
A solution of (-) - 2-chloro-2-phenylethane in toluene racemises slowly in the presence of a small amount of $\text{SbC}{{\text{l}}_{5}}$, due to the formation of:
A. Carbene
B. Carbocation
C. Free radical
D. Carbanion
Answer
589.8k+ views
Hint: For this problem, we have to write the complete reaction in which firstly the antimony pentachloride will remove the chlorine atom from the given compound. Due to which the formation of the intermediate will take place.
Complete step by step answer:
- In the given question, we have to determine the correct intermediate which will be formed when (-) - 2-chloro-2-phenylethane in toluene will react with antimony pentachloride.
- As we know that the toluene is the 6-membered ring structure on which one methyl group is also attached.
- Now, when antimony pentafluoride reacts with the 2 - chloro - 2 - phenylethane which is present in the solution of toluene, it removes the chlorine molecule which is attached with the carbon atom as shown below:
$\text{Cl - CH(Ph) - C}{{\text{H}}_{3}}\text{ }\xrightarrow[\text{Toluene}]{\text{SbC}{{\text{l}}_{5}}}\text{ Ph - C}{{\text{H}}^{+}}\text{ - C}{{\text{H}}_{3}}\text{ + SbCl}_{6}^{-}$
- Here, the carbocation formed is known to have planar geometry.
- Also, the central carbon atom is known as chiral carbon because it is attached to the four different groups that are chlorine, phenyl, hydrogen and methyl group.
- Now, when an electrophile attaches to the carbocation then it will form two types of the compound and forms a racemic mixture.
- The attack of the electrophile take place from two places that are upward and lower as shown below
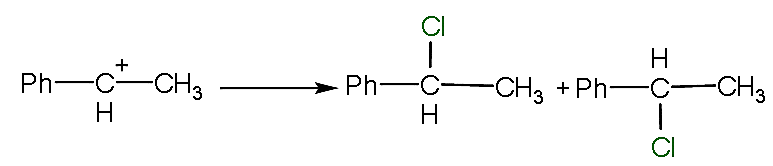
- Here, the mixture is known as d and l mixture which is also known as a racemic mixture.
So, the correct answer is “Option D”.
Note: As free radical is the unpaired pair of electrons whereas carbanion is the carbon species which consist of a negative charge or electrons. In carbene, the carbon molecule consists of two valence electrons and two unshared electrons.
Complete step by step answer:
- In the given question, we have to determine the correct intermediate which will be formed when (-) - 2-chloro-2-phenylethane in toluene will react with antimony pentachloride.
- As we know that the toluene is the 6-membered ring structure on which one methyl group is also attached.
- Now, when antimony pentafluoride reacts with the 2 - chloro - 2 - phenylethane which is present in the solution of toluene, it removes the chlorine molecule which is attached with the carbon atom as shown below:
$\text{Cl - CH(Ph) - C}{{\text{H}}_{3}}\text{ }\xrightarrow[\text{Toluene}]{\text{SbC}{{\text{l}}_{5}}}\text{ Ph - C}{{\text{H}}^{+}}\text{ - C}{{\text{H}}_{3}}\text{ + SbCl}_{6}^{-}$
- Here, the carbocation formed is known to have planar geometry.
- Also, the central carbon atom is known as chiral carbon because it is attached to the four different groups that are chlorine, phenyl, hydrogen and methyl group.
- Now, when an electrophile attaches to the carbocation then it will form two types of the compound and forms a racemic mixture.
- The attack of the electrophile take place from two places that are upward and lower as shown below

- Here, the mixture is known as d and l mixture which is also known as a racemic mixture.
So, the correct answer is “Option D”.
Note: As free radical is the unpaired pair of electrons whereas carbanion is the carbon species which consist of a negative charge or electrons. In carbene, the carbon molecule consists of two valence electrons and two unshared electrons.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

The largest wind power cluster is located in the state class 11 social science CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

State and prove Bernoullis theorem class 11 physics CBSE

What steps did the French revolutionaries take to create class 11 social science CBSE

Which among the following are examples of coming together class 11 social science CBSE




