
A tower has a flag staff at its top which subtends equal angles $\alpha $ at a points distance $9\,yds$ and $11\,yds$ from the foot of the tower. If $\tan \alpha = \dfrac{1}{{10}}$, find the height of the tower and the flag staff.
Answer
511.8k+ views
Hint:The given question belongs to the height and distances concept of trigonometry domain. In the problem, a tower is given to us with a flag staff above it. The flag staff subtends equal angle at two points whose distances from the foot of the tower are given to us. So, we first draw a figure to represent the situation and understand the problem more clearly. We introduce some variables for the length of tower and flag staff and form a relation between them.
Complete step by step answer:
The situation can be represented as in the figure below:
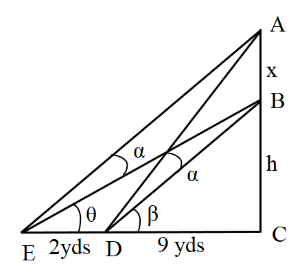
Let the height of the tower be $h$ yards and height of flag staff be $x$ yards. Also, let the angles $\angle BEC = \theta $ and $\angle BDC = \beta $. Then, in triangle BDC,
\[\tan \beta = \dfrac{{{\text{Altitude}}}}{{{\text{Base}}}} = \dfrac{{BC}}{{DC}}\]
\[ \Rightarrow \tan \beta = \dfrac{h}{9} - - - - \left( 1 \right)\]
Also, in triangle BEC,
\[\tan \theta = \dfrac{{{\text{Altitude}}}}{{{\text{Base}}}} = \dfrac{{BC}}{{CE}}\]
Now, we know that $CE = CD + DE = 11$yards. So, we get,
\[ \Rightarrow \tan \theta = \dfrac{h}{{11}} - - - - \left( 2 \right)\]
Now, in triangle ACD, we have,
$\tan \left( {\alpha + \beta } \right) = \dfrac{{{\text{Altitude}}}}{{{\text{Base}}}} = \dfrac{{x + h}}{9}$
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{\tan \alpha + \tan \beta }}{{1 - \tan \alpha \tan \beta }} = \dfrac{{x + h}}{9}$
Now, putting in the value of $\tan \alpha $ and $\tan \beta $ in the expression, we get,
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{\dfrac{1}{{10}} + \dfrac{h}{9}}}{{1 - \dfrac{1}{{10}} \times \dfrac{h}{9}}} = \dfrac{{x + h}}{9}$
Simplifying the expression, we get,
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{\dfrac{{9 + 10h}}{{90}}}}{{1 - \dfrac{h}{{90}}}} = \dfrac{{x + h}}{9}$
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{\dfrac{{9 + 10h}}{{90}}}}{{\dfrac{{90 - h}}{{90}}}} = \dfrac{{x + h}}{9}\]
Cancelling the common factors in numerator and denominator, we get,
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{9 + 10h}}{{90 - h}} = \dfrac{{x + h}}{9}\]
Cross multiplying the terms, we get,
\[ \Rightarrow 81 + 90h = 90x - xh - {h^2} + 90h\]
Cancelling like terms with opposite signs, we get,
\[ \Rightarrow 81 = 90x - xh - {h^2} - - - - \left( 3 \right)\]
Now, in triangle ACE, we have,
$\tan \left( {\alpha + \theta } \right) = \dfrac{{{\text{Altitude}}}}{{{\text{Base}}}} = \dfrac{{x + h}}{{11}}$
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{\tan \alpha + \tan \theta }}{{1 - \tan \alpha \tan \theta }} = \dfrac{{x + h}}{{11}}$
Now, putting in the value of $\tan \alpha $ and $\tan \theta $ in the expression, we get,
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{\dfrac{1}{{10}} + \dfrac{h}{{11}}}}{{1 - \dfrac{1}{{10}} \times \dfrac{h}{{11}}}} = \dfrac{{x + h}}{{11}}$
Simplifying the expression, we get,
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{\dfrac{{11 + 10h}}{{110}}}}{{1 - \dfrac{h}{{110}}}} = \dfrac{{x + h}}{{11}}$
