
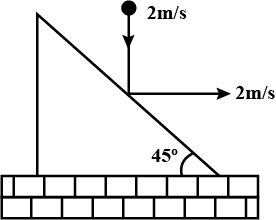
A small ball falling vertically downward with constant velocity, $v=2m/s$, strikes elastically an inclined plane moving with velocity, $2m/s$ as shown in the figure. The velocity of rebound of the ball with respect to the ground is:
$(a)4m/s$
$(b)2\sqrt{5}m/s$
$(c)2\sqrt{2}m/s$
$(d)2m/s$

Answer
546.9k+ views
Hint: By Conservation of Momentum, when the ball rebounds off the surface of the inclined plane elastically, it experiences same momentum but in the opposite direction so the net change in momentum is twice the initial momentum of the ball. We will also make use of the relative velocity of the ball with respect to the incline, it will help us visualize the problem better.
Complete answer:
Let the initial momentum of the ball be p.
Since the ball rebounds elastically, total change in momentum is $=2p$.
Now, the Relative velocity of ball with respect to the incline is given by:
Before collision:
$=-v$ directed to the right (horizontal component)
$=-v$ directed upwards (vertical component)
After collision:
$=+v$ directed left (horizontal component)
$=+v$ directed downwards (vertical component)
Therefore, the Velocity of the rebound ball can be written as:
$\Rightarrow {{V}_{rb,g}}=\sqrt{{{(2V\widehat{i})}^{2}}+{{(V\widehat{j})}^{2}}}$ [equation number $(1)$ ]
Where,
${{V}_{rb,g}}=$ velocity of rebound ball with respect to the ground
$2V\widehat{i}=$ horizontal component of rebound ball velocity
$V\widehat{j}=$ vertical component of rebound ball velocity
Putting the values of each term in equation number $(1)$ , we get:
$\Rightarrow {{V}_{rb,g}}=\sqrt{{{(2\times 2)}^{2}}+{{(2)}^{2}}}m/s$
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow {{V}_{rb,g}}=\sqrt{20}m/s \\
& \Rightarrow {{V}_{rb,g}}=2\sqrt{5}m/s \\
\end{align}$
Hence, the rebound velocity of the ball is $2\sqrt{5}m/s$ .
Hence, option (b) is the correct option.
Note:
While solving these types of questions, we can choose the frame of reference according to our ease and the velocity of our frame of reference should be kept zero to help solve the question properly and quickly. Hence, making our calculations easier and faster.
Complete answer:
Let the initial momentum of the ball be p.
Since the ball rebounds elastically, total change in momentum is $=2p$.
Now, the Relative velocity of ball with respect to the incline is given by:
Before collision:
$=-v$ directed to the right (horizontal component)
$=-v$ directed upwards (vertical component)
After collision:
$=+v$ directed left (horizontal component)
$=+v$ directed downwards (vertical component)
Therefore, the Velocity of the rebound ball can be written as:
$\Rightarrow {{V}_{rb,g}}=\sqrt{{{(2V\widehat{i})}^{2}}+{{(V\widehat{j})}^{2}}}$ [equation number $(1)$ ]
Where,
${{V}_{rb,g}}=$ velocity of rebound ball with respect to the ground
$2V\widehat{i}=$ horizontal component of rebound ball velocity
$V\widehat{j}=$ vertical component of rebound ball velocity
Putting the values of each term in equation number $(1)$ , we get:
$\Rightarrow {{V}_{rb,g}}=\sqrt{{{(2\times 2)}^{2}}+{{(2)}^{2}}}m/s$
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow {{V}_{rb,g}}=\sqrt{20}m/s \\
& \Rightarrow {{V}_{rb,g}}=2\sqrt{5}m/s \\
\end{align}$
Hence, the rebound velocity of the ball is $2\sqrt{5}m/s$ .
Hence, option (b) is the correct option.
Note:
While solving these types of questions, we can choose the frame of reference according to our ease and the velocity of our frame of reference should be kept zero to help solve the question properly and quickly. Hence, making our calculations easier and faster.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

Name the part of the brain responsible for the precision class 11 biology CBSE

The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to AEffect class 11 biology CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE




