
A telegraph post gets broken at a point against a storm and its top touches the ground at a distance 20 m from the base of the post making an angle \[30^\circ \] with the ground. What is the height of the post?
A) \[\dfrac{{40}}{{\sqrt 3 }}\] m
B) \[20\sqrt 3 \] m
C) \[40\sqrt 3 \] m
D) 30 m
Answer
594.9k+ views
Hint: Use trigonometry ratio \[\tan \theta = \dfrac{{{\text{Perpendicular}}}}{{{\text{Base}}}}\] to find remaining height of the post after breakage and \[\sec \theta = \dfrac{{{\text{Hypotenuses}}}}{{{\text{Base}}}}\] to find the broken height of the post and then add both the heights to find the total height of the post.
Complete Step-by-Step solution:
First, we will draw the figure to understand the question,
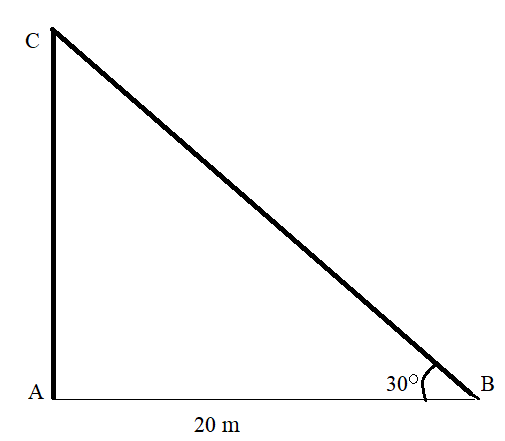
From the figure, the height of the post is \[AC + CB\] where AC is the remaining height of the post after breakage and CB is the broken height of the post.
Our first task is to find AC and BC. So, let’s move forward to find AC first.
As we know that, \[\tan \theta = \dfrac{{{\text{Perpendicular}}}}{{{\text{Base}}}}\] and we have the value of \[\theta \] and base and have to find perpendicular so, this trigonometry is best fit to find AC.
Now we are applying this trigonometric ratio into the triangle ABC and substituting the values into trigonometric ratio,
\[
\tan 30^\circ = \dfrac{{{\text{AC}}}}{{{\text{AB}}}} \\
\tan 30^\circ = \dfrac{{{\text{AC}}}}{{{\text{20}}}} \\
\]
From this, we can find AC as,
\[AC = 20\tan 30^\circ \]
We know that \[\tan 30^\circ = \dfrac{{\text{1}}}{{\sqrt 3 }}\], substituting this in the last result, we get
\[AC = \dfrac{{20}}{{\sqrt 3 }}\]
Now we will find CB, means we have to find hypotenuses of the triangle and for this the trigonometry ratio \[\sec \theta = \dfrac{{{\text{Hypotenuses}}}}{{{\text{Base}}}}\] is best fit.
Now we are applying this trigonometric ratio into the triangle ABC and substituting the values into trigonometric ratio,
\[
\sec 30^\circ = \dfrac{{{\text{CB}}}}{{{\text{AB}}}} \\
\sec 30^\circ = \dfrac{{{\text{CB}}}}{{{\text{20}}}} \\
\]
From this, we can find CB as,
\[CB = 20\sec 30^\circ \]
We know that \[\sec 30^\circ = \dfrac{2}{{\sqrt 3 }}\], substituting this in the last result, we get
\[
CB = \dfrac{{20 \cdot 2}}{{\sqrt 3 }} \\
= \dfrac{{40}}{{\sqrt 3 }} \\
\]
Now we have both AC and CB.
We are adding AC and CB to find the actual height of the post,
\[
AC + CB = \dfrac{{20}}{{\sqrt 3 }} + \dfrac{{40}}{{\sqrt 3 }} \\
= \dfrac{{20 + 40}}{{\sqrt 3 }} \\
= \dfrac{{60}}{{\sqrt 3 }} \\
\]
This is not an option.
So, we will rationalize denominator to get the correct option,
\[
AC + CB = \dfrac{{60}}{{\sqrt 3 }} \cdot \dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{{\sqrt 3 }} \\
= \dfrac{{60\sqrt 3 }}{3} \\
= 20\sqrt 3 \\
\]
Thus, the height of the post is \[20\sqrt 3 \] meters.
Hence option B is correct.
Note:
Any of the trigonometric functions can be used to find the answer but while solving these types of questions we have to first focus on “what we have to find” and then on “what data we have” so make our calculation shorter.
Complete Step-by-Step solution:
First, we will draw the figure to understand the question,

From the figure, the height of the post is \[AC + CB\] where AC is the remaining height of the post after breakage and CB is the broken height of the post.
Our first task is to find AC and BC. So, let’s move forward to find AC first.
As we know that, \[\tan \theta = \dfrac{{{\text{Perpendicular}}}}{{{\text{Base}}}}\] and we have the value of \[\theta \] and base and have to find perpendicular so, this trigonometry is best fit to find AC.
Now we are applying this trigonometric ratio into the triangle ABC and substituting the values into trigonometric ratio,
\[
\tan 30^\circ = \dfrac{{{\text{AC}}}}{{{\text{AB}}}} \\
\tan 30^\circ = \dfrac{{{\text{AC}}}}{{{\text{20}}}} \\
\]
From this, we can find AC as,
\[AC = 20\tan 30^\circ \]
We know that \[\tan 30^\circ = \dfrac{{\text{1}}}{{\sqrt 3 }}\], substituting this in the last result, we get
\[AC = \dfrac{{20}}{{\sqrt 3 }}\]
Now we will find CB, means we have to find hypotenuses of the triangle and for this the trigonometry ratio \[\sec \theta = \dfrac{{{\text{Hypotenuses}}}}{{{\text{Base}}}}\] is best fit.
Now we are applying this trigonometric ratio into the triangle ABC and substituting the values into trigonometric ratio,
\[
\sec 30^\circ = \dfrac{{{\text{CB}}}}{{{\text{AB}}}} \\
\sec 30^\circ = \dfrac{{{\text{CB}}}}{{{\text{20}}}} \\
\]
From this, we can find CB as,
\[CB = 20\sec 30^\circ \]
We know that \[\sec 30^\circ = \dfrac{2}{{\sqrt 3 }}\], substituting this in the last result, we get
\[
CB = \dfrac{{20 \cdot 2}}{{\sqrt 3 }} \\
= \dfrac{{40}}{{\sqrt 3 }} \\
\]
Now we have both AC and CB.
We are adding AC and CB to find the actual height of the post,
\[
AC + CB = \dfrac{{20}}{{\sqrt 3 }} + \dfrac{{40}}{{\sqrt 3 }} \\
= \dfrac{{20 + 40}}{{\sqrt 3 }} \\
= \dfrac{{60}}{{\sqrt 3 }} \\
\]
This is not an option.
So, we will rationalize denominator to get the correct option,
\[
AC + CB = \dfrac{{60}}{{\sqrt 3 }} \cdot \dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{{\sqrt 3 }} \\
= \dfrac{{60\sqrt 3 }}{3} \\
= 20\sqrt 3 \\
\]
Thus, the height of the post is \[20\sqrt 3 \] meters.
Hence option B is correct.
Note:
Any of the trigonometric functions can be used to find the answer but while solving these types of questions we have to first focus on “what we have to find” and then on “what data we have” so make our calculation shorter.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

State and prove converse of BPT Basic Proportionality class 10 maths CBSE




