
What is a solenoid? Draw the pattern of magnetic field lines of
(i) A current carrying solenoid and
(ii) A bar magnet.
List two distinguishing features between the two fields.
Answer
605.4k+ views
Hint: The word solenoid has been coined from a Greek word meaning “pipe-shaped”. Which can tell us a lot about its features. The magnetic field lines of a solenoid behave almost similar to that of a bar magnet but have some distinct features because solenoid behaves as an electromagnet, while a bar magnet is a natural magnet.
Complete step by step solution:
Solenoid is a coil which has been wound into a tightly packed helix having its length substantially greater than the diameter. A solenoid is used to generate a controlled magnetic field by passing current through it and which makes it an electromagnet. The coil is so arranged to generate a uniform field in the space around it.
(i) The magnetic field lines around a solenoid are the same as that of a bar magnet. The lines emerge from the north pole and passing through the south pole makes a continuous loop. The magnetic field lines inside the solenoid become almost straight and parallel to each other. A schematic representation has been shown below
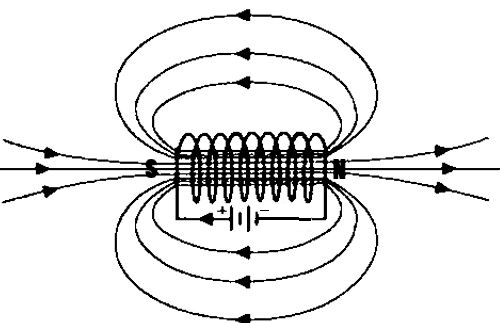
(ii) The magnetic field lines in the bar magnet also form closed lines and by convention are considered to emerge from the north pole and enter the south pole. The field lines density is highest at the poles and minimum at the midpoint of the line joining the poles. A schematic representation has been shown below,
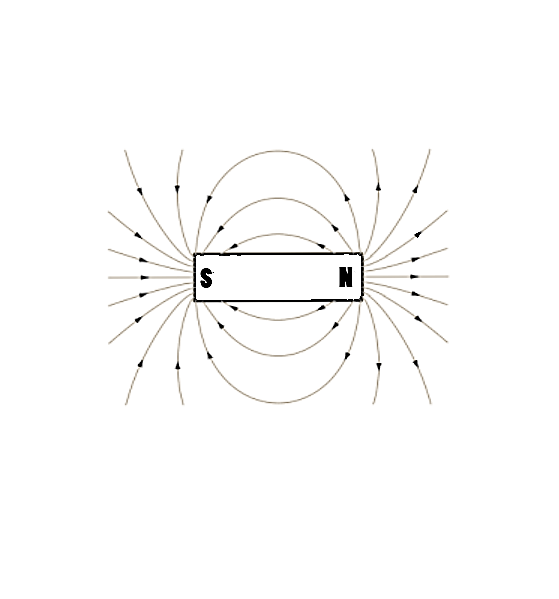
Distinguishing features of field lines of a bar magnet and a solenoid:
(i).When we cut a bar magnet into two halves, the magnetic properties do not change and both act as a magnet. While if cut a solenoid into two halves, the magnetic field strength of the halves gets decreased.
(ii).The poles of a solenoid can be altered and hence the direction of magnetic field lines, while in case of a bar magnet, it is fixed.
Note: We can notice from the magnetic field line diagrams of both bar magnet and a solenoid that they are almost similar; both have the property to align itself in any external magnetic field and the magnetic moment of both is also the same.
Complete step by step solution:
Solenoid is a coil which has been wound into a tightly packed helix having its length substantially greater than the diameter. A solenoid is used to generate a controlled magnetic field by passing current through it and which makes it an electromagnet. The coil is so arranged to generate a uniform field in the space around it.
(i) The magnetic field lines around a solenoid are the same as that of a bar magnet. The lines emerge from the north pole and passing through the south pole makes a continuous loop. The magnetic field lines inside the solenoid become almost straight and parallel to each other. A schematic representation has been shown below

(ii) The magnetic field lines in the bar magnet also form closed lines and by convention are considered to emerge from the north pole and enter the south pole. The field lines density is highest at the poles and minimum at the midpoint of the line joining the poles. A schematic representation has been shown below,

Distinguishing features of field lines of a bar magnet and a solenoid:
(i).When we cut a bar magnet into two halves, the magnetic properties do not change and both act as a magnet. While if cut a solenoid into two halves, the magnetic field strength of the halves gets decreased.
(ii).The poles of a solenoid can be altered and hence the direction of magnetic field lines, while in case of a bar magnet, it is fixed.
Note: We can notice from the magnetic field line diagrams of both bar magnet and a solenoid that they are almost similar; both have the property to align itself in any external magnetic field and the magnetic moment of both is also the same.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

Name the part of the brain responsible for the precision class 11 biology CBSE

The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to AEffect class 11 biology CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE




