
A right triangle, whose sides are 15cm and 20cm is made to revolve about its hypotenuse. Find the volume and surface area of the double cone so formed. \[\left( \text{Use }\pi =\dfrac{22}{7} \right)\]

Answer
598.2k+ views
Hint: In this question, we can get the values of x and y by using the pythagoras theorem as given that the total base length is 25cm. Then we get a equation in x which on solving gives the value of x. Now, by substituting this in any of the pythagoras equation we get y. Now, on substituting the respective values in the formula of volume of cone and surface area of cone and simplifying gives the result.
Complete step-by-step answer:
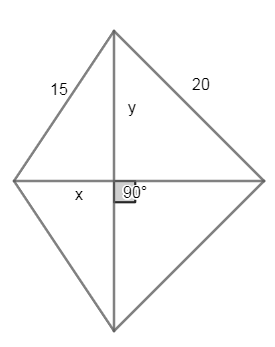
Now, on considering the triangle with hypotenuse of 15cm and applying the pythagoras theorem we get,
\[{{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}={{15}^{2}}........\left( 1 \right)\]
As we already know that the complete base of the given diagram is 25cm we get the base of the second right triangle as \[25-x\]
Now, on again applying the pythagorean theorem to this right triangle we get,
\[{{\left( 25-x \right)}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}={{20}^{2}}\]
Now, on further expanding and simplifying the above equation we get,
\[{{x}^{2}}-50x+{{25}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}={{20}^{2}}\]
Now, on further rearranging the terms we get,
\[{{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}-50x={{20}^{2}}-{{25}^{2}}.......\left( 2 \right)\]
Let us now subtract the equations (1) and (2)
\[\Rightarrow {{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}-50x-{{x}^{2}}-{{y}^{2}}={{20}^{2}}-{{25}^{2}}-{{15}^{2}}\]
Now, on further simplification we get,
\[\Rightarrow -50x=400-625-225\]
\[\Rightarrow -50x=-450\]
Now, on dividing with -50 on both sides we get,
\[\therefore x=9\]
Now, by substituting back this in the equation (1) we get,
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow {{9}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}={{15}^{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow {{y}^{2}}={{15}^{2}}-{{9}^{2}} \\
\end{align}\]
Now, on further simplification we get,
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow {{y}^{2}}=144 \\
& \therefore y=12 \\
\end{align}\]
As we already know that the volume of a cone of base radius r and height h is given by the formula
\[V=\dfrac{1}{3}\pi {{r}^{2}}h\]
The surface area of a cone of radius r and slant height l is given by the formula
\[S=\pi r\left( l+r \right)\]
Let us assume the volume and surface area of the first cone and second cone as
\[{{V}_{1}},{{S}_{1}}\text{ and }{{V}_{2}},{{S}_{2}}\]
Now, the volume and surface area of the first cone can be calculated as follows.
Let us compare the dimensions of the cone with the formulae.
\[\begin{align}
& h=x=9 \\
& r=y=12 \\
& l=15 \\
\end{align}\]
Now, let us calculate the volume of the cone
\[\Rightarrow {{V}_{1}}=\dfrac{1}{3}\pi {{r}^{2}}h\]
Now, on substituting the respective values in the above equation we get,
\[\Rightarrow {{V}_{1}}=\dfrac{1}{3}\pi \times {{\left( 12 \right)}^{2}}\times 9\]
Now, on further simplification we get,
\[\Rightarrow {{V}_{1}}=\dfrac{1}{3}\times \dfrac{22}{7}\times 144\times 9\]
Now, on cancelling out the common terms we get,
\[\therefore {{V}_{1}}=\dfrac{9504}{7}c{{m}^{3}}\]
Let us now calculate the surface area of this cone
\[\Rightarrow {{S}_{1}}=\pi r\left( l+r \right)\]
Now, on substituting the respective values we get,
\[\Rightarrow {{S}_{1}}=\pi \times 12\times \left( 12+15 \right)\]
Now, on further simplification we get,
\[\Rightarrow {{S}_{1}}=\dfrac{22}{7}\times 12\times 27\]
\[\therefore {{S}_{1}}=\dfrac{7128}{7}c{{m}^{2}}\]
Now, the volume and surface area of the second cone can be calculated as follows.
