
A stage in cell division is shown in the figure. Select the answer which gives the correct identification of the stage with its characteristics.
A. Telophase 1. Nuclear envelope reforms, Golgi complex reform. B. Late anaphase 2. Chromosomes move away from the poles, Golgi complex not present. C. Cytokinesis 3. Nuclear envelope disappears and mitochondria distributed between two daughter cells. D. Prophase 4.Endoplasmic reticulum and nucleolus are not reformed.
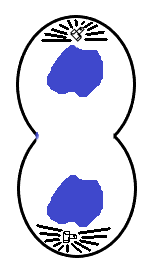
I. A-1
II. B-2
III. C-3
IV. D-4
| A. Telophase | 1. Nuclear envelope reforms, Golgi complex reform. |
| B. Late anaphase | 2. Chromosomes move away from the poles, Golgi complex not present. |
| C. Cytokinesis | 3. Nuclear envelope disappears and mitochondria distributed between two daughter cells. |
| D. Prophase | 4.Endoplasmic reticulum and nucleolus are not reformed. |

Answer
581.7k+ views
Hint:
Complete answer: A cell cycle can be defined as a series of events wherein a cell divides and grows. The two stages that describe the cell division include interphase and mitosis. Interphase is considered the phase wherein the cell spends a prominent amount of time. The interphase is sub-categorized into three stages. The gap 1 stage or G1 stage, the synthesis stage or S stage, and the gap 2 stage or G2 stage.
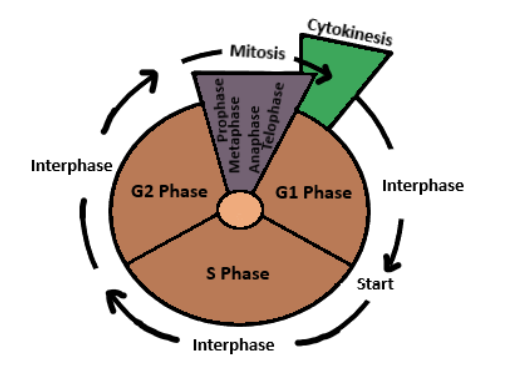
Gap 1 or G1 stage – During this stage, the cell grows in size and accumulates enough amount of chromosomal DNA, associated proteins, and sufficient energy to participate in the replication process of each chromosome present in the nucleus.
Synthesis of DNA or S stage – This stage involves the replication of DNA. The replication of DNA results in the production or formation of sister chromatids. Sister chromatids are identical pairs of DNA molecules and are adhered to the centromeric region. Similarly, the centrosomes present in the cell also undergo replication and form mitotic spindles. Mitotic spindles choreograph the chromosomal movement during mitosis. In the case of an animal cell, centrosomes consist of centrioles which are rod-shaped objects at right angles to each other. The centrioles are also involved in the cell cycle process and help assemble the cell cycle. Centrioles are absent in plant cells and most fungi.
Gap 2 or G2 stage – In this stage, the cell is prepared before it enters the mitotic phase wherein it undergoes further and final cell division. Some of the cell organelles undergo replication, necessary proteins are synthesized for chromosomal manipulation and energy stores are replenished for the same reason.
MitosisThe cell now enters the mitotic phase which is a multistep process. The mitotic phase is divided into two categories. The first portion is called karyokinesis, also known as nuclear division. Karyokinesis is further subcategorized into a series of phases namely prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. And the second part is called cytokinesis. Cytokinesis involves the cytoplasmic components to separate physically to form two daughter cells. These cells each enter an interphase of their own and begin a new cell cycle round.
I. Prophase:
-Condensation of chromosomes occurs.
-The nuclear envelop breaks down and the nucleolus disappears.
-The emergence of spindle fibres from centrosomes occurs.
II. Pro-metaphase
-Mitotic spindles attach to the kinetochores appearing at the centromere.
-Condensation of chromosomes continuous.
-In this stage, the centrosomes travel towards the opposite poles.
III. Metaphase
-Chromosomes line up at the middle of the metaphase plate.
-Sister chromatids have adhered to the spindle fibres present at the opposite poles
IV. Anaphase
-The proteins joining or binding the sister chromatids start to break.
-This results in sister chromatids moving towards opposite poles.
V. Telophase
-Mitotic spindles break down.
-Decondensation of chromosomes present at opposite poles occur
-Nuclear envelop begins to form around each chromosomal set.
Based on the above particulars provided one can conclude that the correct option is A.
Note: The cell cycle concept was first ascribed by Howard and Pelc. They proposed the four-stage cell division called the cell division period, the G1 stage where the cell grows, the S stage that involves the synthesis of DNA, and the pre-mitotic stage called the G2 stage.
Complete answer: A cell cycle can be defined as a series of events wherein a cell divides and grows. The two stages that describe the cell division include interphase and mitosis. Interphase is considered the phase wherein the cell spends a prominent amount of time. The interphase is sub-categorized into three stages. The gap 1 stage or G1 stage, the synthesis stage or S stage, and the gap 2 stage or G2 stage.

