
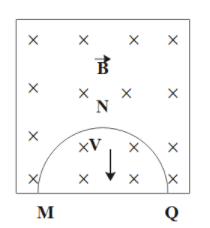
A thin semi – circular conducting ring of radius R is falling with its plane vertical in a horizontal magnetic induction $\vec B$. At the position MNQ the speed of the ring is V, and the potential difference developed across the ring is
A. Zero
B. $BV\pi {R^2}/2$ and M is at higher potential
C. $\pi RBV$ and Q is at higher potential
D. 2RBV and Q is at higher potential

Answer
579.9k+ views
Hint: Faraday's law of induction is a basic law of electromagnetism which is used to predict how a magnetic field would interact with an electric circuit in order to produce an electromotive force, this phenomenon is known as electromagnetic induction. To find the solution of the given question we will use faraday’s law of induction.
Formula Used: $\varepsilon = - N\dfrac{{\Delta \phi }}{{\Delta t}}$
Complete answer:
The rate of decrease of area of the semi-circular ring is given as,
$\dfrac{{dA}}{{dt}} = \left( {2R} \right)V$
The faraday’s second law of electromagnetic induction is defined as the induced emf in a coil which is equal to the rate of change of flux linkage.
Mathematically it is given as,
$\varepsilon = - N\dfrac{{\Delta \phi }}{{\Delta t}}$
Where ‘$\varepsilon $’ is expressed as the electromotive force, ‘$\phi $’ is expressed as the magnetic flux, and ‘N’ is expressed as the number of turns.
The negative (-) sign in the formula indicates the direction of the induced emf and change in the direction of magnetic fields have opposite signs.
Now, according to the faraday’s second law of induction of induced emf,
$e = - \dfrac{{d\phi }}{{dt}} = - B\dfrac{{dA}}{{dt}} = - B\left( {2RV} \right)$
$\therefore e = 2BRV$
The induced current in the ring must generate a magnetic field in the upward direction. So, Q is at a higher potential.
Thus, the potential difference developed across the ring is 2RBV and Q is at higher potential.
Hence, option (D) is the correct answer.
Note:
We see that the Lenz law is reflected in the faraday’s law. Lenz law is defined as the induced electromotive force with non – identical polarities which induces a current whose magnetic field opposes the change in the magnetic flux through the loop in order to make sure that the original flux is maintained through the loop when current flows in it.
Formula Used: $\varepsilon = - N\dfrac{{\Delta \phi }}{{\Delta t}}$
Complete answer:
The rate of decrease of area of the semi-circular ring is given as,
$\dfrac{{dA}}{{dt}} = \left( {2R} \right)V$
The faraday’s second law of electromagnetic induction is defined as the induced emf in a coil which is equal to the rate of change of flux linkage.
Mathematically it is given as,
$\varepsilon = - N\dfrac{{\Delta \phi }}{{\Delta t}}$
Where ‘$\varepsilon $’ is expressed as the electromotive force, ‘$\phi $’ is expressed as the magnetic flux, and ‘N’ is expressed as the number of turns.
The negative (-) sign in the formula indicates the direction of the induced emf and change in the direction of magnetic fields have opposite signs.
Now, according to the faraday’s second law of induction of induced emf,
$e = - \dfrac{{d\phi }}{{dt}} = - B\dfrac{{dA}}{{dt}} = - B\left( {2RV} \right)$
$\therefore e = 2BRV$
The induced current in the ring must generate a magnetic field in the upward direction. So, Q is at a higher potential.
Thus, the potential difference developed across the ring is 2RBV and Q is at higher potential.
Hence, option (D) is the correct answer.
Note:
We see that the Lenz law is reflected in the faraday’s law. Lenz law is defined as the induced electromotive force with non – identical polarities which induces a current whose magnetic field opposes the change in the magnetic flux through the loop in order to make sure that the original flux is maintained through the loop when current flows in it.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

The largest wind power cluster is located in the state class 11 social science CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

State and prove Bernoullis theorem class 11 physics CBSE

What steps did the French revolutionaries take to create class 11 social science CBSE

Which among the following are examples of coming together class 11 social science CBSE




