
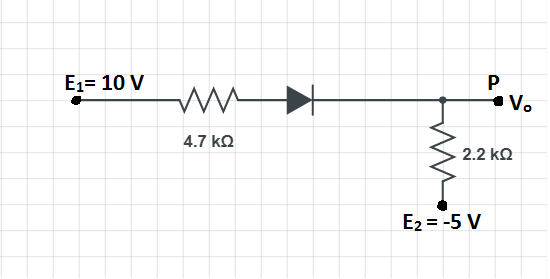
A silicon diode has a ‘knee voltage’ or a ‘threshold voltage of 0.7V. This Si diode connected in the circuit, as shown in the figure below. Calculate the voltage ${{\text{V}}_{\text{o}}}$ at point P:
A. $-0.44\text{ V}$
B. \[0.44\text{ V}\]
C. $4.4\text{ V}$
D. $-4.4\text{ V}$

Answer
596.1k+ views
Hint: A diode in forward bias can be considered as an element that provides a potential drop in the circuit. In order to find the potential at point P, we have to use Kirchoff’s voltage law to find the current across the circuit. If we know the current across the circuit, we can find the potential at P.
Complete step by step answer:
Kirchoff’s voltage law states that the algebraic sum of all the potentials across a closed loop is zero. So, from the circuit, we can write,
${{E}_{1}}-{{V}_{1}}-{{V}_{D}}-{{V}_{2}}-{{E}_{2}}=0$
${{\text{V}}_{\text{1}}}\text{ and }{{\text{V}}_{2}}$ are the voltage drop across the $4.7\text{K}\Omega \text{ and 2}\text{.2K}\Omega $ resistors. Which can be expressed as the product of the current flowing through the resistors and their respective resistance.
${{\text{V}}_{\text{D}}}$ is the voltage drop across the diode.
Substituting the values in the above equation, we get,
$10V-\left( 4.7K\Omega \right)i-0.7V-\left( 2.2K\Omega \right)i-(-5V)=0$
$\Rightarrow i=\dfrac{\left( 10-0.7+5 \right)V}{\left( 4.7+2.2 \right)K\Omega }$
$\therefore i\approx 2mA$
The potential at point P is the potential across the resistor of resistance $2.2K\Omega $. So, the voltage at point P is,
${{V}_{0}}=(2mA)\times 2.2K\Omega $
$\therefore {{V}_{o}}=4.4\text{V}$
So, the answer to the question is option (C).
Note: The p-n junction is the basic building block for many electronic devices like diodes, transistors, FET's etc..
When a p-type semiconductor and an n-type semiconductor forms an interface or boundary a p-n junction is formed.
A diode connected to a circuit in reverse bias shows a huge resistance typically in the mega-ohm range. So, we can say that the current flowing through the circuit in which the diode is connected in reverse bias is negligible or zero.
Kirchoff’s current law: This law states that the algebraic sum all the currents leaving and entering a junction in the circuit should be zero.
Kirchoff’s current law signifies the conservation of charge, while the Kirchoff’s voltage law signifies conservation of energy.
Complete step by step answer:
Kirchoff’s voltage law states that the algebraic sum of all the potentials across a closed loop is zero. So, from the circuit, we can write,
${{E}_{1}}-{{V}_{1}}-{{V}_{D}}-{{V}_{2}}-{{E}_{2}}=0$
${{\text{V}}_{\text{1}}}\text{ and }{{\text{V}}_{2}}$ are the voltage drop across the $4.7\text{K}\Omega \text{ and 2}\text{.2K}\Omega $ resistors. Which can be expressed as the product of the current flowing through the resistors and their respective resistance.
${{\text{V}}_{\text{D}}}$ is the voltage drop across the diode.
Substituting the values in the above equation, we get,
$10V-\left( 4.7K\Omega \right)i-0.7V-\left( 2.2K\Omega \right)i-(-5V)=0$
$\Rightarrow i=\dfrac{\left( 10-0.7+5 \right)V}{\left( 4.7+2.2 \right)K\Omega }$
$\therefore i\approx 2mA$
The potential at point P is the potential across the resistor of resistance $2.2K\Omega $. So, the voltage at point P is,
${{V}_{0}}=(2mA)\times 2.2K\Omega $
$\therefore {{V}_{o}}=4.4\text{V}$
So, the answer to the question is option (C).
Note: The p-n junction is the basic building block for many electronic devices like diodes, transistors, FET's etc..
When a p-type semiconductor and an n-type semiconductor forms an interface or boundary a p-n junction is formed.
A diode connected to a circuit in reverse bias shows a huge resistance typically in the mega-ohm range. So, we can say that the current flowing through the circuit in which the diode is connected in reverse bias is negligible or zero.
Kirchoff’s current law: This law states that the algebraic sum all the currents leaving and entering a junction in the circuit should be zero.
Kirchoff’s current law signifies the conservation of charge, while the Kirchoff’s voltage law signifies conservation of energy.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