Gap 1 or G1 stage – During this stage, the cell grows in size and accumulates enough amount of chromosomal DNA, associated proteins, and sufficient energy to participate in the replication process of each chromosome present in the nucleus.
Synthesis of DNA or S stage – This stage involves the replication of DNA. The replication of DNA results in the production or formation of sister chromatids. Sister chromatids are identical pairs of DNA molecules and are adhered to the centromeric region. Similarly, the centrosomes present in the cell also undergo replication and form mitotic spindles. Mitotic spindles choreograph the chromosomal movement during mitosis. In the case of an animal cell, centrosomes consist of centrioles which are rod-shaped objects at right angles to each other. The centrioles are also involved in the cell cycle process and help assemble the cell cycle. Centrioles are absent in plant cells and most fungi.
Gap 2 or G2 stage – In this stage, the cell is prepared before it enters the mitotic phase wherein it undergoes further and final cell division. Some of the cell organelles undergo replication, necessary proteins are synthesized for chromosomal manipulation and energy stores are replenished for the same reason.
MitosisThe cell now enters the mitotic phase which is a multistep process. The mitotic phase is divided into two categories. The first portion is called karyokinesis, also known as nuclear division. Karyokinesis is further subcategorized into a series of phases namely prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. And the second part is called cytokinesis. Cytokinesis involves the cytoplasmic components to separate physically to form two daughter cells. These cells each enter an interphase of their own and begin a new cell cycle round.
I. Prophase:
-Condensation of chromosomes occurs.
-The nuclear envelop breaks down and the nucleolus disappears.
-The emergence of spindle fibres from centrosomes occurs.
II. Pro-metaphase
-Mitotic spindles attach to the kinetochores appearing at the centromere.
-Condensation of chromosomes continuous.
-In this stage, the centrosomes travel towards the opposite poles.
III. Metaphase
-Chromosomes line up at the middle of the metaphase plate.
-Sister chromatids have adhered to the spindle fibres present at the opposite poles
IV. Anaphase
-The proteins joining or binding the sister chromatids start to break.
-This results in sister chromatids moving towards opposite poles.
V. Telophase
-Mitotic spindles break down.
-Decondensation of chromosomes present at opposite poles occur
-Nuclear envelop begins to form around each chromosomal set.
Based on the above particulars provided one can conclude that the correct option is A.
Note: The cell cycle concept was first ascribed by Howard and Pelc. They proposed the four-stage cell division called the cell division period, the G1 stage where the cell grows, the S stage that involves the synthesis of DNA, and the pre-mitotic stage called the G2 stage.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

The largest wind power cluster is located in the state class 11 social science CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

State and prove Bernoullis theorem class 11 physics CBSE

What steps did the French revolutionaries take to create class 11 social science CBSE

Which among the following are examples of coming together class 11 social science CBSE