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{\dfrac{{11 + 10h}}{{110}}}}{{\dfrac{{110 - h}}{{110}}}} = \dfrac{{x + h}}{{11}}$
Cancelling the common factors in numerator and denominator, we get,
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{11 + 10h}}{{110 - h}} = \dfrac{{x + h}}{{11}}$
Cross multiplying the terms, we get,
$ \Rightarrow 121 + 110h = 110x - xh - {h^2} + 110h$
$ \Rightarrow 121 = 110x - xh - {h^2} - - - - \left( 4 \right)$
Subtracting equation $\left( 3 \right)$ from equation $\left( 4 \right)$, we get,
\[ \Rightarrow 121 - 81 = 110x - xh - {h^2} - \left( {90x - xh - {h^2}} \right)\]
Cancelling common terms with opposite signs, we get,
\[ \Rightarrow 121 - 81 = 110x - xh - {h^2} - 90x + xh + {h^2}\]
\[ \Rightarrow 40 = 20x\]
Dividing both sides of the equation by $20$
\[ \Rightarrow x = 2\]
So, the value of $x$ is two. Putting this in equation $\left( 4 \right)$, we get,
$ \Rightarrow 121 = 110\left( 2 \right) - 2h - {h^2}$
Simplifying the equation, we get,
$ \Rightarrow {h^2} + 2h - 220 + 121 = 0$
$ \Rightarrow {h^2} + 2h - 99 = 0$
Now, we will solve the quadratic equation in h by using splitting the middle term method.
$ \Rightarrow {h^2} + 11h - 9h - 99 = 0$
Taking common terms outside the bracket, we get,
$ \Rightarrow h\left( {h + 11} \right) - 9\left( {h + 11} \right) = 0$
$ \Rightarrow \left( {h + 11} \right)\left( {h - 9} \right) = 0$
So, either $h + 11 = 0$ or $h - 9 = 0$
Either $h = - 11$ or $h = 9$.
We know that h represents a length. So, it can't be negative.
Hence, $h = 9$.
Therefore, the height of tower $ = h = 9$ yards and Length of flagstaff $ = x = 2$ yards.
Note:We should have a strong grip over the concepts of trigonometry and height and distances in order to deal with such kinds of problems. We should have accuracy in calculations, derivatives and arithmetic in order to be sure of the final answer. We should be patient while solving such a problem as it requires a lot of time and concepts.
Complete step by step answer:
The situation can be represented as in the figure below:

Let the height of the tower be $h$ yards and height of flag staff be $x$ yards. Also, let the angles $\angle BEC = \theta $ and $\angle BDC = \beta $. Then, in triangle BDC,
\[\tan \beta = \dfrac{{{\text{Altitude}}}}{{{\text{Base}}}} = \dfrac{{BC}}{{DC}}\]
\[ \Rightarrow \tan \beta = \dfrac{h}{9} - - - - \left( 1 \right)\]
Also, in triangle BEC,
\[\tan \theta = \dfrac{{{\text{Altitude}}}}{{{\text{Base}}}} = \dfrac{{BC}}{{CE}}\]
Now, we know that $CE = CD + DE = 11$yards. So, we get,
\[ \Rightarrow \tan \theta = \dfrac{h}{{11}} - - - - \left( 2 \right)\]
Now, in triangle ACD, we have,
$\tan \left( {\alpha + \beta } \right) = \dfrac{{{\text{Altitude}}}}{{{\text{Base}}}} = \dfrac{{x + h}}{9}$
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{\tan \alpha + \tan \beta }}{{1 - \tan \alpha \tan \beta }} = \dfrac{{x + h}}{9}$
Now, putting in the value of $\tan \alpha $ and $\tan \beta $ in the expression, we get,
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{\dfrac{1}{{10}} + \dfrac{h}{9}}}{{1 - \dfrac{1}{{10}} \times \dfrac{h}{9}}} = \dfrac{{x + h}}{9}$
Simplifying the expression, we get,
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{\dfrac{{9 + 10h}}{{90}}}}{{1 - \dfrac{h}{{90}}}} = \dfrac{{x + h}}{9}$
