
A sunlight falls on the mirror ${{\text{M}}_1}$ such that sunlight is parallel to ${{\text{M}}_2}$. When light reflected from a mirror ${{\text{M}}_2}$ is parallel to ${{\text{M}}_1}$. Then angle between two mirrors is
A. ${60^ \circ }$
B. ${70^ \circ }$
C. ${45^ \circ }$
D. ${90^ \circ }$
Answer
580.2k+ views
Hint: This question is based on the principles of ray optics. The incident ray and the reflected ray will make the same angle with the normal of the mirror and all three vectors i.e incident and normal and reflected lie in the same plane.
Complete answer:
This question will be easy if we solve it by using the ray diagram. The ray diagram which illustrates the given situation is given below.
Where ${{\text{M}}_1}$ and ${{\text{M}}_2}$ are the two mirrors and their respective normal are denoted by ${{\text{N}}_1}$ and ${{\text{N}}_2}$
Let the angle between the two mirrors be ‘a’
Now to solve this we use the properties of reflection and properties of a triangle.
Since the incident ray is parallel to second mirror, from the corresponding angle property it will make angle ‘a’ with the first mirror
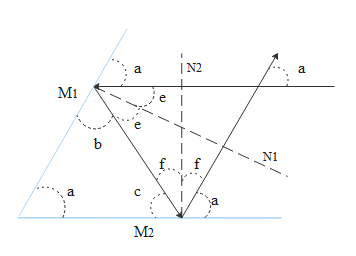
After the first reflection from the first mirror incident and reflected rays make angle ‘e’ with the normal of the first mirror. After the reflection from the second mirror, incident and reflected rays make angle ‘f’ with the second mirror.
The triangle which the reflected ray from the first mirror forms with the two mirrors has angles a, b, c as the sides of the triangle.
We know
$\eqalign{
& a + e = {90^0},b + e = {90^0} \cr
& \Rightarrow a = b \cr} $
We know
$\eqalign{
& c + f = {90^0},a + f = {90^0} \cr
& \Rightarrow a = c \cr} $
Over all from the above two steps we have
$a = b = c$
The sum of three angles of a triangle will be equal to ${180^0}$
So
$\eqalign{
& a + b + c = {180^0} \cr
& \Rightarrow a + a + a = {180^0} \cr
& \Rightarrow 3a = {180^0} \cr
& \Rightarrow a = \dfrac{{{{180}^0}}}{3} \cr
& \Rightarrow a = {60^0} \cr} $
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Note:
This we can remember in general as a rule like if the incident ray is parallel to the second mirror and if the ultimate reflected ray is parallel to the first mirror then the angle between the mirrors must be sixty degrees.
Complete answer:
This question will be easy if we solve it by using the ray diagram. The ray diagram which illustrates the given situation is given below.
Where ${{\text{M}}_1}$ and ${{\text{M}}_2}$ are the two mirrors and their respective normal are denoted by ${{\text{N}}_1}$ and ${{\text{N}}_2}$
Let the angle between the two mirrors be ‘a’
Now to solve this we use the properties of reflection and properties of a triangle.
Since the incident ray is parallel to second mirror, from the corresponding angle property it will make angle ‘a’ with the first mirror

After the first reflection from the first mirror incident and reflected rays make angle ‘e’ with the normal of the first mirror. After the reflection from the second mirror, incident and reflected rays make angle ‘f’ with the second mirror.
The triangle which the reflected ray from the first mirror forms with the two mirrors has angles a, b, c as the sides of the triangle.
We know
$\eqalign{
& a + e = {90^0},b + e = {90^0} \cr
& \Rightarrow a = b \cr} $
We know
$\eqalign{
& c + f = {90^0},a + f = {90^0} \cr
& \Rightarrow a = c \cr} $
Over all from the above two steps we have
$a = b = c$
The sum of three angles of a triangle will be equal to ${180^0}$
So
$\eqalign{
& a + b + c = {180^0} \cr
& \Rightarrow a + a + a = {180^0} \cr
& \Rightarrow 3a = {180^0} \cr
& \Rightarrow a = \dfrac{{{{180}^0}}}{3} \cr
& \Rightarrow a = {60^0} \cr} $
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Note:
This we can remember in general as a rule like if the incident ray is parallel to the second mirror and if the ultimate reflected ray is parallel to the first mirror then the angle between the mirrors must be sixty degrees.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

State and prove converse of BPT Basic Proportionality class 10 maths CBSE




