
A tower 51mts high has a mark at a height of \[25\] mts from the ground. At what distance the two parts subtend equal angle to an eye at the height of \[5\] mts from the ground
A. $20mts$
B. $30mts$
C. $15mts$
D. $160mts$
Answer
588k+ views
Hint: We will make a given diagram according to the given information in the question .Then we will take two triangles separately and find a side by using Pythagora's theorem.
Complete step-by-step answer:
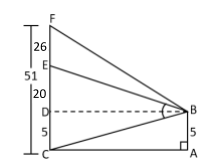
Here, $CF$ is the height of the tower and it has a mark at height of $25$meters from the ground.
$AB = CD = 5\,meters,\,\,DE = 2\,meters$
$
DE = EC - CD \\
DE = 25 - 5 \\
DE = 20meters \\
$
$CF = 51\,meters$
$
DF = DE + EF \\
DF = 20 + 26 \\
DF = 46meters \\
$
Now, according to the question:
$\angle FBE = \angle EBC$ ($\because $given)
$\therefore BE$ is the bisector of $\angle CBF$ and as such it divides the base $CF$ in the ratio of the arm of the angle. Then by the angle bisector theorem .
$\dfrac{{BC}}{{BF}} = \dfrac{{CE}}{{EF}}$ …..(i)
Now, In $\Delta BDE,$ at point $D = {90^o}$
By using Pythagoras theorem, we have
(Hypotenuse)2 = (base)2+(perpendicular)2
${(BF)^2} = {(BD)^2} + {(DF)^2}$
${(BF)^2} = {(BD)^2} + {(DF)^2}$
We will substitute the value of DF,$DF = 46$
$
{(BF)^2} = {(BD)^2} + {(46)^2} \\
\Rightarrow BF = \sqrt {{{(D)}^2} + {{(46)}^2}} \\
$
In $\Delta BCD$at point Dis$90$, so by using Pythagoras theorem, we have
(Hypotenuse)2 = (base)2+(perpendicular)2
\[{(BC)^2} = {(BD)^2} + {(DC)^2}\]
$BC = \sqrt {{{(BD)}^2} + {{(DC)}^2}} $
We will substitute the value of DC,$DC = 5$
$BC = \sqrt {{{(BD)}^2} + {{(5)}^2}} $
Now, we will put the value of $BF$and $BC$ in equation (i) ,we have
$\dfrac{{\sqrt {{{(BD)}^2} + {{(5)}^2}} }}{{\sqrt {{{(BD)}^2} + {{(46)}^2}} }} = \dfrac{{CE}}{{EF}}$
Squaring both sides, we will get
$\dfrac{{{{\left( {\sqrt {{{(BD)}^2} + {{(5)}^2}} } \right)}^2}}}{{{{\left( {\sqrt {{{(BD)}^2} + {{(46)}^2}} } \right)}^2}}} = {\left( {\dfrac{{CE}}{{EF}}} \right)^2}$
\[\dfrac{{{{(BD)}^2} + {{(5)}^2}}}{{{{(BD)}^2} + {{(46)}^2}}} = {\left( {\dfrac{{25}}{{26}}} \right)^2}\]
$\dfrac{{{{(BD)}^2} + 25}}{{{{(BD)}^2} + 2116}} = \dfrac{{625}}{{676}}$
$676[{(BD)^2} + 25] = 625[{(BD)^2} + 2116]$
We will equate the values of ${(BD)^2}$, we have
\[676{(BD)^2} + 676 \times 25 = 625 \times {(BD)^2} + 625 \times 2116\]
$676{(BD)^2} - 625{(BD)^2} = 625 \times 2116 - 676 \times 25$
$(672 - 625){(BD)^2} = 25(25 \times 2116 - 676)$
$51{(BD)^2} = 25 \times 4(25 \times 529 - 169)$
$51{(BD)^2} = 100(13225 - 169)$
$51{(BD)^2} = 100(13056)$
${(BD)^2} = \dfrac{{100 \times 13056}}{{51}}$
${(BD)^2} = 100 \times 256$ …..(ii)
$256 = 2 \times 2 \times 2 \times 2 \times 2 \times 2 \times 2 \times 2$
$256 = {(2 \times 2 \times 2 \times 2)^2}$
$256 = {(16)^2}$
Now, we will substitute the value of $256$ in equation (ii) , we have
So, ${(BD)^2} = 100 \times {(16)^2}$
${(BD)^2} = {(10)^2} \times {(16)^2}$
${(BD)^2} = {(10 \times 16)^2}$
So, $BD = \sqrt {{{(10 \times 16)}^2}} $
$BD = 160$meters
Hence, the required answer is 160 meters.