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{\dfrac{{9 + 10h}}{{90}}}}{{\dfrac{{90 - h}}{{90}}}} = \dfrac{{x + h}}{9}\]
Cancelling the common factors in numerator and denominator, we get,
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{9 + 10h}}{{90 - h}} = \dfrac{{x + h}}{9}\]
Cross multiplying the terms, we get,
\[ \Rightarrow 81 + 90h = 90x - xh - {h^2} + 90h\]
Cancelling like terms with opposite signs, we get,
\[ \Rightarrow 81 = 90x - xh - {h^2} - - - - \left( 3 \right)\]
Now, in triangle ACE, we have,
$\tan \left( {\alpha + \theta } \right) = \dfrac{{{\text{Altitude}}}}{{{\text{Base}}}} = \dfrac{{x + h}}{{11}}$
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{\tan \alpha + \tan \theta }}{{1 - \tan \alpha \tan \theta }} = \dfrac{{x + h}}{{11}}$
Now, putting in the value of $\tan \alpha $ and $\tan \theta $ in the expression, we get,
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{\dfrac{1}{{10}} + \dfrac{h}{{11}}}}{{1 - \dfrac{1}{{10}} \times \dfrac{h}{{11}}}} = \dfrac{{x + h}}{{11}}$
Simplifying the expression, we get,
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{\dfrac{{11 + 10h}}{{110}}}}{{1 - \dfrac{h}{{110}}}} = \dfrac{{x + h}}{{11}}$
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{\dfrac{{11 + 10h}}{{110}}}}{{\dfrac{{110 - h}}{{110}}}} = \dfrac{{x + h}}{{11}}$
Cancelling the common factors in numerator and denominator, we get,
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{11 + 10h}}{{110 - h}} = \dfrac{{x + h}}{{11}}$
Cross multiplying the terms, we get,
$ \Rightarrow 121 + 110h = 110x - xh - {h^2} + 110h$
$ \Rightarrow 121 = 110x - xh - {h^2} - - - - \left( 4 \right)$
Subtracting equation $\left( 3 \right)$ from equation $\left( 4 \right)$, we get,
\[ \Rightarrow 121 - 81 = 110x - xh - {h^2} - \left( {90x - xh - {h^2}} \right)\]
Cancelling common terms with opposite signs, we get,
\[ \Rightarrow 121 - 81 = 110x - xh - {h^2} - 90x + xh + {h^2}\]
\[ \Rightarrow 40 = 20x\]
Dividing both sides of the equation by $20$
\[ \Rightarrow x = 2\]
So, the value of $x$ is two. Putting this in equation $\left( 4 \right)$, we get,
$ \Rightarrow 121 = 110\left( 2 \right) - 2h - {h^2}$
Simplifying the equation, we get,
$ \Rightarrow {h^2} + 2h - 220 + 121 = 0$
$ \Rightarrow {h^2} + 2h - 99 = 0$
Now, we will solve the quadratic equation in h by using splitting the middle term method.
$ \Rightarrow {h^2} + 11h - 9h - 99 = 0$
Taking common terms outside the bracket, we get,
$ \Rightarrow h\left( {h + 11} \right) - 9\left( {h + 11} \right) = 0$
$ \Rightarrow \left( {h + 11} \right)\left( {h - 9} \right) = 0$
So, either $h + 11 = 0$ or $h - 9 = 0$
Either $h = - 11$ or $h = 9$.
We know that h represents a length. So, it can't be negative.
Hence, $h = 9$.
Therefore, the height of tower $ = h = 9$ yards and Length of flagstaff $ = x = 2$ yards.
Note:We should have a strong grip over the concepts of trigonometry and height and distances in order to deal with such kinds of problems. We should have accuracy in calculations, derivatives and arithmetic in order to be sure of the final answer. We should be patient while solving such a problem as it requires a lot of time and concepts.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

State and prove converse of BPT Basic Proportionality class 10 maths CBSE




