
A solid in hemisphere at the bottom and conical above. If the surface area of the part is equal, find the ratio of radius and height of the conical part.
Answer
551.4k+ views
Hint: Here, we will use the given information and find the relation between the slant height of the cone and the radius of the hemisphere. Then we will use the relation obtained in the formula of the height of the cone and simplify it further to get the required ratio of radius and height.
Formula Used:
We will use the following formula:
1. Surface area of the Hemisphere is given by the formula \[S.A. = 2\pi {r^2}\] where \[r\] is the radius of the hemisphere.
2. Surface area of the Cone is given by the formula \[S.A. = \pi rl\] where \[r{\text{ }}and{\text{ }}l\] are the radius and slant height of the cone respectively.
3. Height of the Cone is given by the formula \[h = \sqrt {{l^2} - {r^2}} \] where \[r,l{\text{ }}and{\text{ }}h\] are the radius, slant height and height of the cone respectively.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
We will draw a cone mounted on a solid hemisphere.
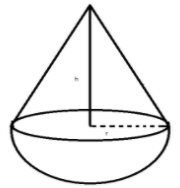
We are given that the surface area of the hemispherical part and surface area of the conical part are equal. Therefore
Surface area of the Hemispherical Part \[ = \] Surface area of the Conical Part.
By substituting the surface area of the hemisphere and the surface area of the cone formula, we get
\[ \Rightarrow 2\pi {r^2} = \pi rl\]
By cancelling the terms, we get
\[ \Rightarrow 2r = l\] ………………………………………………………\[\left( 1 \right)\]
Now, we will find the height of the cone
Height of the Cone is given by the formula \[h = \sqrt {{l^2} - {r^2}} \].
By substituting equation \[\left( 1 \right)\] in the formula of height, we get
\[ \Rightarrow h = \sqrt {{{\left( {2r} \right)}^2} - {r^2}} units\]
Applying the exponent on the terms, we get
\[ \Rightarrow h = \sqrt {4{r^2} - {r^2}} \]
Subtracting the terms, we get
\[ \Rightarrow h = \sqrt {3{r^2}} \]
By simplifying the equation, we get
\[ \Rightarrow h = \sqrt 3 r\]
Dividing both side by \[r\], we get
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{h}{r} = \dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{1}\]
Since it is the ratio of height and radius of a conical part, it gets reciprocal to find the ratio of radius and height, so we get
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{r}{h} = \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 3 }}\]
Therefore, the ratio of radius and height of the conical part is \[1:\sqrt 3 \].
Note:
We know that the surface area of the cone is the area occupied by the cone. The curved surface area of the hemisphere is the area occupied by the hemisphere. The slant height of a right cone is defined as the length of the line segment from the vertex of the cone to the base of the circle. We should be clear that while comparing two things the units should be similar. Ratio is defined as the representation of fractions.
Formula Used:
We will use the following formula:
1. Surface area of the Hemisphere is given by the formula \[S.A. = 2\pi {r^2}\] where \[r\] is the radius of the hemisphere.
2. Surface area of the Cone is given by the formula \[S.A. = \pi rl\] where \[r{\text{ }}and{\text{ }}l\] are the radius and slant height of the cone respectively.
3. Height of the Cone is given by the formula \[h = \sqrt {{l^2} - {r^2}} \] where \[r,l{\text{ }}and{\text{ }}h\] are the radius, slant height and height of the cone respectively.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
We will draw a cone mounted on a solid hemisphere.

We are given that the surface area of the hemispherical part and surface area of the conical part are equal. Therefore
Surface area of the Hemispherical Part \[ = \] Surface area of the Conical Part.
By substituting the surface area of the hemisphere and the surface area of the cone formula, we get
\[ \Rightarrow 2\pi {r^2} = \pi rl\]
By cancelling the terms, we get
\[ \Rightarrow 2r = l\] ………………………………………………………\[\left( 1 \right)\]
Now, we will find the height of the cone
Height of the Cone is given by the formula \[h = \sqrt {{l^2} - {r^2}} \].
By substituting equation \[\left( 1 \right)\] in the formula of height, we get
\[ \Rightarrow h = \sqrt {{{\left( {2r} \right)}^2} - {r^2}} units\]
Applying the exponent on the terms, we get
\[ \Rightarrow h = \sqrt {4{r^2} - {r^2}} \]
Subtracting the terms, we get
\[ \Rightarrow h = \sqrt {3{r^2}} \]
By simplifying the equation, we get
\[ \Rightarrow h = \sqrt 3 r\]
Dividing both side by \[r\], we get
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{h}{r} = \dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{1}\]
Since it is the ratio of height and radius of a conical part, it gets reciprocal to find the ratio of radius and height, so we get
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{r}{h} = \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 3 }}\]
Therefore, the ratio of radius and height of the conical part is \[1:\sqrt 3 \].
Note:
We know that the surface area of the cone is the area occupied by the cone. The curved surface area of the hemisphere is the area occupied by the hemisphere. The slant height of a right cone is defined as the length of the line segment from the vertex of the cone to the base of the circle. We should be clear that while comparing two things the units should be similar. Ratio is defined as the representation of fractions.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

The Equation xxx + 2 is Satisfied when x is Equal to Class 10 Maths

Which Country is Called "The Land of Festivals"?

What is Contraception List its four different methods class 10 biology CBSE




