
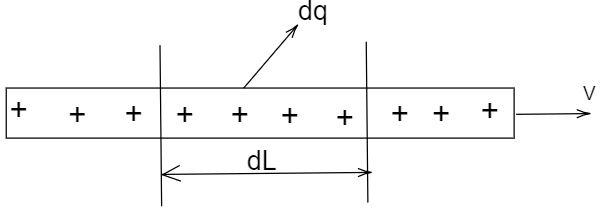
A straight wire of linear charge density $\lambda = 3\mu C/m$ and area of cross section $A = 4\,m{m^2}$ is given as shown in figure. When wire is pulled with speed $2\,m/s$ , then current associated with it is

Answer
568.2k+ views
Hint: This problem is based on the concept on the finding of the charge density. It is the ratio of the charge to the length of the conductor. The charge is obtained by the product of the current and the time taken for the movement of the electrons.
Formula used:
(1) The formula of the charge is given by
$q = It$
Where $q$ is the charge, $I$ is the current through the wire and $t$ is the time taken.
(2) The charge density is given as
$\lambda = \dfrac{{dq}}{{dL}}$
Where $\lambda $ is the linear charge density.
Complete step by step answer:
Given: Linear charge density of the wire, $\lambda = 3\mu C/m$
Area of cross section, $A = 4\,m{m^2}$
The speed at which the wire pulled, $v = 2\,m{s^{ - 1}}$
By using the formula of the charge,
$q = It$
Multiplying and dividing the left hand side of the equation by $dL$ , we get
$q\dfrac{{dL}}{{dL}} = It$
By rearranging the equation and differentiating both sides, we get
$dL\dfrac{{dq}}{{dL}} = Idt$
By substituting the formula (2) in the above equation,
$\lambda dL = Idt$
It is known that the rate of the change of the length with respect to time is the speed, Hence $\dfrac{{dL}}{{dt}} = v$
$I = \lambda v$
Substituting the value of the charge density and the speed,
$I = 3 \times 2$
By performing the multiplication in the above step, we get
$I = 6\,\mu A$
Hence, the current flowing through the circuit is obtained as $6\,\mu A$.
Note: The obtained value of the current flowing through the circuit is $6\,\mu A$ . The value of the $\mu $ can also be substituted as $1 \times {10^{ - 6}}\,m$ . Remember the difference between the velocity and the charge density. Change of length with respect to the time is velocity and the change of the charge with respect to the length is the charge density.
Formula used:
(1) The formula of the charge is given by
$q = It$
Where $q$ is the charge, $I$ is the current through the wire and $t$ is the time taken.
(2) The charge density is given as
$\lambda = \dfrac{{dq}}{{dL}}$
Where $\lambda $ is the linear charge density.
Complete step by step answer:
Given: Linear charge density of the wire, $\lambda = 3\mu C/m$
Area of cross section, $A = 4\,m{m^2}$
The speed at which the wire pulled, $v = 2\,m{s^{ - 1}}$
By using the formula of the charge,
$q = It$
Multiplying and dividing the left hand side of the equation by $dL$ , we get
$q\dfrac{{dL}}{{dL}} = It$
By rearranging the equation and differentiating both sides, we get
$dL\dfrac{{dq}}{{dL}} = Idt$
By substituting the formula (2) in the above equation,
$\lambda dL = Idt$
It is known that the rate of the change of the length with respect to time is the speed, Hence $\dfrac{{dL}}{{dt}} = v$
$I = \lambda v$
Substituting the value of the charge density and the speed,
$I = 3 \times 2$
By performing the multiplication in the above step, we get
$I = 6\,\mu A$
Hence, the current flowing through the circuit is obtained as $6\,\mu A$.
Note: The obtained value of the current flowing through the circuit is $6\,\mu A$ . The value of the $\mu $ can also be substituted as $1 \times {10^{ - 6}}\,m$ . Remember the difference between the velocity and the charge density. Change of length with respect to the time is velocity and the change of the charge with respect to the length is the charge density.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

Name the part of the brain responsible for the precision class 11 biology CBSE

The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to AEffect class 11 biology CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE




