
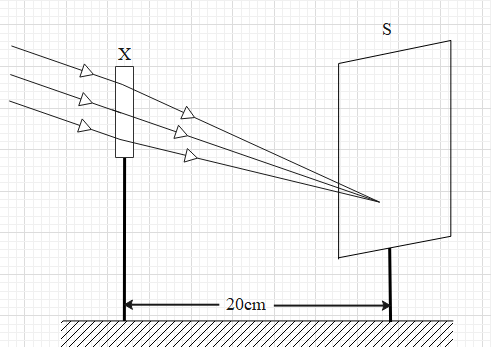
A student focused the Sun rays using an optical device X on a screen S as shown. From this, it may be concluded that he device X is a (select the correct option)
A. convex lens of focal length 10cm
B. convex lens of radius of curvature 20cm
C. convex lens of focal length 20cm
D. concave mirror of focal length 20cm

Answer
587.1k+ views
Hint: To solve the given question, one must have the knowledge about the properties of mirrors and lens. Analyse what is happening to the light rays that are incident on the optical device X. Since, the rays are converging at a point, the device must be a converging lens.
Formula used:
$\dfrac{1}{v}-\dfrac{1}{u}=\dfrac{1}{f}$
Complete answer:
Let us first analyse what is happening in the given case. In the given case, parallel rays of light are incident on the optical device X. We can see that the parallel light rays are passing through the device X. After passing through the device, we also see that the rays are being deflected and are meeting at a single point on the screen that is placed at a distance of 20 cm from the optical device.
The optical devices that we know about are mirrors and lenses. The given device X cannot be a mirror because a mirror reflects the light rays. Whereas in the given case, the lights rays are refracting. Therefore, the optical device X must be a lens.
We see that the parallel rays are converging at a single point on the screen, after passing through the device. Therefore, the device X must be a converging lens. A converging lens is called a convex lens.
Hence, the optical device is a convex lens.
Let us find the focal length of the convex lens. When parallel rays of light pass through a convex lens, they converge and meet at the focus of the lens on the other side. In this case, the focus of the lens lies on the screen and the distance between the device X and screen is 20cm.
Therefore, the focal length of the lens is 20cm.
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Note:
We can also find the focal length of the lens by the lens maker’s formula i.e. $\dfrac{1}{v}-\dfrac{1}{u}=\dfrac{1}{f}$ …. (1).
Here, v and u are the positions of the image and the object respectively, according to the sign convection. f is the focal length of the lens.
In the given case, since the light rays are parallel, the object is at infinity. The image is formed where the light rays meet after refraction through the lens (i.e on the screen). Therefore, v = 20cm.
Substitute the values of v and u in equation (1).
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{20}-\dfrac{1}{\infty }=\dfrac{1}{f}$
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{20}-0=\dfrac{1}{f}$
$\Rightarrow f=20cm$
This means that the focal length of the lens is 20 cm.
Formula used:
$\dfrac{1}{v}-\dfrac{1}{u}=\dfrac{1}{f}$
Complete answer:
Let us first analyse what is happening in the given case. In the given case, parallel rays of light are incident on the optical device X. We can see that the parallel light rays are passing through the device X. After passing through the device, we also see that the rays are being deflected and are meeting at a single point on the screen that is placed at a distance of 20 cm from the optical device.
The optical devices that we know about are mirrors and lenses. The given device X cannot be a mirror because a mirror reflects the light rays. Whereas in the given case, the lights rays are refracting. Therefore, the optical device X must be a lens.
We see that the parallel rays are converging at a single point on the screen, after passing through the device. Therefore, the device X must be a converging lens. A converging lens is called a convex lens.
Hence, the optical device is a convex lens.
Let us find the focal length of the convex lens. When parallel rays of light pass through a convex lens, they converge and meet at the focus of the lens on the other side. In this case, the focus of the lens lies on the screen and the distance between the device X and screen is 20cm.
Therefore, the focal length of the lens is 20cm.
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Note:
We can also find the focal length of the lens by the lens maker’s formula i.e. $\dfrac{1}{v}-\dfrac{1}{u}=\dfrac{1}{f}$ …. (1).
Here, v and u are the positions of the image and the object respectively, according to the sign convection. f is the focal length of the lens.
In the given case, since the light rays are parallel, the object is at infinity. The image is formed where the light rays meet after refraction through the lens (i.e on the screen). Therefore, v = 20cm.
Substitute the values of v and u in equation (1).
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{20}-\dfrac{1}{\infty }=\dfrac{1}{f}$
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{20}-0=\dfrac{1}{f}$
$\Rightarrow f=20cm$
This means that the focal length of the lens is 20 cm.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Giving reasons state the signs positive or negative class 12 physics CBSE

Explain esterification reaction with the help of a class 12 chemistry CBSE

What is defined as a solenoid Depict a diagram with class 12 physics CBSE




