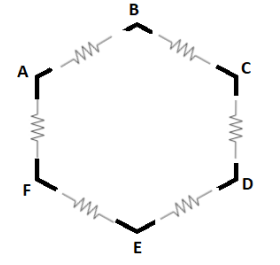
Since the wire is $ 24\Omega $ so by doubling it back on itself. Then it will be divided into six parts and leaving $ 4\Omega $ per segment.
Therefore from this, we will get a resistance of $ 20\Omega $ and $ 4\Omega $ . So by using the formula of resistance in parallel, we will get the equivalent resistance as
$ \Rightarrow {R_T} = \dfrac{{{R_A}{R_B}}}{{{R_A} + {R_B}}} $
Now on substituting the values, we will get
$ \Rightarrow {R_T} = \dfrac{{4 \times 20}}{{4 + 20}} $
And solving the above expression, we get
$ \Rightarrow {R_T} = \dfrac{{80}}{{24}} $
And on solving the division, we will get the equation as
$ \Rightarrow {R_T} = 3.33\Omega $
Therefore, the equivalent resistance of the loop between $ A $ and $ B $ is $ 3.33\Omega $ .
Hence, the option $ \left( b \right) $ is correct.
Additional information
In a parallel circuit, the total current will be equal to the sum of the current in the single circuit whereas in a series circuit, in each of the circuits the current will be similar. In the parallel circuit the voltage across the resistor will be equal to the supply voltage whereas, in a series circuit, the total voltage drop will be the same as the supply voltage.
Note
In a parallel circuit the effective resistance will be more than the minimum value resistance but in parallel, the effective resistance is always less than the minimum value resistance. From this point we can also check if the answer we got is correct or not.
Formula used
When resistance is in parallel, then
$ \dfrac{1}{{{R_T}}} = \dfrac{1}{{{R_1}}} + \dfrac{1}{{{R_2}}} + \dfrac{1}{{{R_3}}} + ... $
Here, $ {R_T} $ will be the equivalent resistance
And $ {R_1},{R_2},{R_3} $ will be the resistance connected to it in parallel.
Complete step by step solution

Since the wire is $ 24\Omega $ so by doubling it back on itself. Then it will be divided into six parts and leaving $ 4\Omega $ per segment.
Therefore from this, we will get a resistance of $ 20\Omega $ and $ 4\Omega $ . So by using the formula of resistance in parallel, we will get the equivalent resistance as
$ \Rightarrow {R_T} = \dfrac{{{R_A}{R_B}}}{{{R_A} + {R_B}}} $
Now on substituting the values, we will get
$ \Rightarrow {R_T} = \dfrac{{4 \times 20}}{{4 + 20}} $
And solving the above expression, we get
$ \Rightarrow {R_T} = \dfrac{{80}}{{24}} $
And on solving the division, we will get the equation as
$ \Rightarrow {R_T} = 3.33\Omega $
Therefore, the equivalent resistance of the loop between $ A $ and $ B $ is $ 3.33\Omega $ .
Hence, the option $ \left( b \right) $ is correct.
Additional information
In a parallel circuit, the total current will be equal to the sum of the current in the single circuit whereas in a series circuit, in each of the circuits the current will be similar. In the parallel circuit the voltage across the resistor will be equal to the supply voltage whereas, in a series circuit, the total voltage drop will be the same as the supply voltage.
Note
In a parallel circuit the effective resistance will be more than the minimum value resistance but in parallel, the effective resistance is always less than the minimum value resistance. From this point we can also check if the answer we got is correct or not.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Giving reasons state the signs positive or negative class 12 physics CBSE

Explain esterification reaction with the help of a class 12 chemistry CBSE

What is defined as a solenoid Depict a diagram with class 12 physics CBSE




