
A uniform disc of mass m, radius r and a point mass m are arranged as shown in the figure. The acceleration of point mass is : (Assume there is no slipping between the pulley and thread and the disc can rotate smoothly about a fixed horizontal axis passing through its centre and perpendicular to its plane).
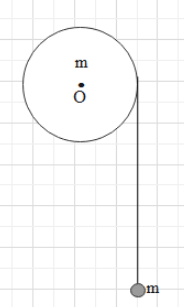
A. $\dfrac{g}{2}$
B. $\dfrac{g}{3}$
C. $\dfrac{2g}{3}$
D. None of these

Answer
569.7k+ views
Hint: To solve the given question we must know about rotational mechanics. Calculate the torque and find the angular acceleration of the disc. With this find the tension in the rope and acceleration of the point mass.
Formula used:
$\tau =F{{r}_{\bot }}$
$\tau =I\alpha $
$a=r\alpha $
${{F}_{g}}=mg$
${{F}_{net}}=ma$
Complete step by step answer:
To the gravitational force acting on the point mass $m$ in the downward direction, the point mass will accelerate downwards. Let its acceleration be $a$.Due to this, there will be a tension created in the thread. Let that tension be $T$.
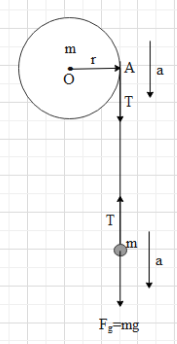
Then the tension in the rope will apply a torque on the disc. As a result, the disc will rotate about the fixed axis at the centre with some angular acceleration.
The magnitude of torque about an axis is given as $\tau =F{{r}_{\bot }}$,
where F is the force acting on the disc,${{r}_{\bot }}$ is the perpendicular distance between the axis of rotation and the force.
In this case, $F=T$ and ${{r}_{\bot }}=r$.
$\Rightarrow \tau =Tr$ …. (i)
The torque is also given as $\tau =I\alpha $ ….. (ii),
where I is the moment of inertia of the body about the axis of rotation and $\alpha $ is the angular acceleration of the body.
The moment of inertia of a disc of mass m and radius r, about a fixed horizontal axis passing through its centre and perpendicular to its plane is equal to $I=\dfrac{m{{r}^{2}}}{2}$.
Substitute the value of I in (ii).
$\Rightarrow \tau =\dfrac{m{{r}^{2}}}{2}\alpha $ …. (iii)
Now equate (i) and (iii).
$\Rightarrow Tr=\dfrac{m{{r}^{2}}}{2}\alpha $
$\Rightarrow \alpha =\dfrac{2T}{mr}$ …(iv)
The linear acceleration of the disc at point A will be $a=r\alpha $
Substitute the value of $\alpha $ from (iv).
$\Rightarrow a=r\left( \dfrac{2T}{mr} \right)=\dfrac{2T}{m}$.
$\Rightarrow T=\dfrac{ma}{2}$ …. (v)
Since it is given that there is no slipping between the thread and the disc, the acceleration of the point mass will be $a$.
Now, let us find the net force on the point mass m.The gravitational force on the mass is ${{F}_{g}}=mg$, where g is acceleration due to gravity (as shown).
Therefore, the net force on the point mass is ${{F}_{net}}={{F}_{g}}-T$.
$\Rightarrow {{F}_{net}}=mg-T$
And from Newton’s second law of motion ${{F}_{net}}=ma$.
$\Rightarrow ma=mg-T$
Substitute the value of T from (v).
$\Rightarrow ma=mg-\dfrac{ma}{2}$
$\Rightarrow a+\dfrac{a}{2}=g$
$\therefore a=\dfrac{2g}{3}$
Therefore, the acceleration of the point mass is equal to $\dfrac{2g}{3}$.
Hence, the correct option is C.
Note:A common mistake that can be done while solving the given question is that the students may assume that the tension in the string to be equal to the gravitational force acting on the point mass, i.e. $T=mg$. However, in that case the mass will be at rest, which is not possible.
Formula used:
$\tau =F{{r}_{\bot }}$
$\tau =I\alpha $
$a=r\alpha $
${{F}_{g}}=mg$
${{F}_{net}}=ma$
Complete step by step answer:
To the gravitational force acting on the point mass $m$ in the downward direction, the point mass will accelerate downwards. Let its acceleration be $a$.Due to this, there will be a tension created in the thread. Let that tension be $T$.

Then the tension in the rope will apply a torque on the disc. As a result, the disc will rotate about the fixed axis at the centre with some angular acceleration.
The magnitude of torque about an axis is given as $\tau =F{{r}_{\bot }}$,
where F is the force acting on the disc,${{r}_{\bot }}$ is the perpendicular distance between the axis of rotation and the force.
In this case, $F=T$ and ${{r}_{\bot }}=r$.
$\Rightarrow \tau =Tr$ …. (i)
The torque is also given as $\tau =I\alpha $ ….. (ii),
where I is the moment of inertia of the body about the axis of rotation and $\alpha $ is the angular acceleration of the body.
The moment of inertia of a disc of mass m and radius r, about a fixed horizontal axis passing through its centre and perpendicular to its plane is equal to $I=\dfrac{m{{r}^{2}}}{2}$.
Substitute the value of I in (ii).
$\Rightarrow \tau =\dfrac{m{{r}^{2}}}{2}\alpha $ …. (iii)
Now equate (i) and (iii).
$\Rightarrow Tr=\dfrac{m{{r}^{2}}}{2}\alpha $
$\Rightarrow \alpha =\dfrac{2T}{mr}$ …(iv)
The linear acceleration of the disc at point A will be $a=r\alpha $
Substitute the value of $\alpha $ from (iv).
$\Rightarrow a=r\left( \dfrac{2T}{mr} \right)=\dfrac{2T}{m}$.
$\Rightarrow T=\dfrac{ma}{2}$ …. (v)
Since it is given that there is no slipping between the thread and the disc, the acceleration of the point mass will be $a$.
Now, let us find the net force on the point mass m.The gravitational force on the mass is ${{F}_{g}}=mg$, where g is acceleration due to gravity (as shown).
Therefore, the net force on the point mass is ${{F}_{net}}={{F}_{g}}-T$.
$\Rightarrow {{F}_{net}}=mg-T$
And from Newton’s second law of motion ${{F}_{net}}=ma$.
$\Rightarrow ma=mg-T$
Substitute the value of T from (v).
$\Rightarrow ma=mg-\dfrac{ma}{2}$
$\Rightarrow a+\dfrac{a}{2}=g$
$\therefore a=\dfrac{2g}{3}$
Therefore, the acceleration of the point mass is equal to $\dfrac{2g}{3}$.
Hence, the correct option is C.
Note:A common mistake that can be done while solving the given question is that the students may assume that the tension in the string to be equal to the gravitational force acting on the point mass, i.e. $T=mg$. However, in that case the mass will be at rest, which is not possible.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




