
(A): The $C-C$ bond length in benzene is intermediate between $C-C$ single bond length and $C-C$ double bond length.
(R): Benzene molecule exhibits resonance
(A) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct explanation of (A)
(B) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is not the correct explanation of (A)
(C) (A) is true but (R) is false
(D) (A) is false but (R) is true
Answer
591.6k+ views
Hint: Due to the delocalization of pi electrons in benzene there is a possibility of resonance. As a result of these the bonds keep switching fast so that the bond can be thought of as an average between the $C-C$ single and double bonds.
Complete step by step answer:
- As we know benzene (${{C}_{6}}{{H}_{6}}$) is an aromatic hydrocarbon which have a cyclic structure with six carbon atoms and six hydrogen atoms. In the benzene molecule, each of the carbon atoms is attached with two other carbon atoms and one hydrogen atom.
- Since benzene has more than one way to place double bonds in the ring, it exhibits resonance and has two resonating structures. During resonance the arrangement of electrons differs and double bonds delocalize and give stability to benzene. The resonance structures of benzene are given below,
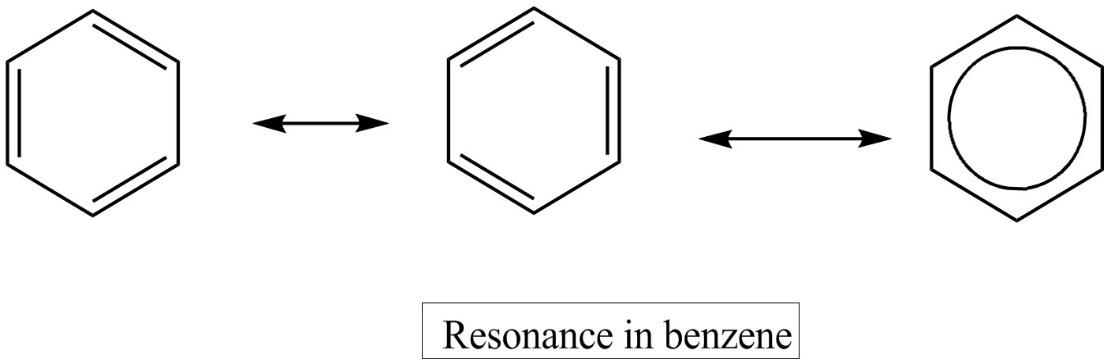
- In benzene each of the carbon atom is $s{{p}^{2}}$ hybridized and due to resonance or the delocalization of $\pi $electron clouds below and above the plane of benzene ring ,all C,C bonds have slightly double bond character. As a result, the carbon-carbon bond length in benzene lies between the $C-C$ single bond length and $C-C$ double bond length.
- It is observed that the $C-C$ bond length in benzene is 139 pm which lies between the standard $C-C$ single bond length (154 pm) and $C-C$ double bond length (134 pm).
- Hence both (A) and (R) are correct and as we have seen (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
Therefore, the answer is option (A).
Note: It should be noted that among the resonance structures of benzene given, the first two are the resonating structure and the third one is the hybrid structure. This hybrid structure is more stable than the other two resonating structures as the hybrid structure has the low energy. These resonance structures are also called Kekule structures.
Complete step by step answer:
- As we know benzene (${{C}_{6}}{{H}_{6}}$) is an aromatic hydrocarbon which have a cyclic structure with six carbon atoms and six hydrogen atoms. In the benzene molecule, each of the carbon atoms is attached with two other carbon atoms and one hydrogen atom.
- Since benzene has more than one way to place double bonds in the ring, it exhibits resonance and has two resonating structures. During resonance the arrangement of electrons differs and double bonds delocalize and give stability to benzene. The resonance structures of benzene are given below,

- In benzene each of the carbon atom is $s{{p}^{2}}$ hybridized and due to resonance or the delocalization of $\pi $electron clouds below and above the plane of benzene ring ,all C,C bonds have slightly double bond character. As a result, the carbon-carbon bond length in benzene lies between the $C-C$ single bond length and $C-C$ double bond length.
- It is observed that the $C-C$ bond length in benzene is 139 pm which lies between the standard $C-C$ single bond length (154 pm) and $C-C$ double bond length (134 pm).
- Hence both (A) and (R) are correct and as we have seen (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
Therefore, the answer is option (A).
Note: It should be noted that among the resonance structures of benzene given, the first two are the resonating structure and the third one is the hybrid structure. This hybrid structure is more stable than the other two resonating structures as the hybrid structure has the low energy. These resonance structures are also called Kekule structures.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

Name the part of the brain responsible for the precision class 11 biology CBSE

The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to AEffect class 11 biology CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE




