
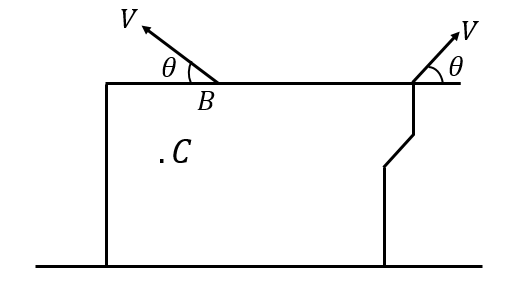
A sheet of wood moves over a smooth surface (shown in the figure). The magnitude of velocity of C is
A. \[v\]
B. $ 2v\cos \theta $
C. $ 2v\sin \theta $
D. $ 2v $

Answer
570.6k+ views
Hint: projectile motion with initial horizontal velocity:
When an object is thrown in the horizontal direction from a height, there is no force acting on a particle in horizontal, hence it is having constant velocity along the horizontal. A gravitational force is acting downwards on the particle; hence it is accelerating downwards.
Hence, as a result, the path of projectile motion is parabolic.
Complete step by step answer:
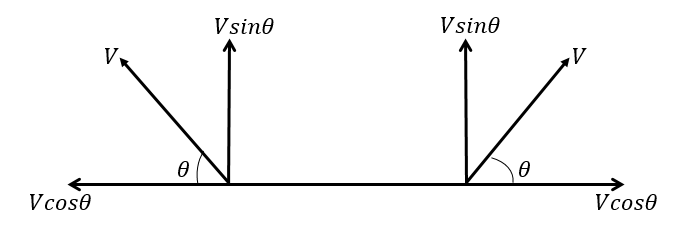
In figure the vertical component is $ V\sin \theta $ and the horizontal component is $ V\cos \theta $ . When we balanced the component both horizontally and vertically the average velocity we get is $ V' = 2V\sin \theta $ . The concept here is basic of projectile motion.
Hence, net velocity is $ {v’} = 2v\sin \theta $
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Note:
Projectile motion is a two dimensional motion in which the two components are independent from each other. Dimension basically means the number of independent values needed to define a position. A projectile is two dimensional. So, it consists of two motions that are independent to each other. A projectile has three important terms related to its time of flight, Range and maximum height. The horizontal velocity of a motion problem deals with motion in the X direction; that is, side to side, not up and down. Gravity, for example, acts only in the vertical direction and doesn’t affect horizontal motion directly. Horizontal velocity comes from forces that are in the X-axis. Vertical velocity is a special case of velocity only because the acceleration due to gravity acts in the vertical direction. This means that any motion in the vertical direction will be affected by the acceleration due to gravity.
When an object is thrown in the horizontal direction from a height, there is no force acting on a particle in horizontal, hence it is having constant velocity along the horizontal. A gravitational force is acting downwards on the particle; hence it is accelerating downwards.
Hence, as a result, the path of projectile motion is parabolic.
Complete step by step answer:
In figure the vertical component is $ V\sin \theta $ and the horizontal component is $ V\cos \theta $ . When we balanced the component both horizontally and vertically the average velocity we get is $ V' = 2V\sin \theta $ . The concept here is basic of projectile motion.
Hence, net velocity is $ {v’} = 2v\sin \theta $

So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Note:
Projectile motion is a two dimensional motion in which the two components are independent from each other. Dimension basically means the number of independent values needed to define a position. A projectile is two dimensional. So, it consists of two motions that are independent to each other. A projectile has three important terms related to its time of flight, Range and maximum height. The horizontal velocity of a motion problem deals with motion in the X direction; that is, side to side, not up and down. Gravity, for example, acts only in the vertical direction and doesn’t affect horizontal motion directly. Horizontal velocity comes from forces that are in the X-axis. Vertical velocity is a special case of velocity only because the acceleration due to gravity acts in the vertical direction. This means that any motion in the vertical direction will be affected by the acceleration due to gravity.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