Note: Students must know that an angle bisector divides the angle into two angles with equal measures. We will find the value of BD with the help of Pythagoras theorem.
Complete step-by-step answer:

Here, $CF$ is the height of the tower and it has a mark at height of $25$meters from the ground.
$AB = CD = 5\,meters,\,\,DE = 2\,meters$
$
DE = EC - CD \\
DE = 25 - 5 \\
DE = 20meters \\
$
$CF = 51\,meters$
$
DF = DE + EF \\
DF = 20 + 26 \\
DF = 46meters \\
$
Now, according to the question:
$\angle FBE = \angle EBC$ ($\because $given)
$\therefore BE$ is the bisector of $\angle CBF$ and as such it divides the base $CF$ in the ratio of the arm of the angle. Then by the angle bisector theorem .
$\dfrac{{BC}}{{BF}} = \dfrac{{CE}}{{EF}}$ …..(i)
Now, In $\Delta BDE,$ at point $D = {90^o}$
By using Pythagoras theorem, we have
(Hypotenuse)2 = (base)2+(perpendicular)2
${(BF)^2} = {(BD)^2} + {(DF)^2}$
${(BF)^2} = {(BD)^2} + {(DF)^2}$
We will substitute the value of DF,$DF = 46$
$
{(BF)^2} = {(BD)^2} + {(46)^2} \\
\Rightarrow BF = \sqrt {{{(D)}^2} + {{(46)}^2}} \\
$
In $\Delta BCD$at point Dis$90$, so by using Pythagoras theorem, we have
(Hypotenuse)2 = (base)2+(perpendicular)2
\[{(BC)^2} = {(BD)^2} + {(DC)^2}\]
$BC = \sqrt {{{(BD)}^2} + {{(DC)}^2}} $
We will substitute the value of DC,$DC = 5$
$BC = \sqrt {{{(BD)}^2} + {{(5)}^2}} $
Now, we will put the value of $BF$and $BC$ in equation (i) ,we have
$\dfrac{{\sqrt {{{(BD)}^2} + {{(5)}^2}} }}{{\sqrt {{{(BD)}^2} + {{(46)}^2}} }} = \dfrac{{CE}}{{EF}}$
Squaring both sides, we will get
$\dfrac{{{{\left( {\sqrt {{{(BD)}^2} + {{(5)}^2}} } \right)}^2}}}{{{{\left( {\sqrt {{{(BD)}^2} + {{(46)}^2}} } \right)}^2}}} = {\left( {\dfrac{{CE}}{{EF}}} \right)^2}$
\[\dfrac{{{{(BD)}^2} + {{(5)}^2}}}{{{{(BD)}^2} + {{(46)}^2}}} = {\left( {\dfrac{{25}}{{26}}} \right)^2}\]
$\dfrac{{{{(BD)}^2} + 25}}{{{{(BD)}^2} + 2116}} = \dfrac{{625}}{{676}}$
$676[{(BD)^2} + 25] = 625[{(BD)^2} + 2116]$
We will equate the values of ${(BD)^2}$, we have
\[676{(BD)^2} + 676 \times 25 = 625 \times {(BD)^2} + 625 \times 2116\]
$676{(BD)^2} - 625{(BD)^2} = 625 \times 2116 - 676 \times 25$
$(672 - 625){(BD)^2} = 25(25 \times 2116 - 676)$
$51{(BD)^2} = 25 \times 4(25 \times 529 - 169)$
$51{(BD)^2} = 100(13225 - 169)$
$51{(BD)^2} = 100(13056)$
${(BD)^2} = \dfrac{{100 \times 13056}}{{51}}$
${(BD)^2} = 100 \times 256$ …..(ii)
$256 = 2 \times 2 \times 2 \times 2 \times 2 \times 2 \times 2 \times 2$
$256 = {(2 \times 2 \times 2 \times 2)^2}$
$256 = {(16)^2}$
Now, we will substitute the value of $256$ in equation (ii) , we have
So, ${(BD)^2} = 100 \times {(16)^2}$
${(BD)^2} = {(10)^2} \times {(16)^2}$
${(BD)^2} = {(10 \times 16)^2}$
So, $BD = \sqrt {{{(10 \times 16)}^2}} $
$BD = 160$meters
Hence, the required answer is 160 meters.
Note: Students must know that an angle bisector divides the angle into two angles with equal measures. We will find the value of BD with the help of Pythagoras theorem.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




