
A thermos flask is designed to prevent the contents of the flask from losing heat. Which of the following statements concerning the design of thermos flasks is incorrect?
A. The stopper helps reduce heat loss by convection.
B. The glass walls are silver coated to reduce emitted radiation.
C. The flask is designed to prevent heat loss by conduction, convection and radiation.
D. The vacuum between the glass walls prevents heat loss by preventing radiation.
Answer
594k+ views
Hint: A vacuum flask or thermos flask is designed so that it will not allow heat loss by any means of conduction or radiation. The vacuum prevents the heat loss by conduction because vacuum is a bad conductor of heat. The stopper prevents the heat loss by convection because it is tightly sealed. And the inner reflecting layer prevents the heat loss by radiation.
Complete step by step answer:
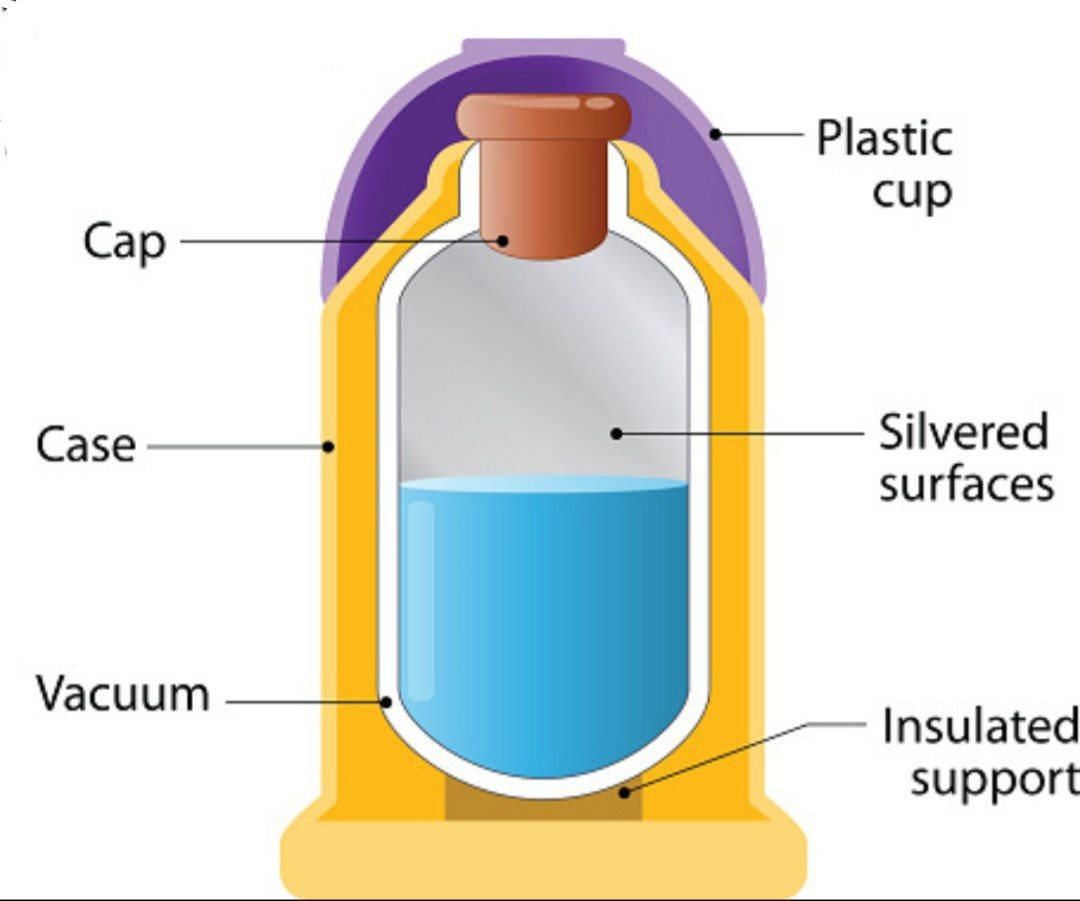
A vacuum flask or thermos flask is similar to a super-protected jug or container. Most vacuum flasks have an internal chamber and an external plastic or metal case isolated by two layers of glass with a vacuum in the middle. The inner side of glass is typically lined with a thin reflecting metal layer to reflect heat. For more durability some vacuum flasks use stainless steel instead of glass, they have two layers of stainless steel with a vacuum and a reflecting layer in the middle of them. There's additionally a tight, screw-down called stopper on the top. These few, basic components prevent any loss of heat either by conduction, convection, or radiation. The vacuum being a bad conductor of heat prevents conduction. The tight plug keeps air from entering or leaving the flask, so there is no heat loss by convection. Shouldn't something be said about radiation? At the point when infrared radiation attempts to leave the hot fluid, the reflective coating of the inward chamber reflects it straight back in once more. There's basically no chance heat to escape from a vacuum flask and a hot beverage put away inside will remain steaming hot for a few hours.
So the fixed plug stops heat getting in by convection; the vacuum stops conduction, and the stainless steel lining between the external case and the internal chamber stops heat for radiating in either.
So options A and B and C are correct but in the option D the vacuum does not prevent the heat loss by radiation. But it prevents the heat loss by conduction.
So, the correct answer is “Option D”.
Note: The conduction is the transfer of heat from one substance to another or to surrounding when there is contact in between them. The heat loss when there is no contact is called convection both the conduction and convection required medium for transfer. The radiation is the emission or transmission of energy in the form of waves or particles through space or material medium.
Complete step by step answer:

A vacuum flask or thermos flask is similar to a super-protected jug or container. Most vacuum flasks have an internal chamber and an external plastic or metal case isolated by two layers of glass with a vacuum in the middle. The inner side of glass is typically lined with a thin reflecting metal layer to reflect heat. For more durability some vacuum flasks use stainless steel instead of glass, they have two layers of stainless steel with a vacuum and a reflecting layer in the middle of them. There's additionally a tight, screw-down called stopper on the top. These few, basic components prevent any loss of heat either by conduction, convection, or radiation. The vacuum being a bad conductor of heat prevents conduction. The tight plug keeps air from entering or leaving the flask, so there is no heat loss by convection. Shouldn't something be said about radiation? At the point when infrared radiation attempts to leave the hot fluid, the reflective coating of the inward chamber reflects it straight back in once more. There's basically no chance heat to escape from a vacuum flask and a hot beverage put away inside will remain steaming hot for a few hours.
So the fixed plug stops heat getting in by convection; the vacuum stops conduction, and the stainless steel lining between the external case and the internal chamber stops heat for radiating in either.
So options A and B and C are correct but in the option D the vacuum does not prevent the heat loss by radiation. But it prevents the heat loss by conduction.
So, the correct answer is “Option D”.
Note: The conduction is the transfer of heat from one substance to another or to surrounding when there is contact in between them. The heat loss when there is no contact is called convection both the conduction and convection required medium for transfer. The radiation is the emission or transmission of energy in the form of waves or particles through space or material medium.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

Name the part of the brain responsible for the precision class 11 biology CBSE

The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to AEffect class 11 biology CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE




