
A small block is connected to one end of a massless spring of unstretched length $4.9m$ . The other end of the spring (see the figure) is fixed. The system lies on a horizontal frictionless surface. The block is stretched by 0.2 m and released from rest at t=0. lt then executes simple harmonic motion with angular frequency $\omega =\dfrac{\pi }{3}rad/s$.
Simultaneously $t=0$ , a small pebble is projected with speed v from point P at an angle of $45{}^\circ $ as shown in the figure. Point P is at a horizontal distance of $10m$ from O. If the pebble hits the block at $t=1s$ , the value of v is $\left( g=10m/{{s}^{-2}} \right)$
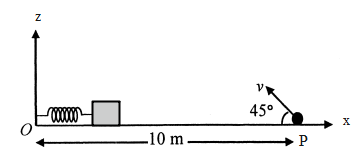
A. $\sqrt{50}m/s$
B. $\sqrt{51}m/s$
C. $\sqrt{52}m/s$
D.$\sqrt{53}m/s$

Answer
537.6k+ views
Hint:When an external force is applied to a mass that is attached to a spring whose one end is fixed the body undergoes an SHM (simple harmonic motion) motion. And when an object is projected at a certain angle with some speed the object performs a projectile motion. For the interaction of the object performing these kinds of motion, the object (pebble) has to cover a certain distance (range of flight) in the given time interval.
Complete answer:
The unstarched distance of the spring is $4.9m$
Angular frequency of SHM $\dfrac{\pi }{3}rad/s$
The angle of projection of pebble is $45{}^\circ $
Time ($t$) is $1s$
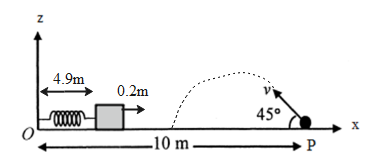
The condition mentioned in the question can be illustrated more with the diagram given billow,
According to the hooke's law, the force required to move a mass attached to a spring whose one end is fixed at a point is given by,
$F=-kx$
Where, $x$ is the distance displaced by the object.
The distance covered by a body performing SHM is given by,
$x=A\cos \omega t$
By putting the values from the given data,
$\begin{align}
& x=0.2\cos \frac{\pi }{3}(1) \\
& x=0.1m \\
\end{align}$
So the new position of the block at a time $t=1s$from the origin (reference point) will be,
\[4.9+0.1=5m\]
Now if the pebble undergoes a projectile position and at$t=1s$ the pebble and block comes in contact. The distance which the pebble have to cover will be,
$10m-5m=5m$
Thus, the range of the projectile is found out to be $5m$.
In the case of projectile motion, the range of flight is given by,
$R=\dfrac{{{v}^{2}}\sin 2\theta }{g}$
By rearranging, the velocity of the pebble is given by,
$v=\sqrt{\dfrac{Rg}{\sin 2\theta }}$
By putting the values, the velocity of the pebble will be,
$\begin{align}
& v=\sqrt{\dfrac{5(10)}{\sin \pi/2 }} \\
& \Rightarrow v=\sqrt{50}m/s \\
\end{align}$
Thus, the correct option which satisfies the question is Option A.
Note:
The distance by which a block is stretched and released to perform an SHM constitutes the initial amplitude of the simple harmonic motion (SHM). If two bodies have to meet at a certain time they have to cover the distance between then in the same interval only. The velocity required by one body to reach a point depends on the distance it has to travel in the given period.
Complete answer:
The unstarched distance of the spring is $4.9m$
Angular frequency of SHM $\dfrac{\pi }{3}rad/s$
The angle of projection of pebble is $45{}^\circ $
Time ($t$) is $1s$
The condition mentioned in the question can be illustrated more with the diagram given billow,

According to the hooke's law, the force required to move a mass attached to a spring whose one end is fixed at a point is given by,
$F=-kx$
Where, $x$ is the distance displaced by the object.
The distance covered by a body performing SHM is given by,
$x=A\cos \omega t$
By putting the values from the given data,
$\begin{align}
& x=0.2\cos \frac{\pi }{3}(1) \\
& x=0.1m \\
\end{align}$
So the new position of the block at a time $t=1s$from the origin (reference point) will be,
\[4.9+0.1=5m\]
Now if the pebble undergoes a projectile position and at$t=1s$ the pebble and block comes in contact. The distance which the pebble have to cover will be,
$10m-5m=5m$
Thus, the range of the projectile is found out to be $5m$.
In the case of projectile motion, the range of flight is given by,
$R=\dfrac{{{v}^{2}}\sin 2\theta }{g}$
By rearranging, the velocity of the pebble is given by,
$v=\sqrt{\dfrac{Rg}{\sin 2\theta }}$
By putting the values, the velocity of the pebble will be,
$\begin{align}
& v=\sqrt{\dfrac{5(10)}{\sin \pi/2 }} \\
& \Rightarrow v=\sqrt{50}m/s \\
\end{align}$
Thus, the correct option which satisfies the question is Option A.
Note:
The distance by which a block is stretched and released to perform an SHM constitutes the initial amplitude of the simple harmonic motion (SHM). If two bodies have to meet at a certain time they have to cover the distance between then in the same interval only. The velocity required by one body to reach a point depends on the distance it has to travel in the given period.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




