
A round balloon of radius ‘a’ subtends an angle \[\alpha \] at the eye of the observer while angle of elevation of its centre is \[\phi \] . Then the height of the centre of the balloon is \[a\sin \phi \csc \dfrac{\alpha }{2}\] .
(a) True
(b) False
Answer
596.7k+ views
Hint: First, we have to draw a figure as per the data given in question. So, will get as
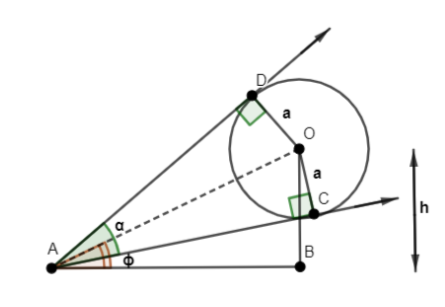
Then, we will prove that \[\Delta ADO\cong \Delta ACO\] and \[\angle OAD=\angle OAC=\dfrac{\alpha }{2}\] . Then we will use trigonometric rule for finding angle i.e. \[\sin \theta =\dfrac{\text{Opposite}}{\text{Hypotenuse}}\] . Using this we will find value of OA and then again applying the rule in \[\Delta AOB\] , we will get value of height h. Then we will compare value with the value given in question.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Here, we will draw the diagram of the data given. So, we will have like this:
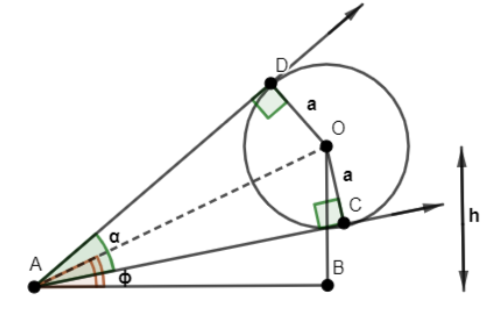
Here, the radius of the balloon is ‘a’. A point is the observer point where the angle made by the observer to see the balloon is \[\alpha \] . Angle of elevation is \[\phi \] . The height of the centre of the balloon is considered to be h. AD and AC are tangents drawn to radius making an angle of \[90{}^\circ \] .
Now, we will take \[\Delta ADO\] and \[\Delta ACO\] . We can see that \[OD=OC=a\] (radius) , \[OA=OA=\text{hypotenuse}\] , \[\angle ADO=\angle ACO=90{}^\circ \] . So, by this we can say that both the triangles are congruent. We can write it as
\[\Delta ADO\cong \Delta ACO\]
So, we can say that \[\angle OAD=\angle OAC=\dfrac{\alpha }{2}\] .
Now, we will take \[\Delta ACO\] . Applying trigonometric rule for finding angle i.e. \[\sin \theta =\dfrac{\text{Opposite}}{\text{Hypotenuse}}\] . So, we will take \[\dfrac{\alpha }{2}\] in place of \[\theta \] . So, we get as
\[\sin \dfrac{\alpha }{2}=\dfrac{OC}{OA}\]
On making OA i.e. hypotenuse as subject variable, we will get as
\[OA=\dfrac{OC}{\sin \dfrac{\alpha }{2}}\]
But we know that \[\dfrac{1}{\sin \theta }=\csc \theta \] . So, using this and OC as radius, we will get as
\[OA=a\csc \dfrac{\alpha }{2}\]
Now, we will take \[\Delta AOB\] . Again, we will apply the rule i.e. \[\sin \theta =\dfrac{\text{Opposite}}{\text{Hypotenuse}}\] where we will be taking \[\phi \] instead of \[\theta \] . So, we can write it as
\[\sin \phi =\dfrac{OB}{OA}\]
But we know that OB is height h which we have to find, and we will put the value of OA as found above. So, we will get as
\[\sin \phi =\dfrac{h}{a\csc \dfrac{\alpha }{2}}\]
On making h as subject variable, we will get as
\[a\sin \phi \csc \dfrac{\alpha }{2}=h\]
Thus, height h is the same as given in question.
Hence, option (a) is the correct answer.
Note: We can also find by taking cos ratio instead of sin ratio but in the question, height is given in the form of sin so, we have to take sin ratio only. Also, figures to this problem is very necessary otherwise, if the figure is not properly drawn then the whole answer might get wrong. So, be careful while drawing the figure as per the data given and understand it properly.

Then, we will prove that \[\Delta ADO\cong \Delta ACO\] and \[\angle OAD=\angle OAC=\dfrac{\alpha }{2}\] . Then we will use trigonometric rule for finding angle i.e. \[\sin \theta =\dfrac{\text{Opposite}}{\text{Hypotenuse}}\] . Using this we will find value of OA and then again applying the rule in \[\Delta AOB\] , we will get value of height h. Then we will compare value with the value given in question.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Here, we will draw the diagram of the data given. So, we will have like this:

Here, the radius of the balloon is ‘a’. A point is the observer point where the angle made by the observer to see the balloon is \[\alpha \] . Angle of elevation is \[\phi \] . The height of the centre of the balloon is considered to be h. AD and AC are tangents drawn to radius making an angle of \[90{}^\circ \] .
Now, we will take \[\Delta ADO\] and \[\Delta ACO\] . We can see that \[OD=OC=a\] (radius) , \[OA=OA=\text{hypotenuse}\] , \[\angle ADO=\angle ACO=90{}^\circ \] . So, by this we can say that both the triangles are congruent. We can write it as
\[\Delta ADO\cong \Delta ACO\]
So, we can say that \[\angle OAD=\angle OAC=\dfrac{\alpha }{2}\] .
Now, we will take \[\Delta ACO\] . Applying trigonometric rule for finding angle i.e. \[\sin \theta =\dfrac{\text{Opposite}}{\text{Hypotenuse}}\] . So, we will take \[\dfrac{\alpha }{2}\] in place of \[\theta \] . So, we get as
\[\sin \dfrac{\alpha }{2}=\dfrac{OC}{OA}\]
On making OA i.e. hypotenuse as subject variable, we will get as
\[OA=\dfrac{OC}{\sin \dfrac{\alpha }{2}}\]
But we know that \[\dfrac{1}{\sin \theta }=\csc \theta \] . So, using this and OC as radius, we will get as
\[OA=a\csc \dfrac{\alpha }{2}\]
Now, we will take \[\Delta AOB\] . Again, we will apply the rule i.e. \[\sin \theta =\dfrac{\text{Opposite}}{\text{Hypotenuse}}\] where we will be taking \[\phi \] instead of \[\theta \] . So, we can write it as
\[\sin \phi =\dfrac{OB}{OA}\]
But we know that OB is height h which we have to find, and we will put the value of OA as found above. So, we will get as
\[\sin \phi =\dfrac{h}{a\csc \dfrac{\alpha }{2}}\]
On making h as subject variable, we will get as
\[a\sin \phi \csc \dfrac{\alpha }{2}=h\]
Thus, height h is the same as given in question.
Hence, option (a) is the correct answer.
Note: We can also find by taking cos ratio instead of sin ratio but in the question, height is given in the form of sin so, we have to take sin ratio only. Also, figures to this problem is very necessary otherwise, if the figure is not properly drawn then the whole answer might get wrong. So, be careful while drawing the figure as per the data given and understand it properly.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

State and prove converse of BPT Basic Proportionality class 10 maths CBSE