Let us compare the dimensions of the cone with the formulae.
\[\begin{align}
& h=25-x=16 \\
& r=y=12 \\
& l=20 \\
\end{align}\]
Now, let us calculate the volume of the cone
\[\Rightarrow {{V}_{2}}=\dfrac{1}{3}\pi {{r}^{2}}h\]
Now, on substituting the respective values in the above equation we get,
\[\Rightarrow {{V}_{2}}=\dfrac{1}{3}\pi \times {{\left( 12 \right)}^{2}}\times 16\]
Now, on further simplification we get,
\[\Rightarrow {{V}_{2}}=\dfrac{1}{3}\times \dfrac{22}{7}\times 144\times 16\]
Now, on cancelling out the common terms we get,
\[\therefore {{V}_{2}}=\dfrac{16896}{7}c{{m}^{3}}\]
Let us now calculate the surface area of this cone
\[\Rightarrow {{S}_{2}}=\pi r\left( l+r \right)\]
Now, on substituting the respective values we get,
\[\Rightarrow {{S}_{2}}=\pi \times 12\times \left( 12+20 \right)\]
Now, on further simplification we get,
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow {{S}_{2}}=\dfrac{22}{7}\times 12\times 32 \\
& \therefore {{S}_{2}}=\dfrac{8448}{7}c{{m}^{2}} \\
\end{align}\]
Now, the volume of the double cone is
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow {{V}_{1}}+{{V}_{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{9504}{7}+\dfrac{16896}{7} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{26400}{7}c{{m}^{3}} \\
\end{align}\]
Now, the surface area of the double cone is given by
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow {{S}_{1}}+{{S}_{2}}-\pi {{r}^{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{7128}{7}+\dfrac{8448}{7}-\dfrac{3168}{7} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{12408}{7}c{{m}^{2}} \\
\end{align}\]
Note:
Instead of finding the value of x and y in the beginning we can also find after substituting them in the volume of double cones. But, it would be a lengthy process to find the values according to the equation obtained.
It is important to note that while calculating the surface area we need to subtract the circular area because in the total surface area calculation we already added the circular area. Here, as the circular area is common for both the cones so when we add the total surface area we are including the circular area twice. So, we need to subtract one circular area.
While calculating and substituting we need to be careful because neglecting any of the term or substituting the incorrect value changes the result completely.
Complete step-by-step answer:
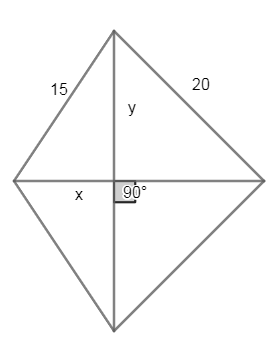
Now, on considering the triangle with hypotenuse of 15cm and applying the pythagoras theorem we get,
\[{{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}={{15}^{2}}........\left( 1 \right)\]
As we already know that the complete base of the given diagram is 25cm we get the base of the second right triangle as \[25-x\]
Now, on again applying the pythagorean theorem to this right triangle we get,
\[{{\left( 25-x \right)}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}={{20}^{2}}\]
Now, on further expanding and simplifying the above equation we get,
\[{{x}^{2}}-50x+{{25}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}={{20}^{2}}\]
Now, on further rearranging the terms we get,
\[{{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}-50x={{20}^{2}}-{{25}^{2}}.......\left( 2 \right)\]
Let us now subtract the equations (1) and (2)
\[\Rightarrow {{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}-50x-{{x}^{2}}-{{y}^{2}}={{20}^{2}}-{{25}^{2}}-{{15}^{2}}\]
Now, on further simplification we get,
\[\Rightarrow -50x=400-625-225\]
\[\Rightarrow -50x=-450\]
Now, on dividing with -50 on both sides we get,
\[\therefore x=9\]
Now, by substituting back this in the equation (1) we get,
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow {{9}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}={{15}^{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow {{y}^{2}}={{15}^{2}}-{{9}^{2}} \\
\end{align}\]
Now, on further simplification we get,
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow {{y}^{2}}=144 \\
& \therefore y=12 \\
\end{align}\]

As we already know that the volume of a cone of base radius r and height h is given by the formula
\[V=\dfrac{1}{3}\pi {{r}^{2}}h\]
The surface area of a cone of radius r and slant height l is given by the formula
\[S=\pi r\left( l+r \right)\]
Let us assume the volume and surface area of the first cone and second cone as
\[{{V}_{1}},{{S}_{1}}\text{ and }{{V}_{2}},{{S}_{2}}\]
Now, the volume and surface area of the first cone can be calculated as follows.
Let us compare the dimensions of the cone with the formulae.
\[\begin{align}
& h=x=9 \\
& r=y=12 \\
& l=15 \\
\end{align}\]
Now, let us calculate the volume of the cone
\[\Rightarrow {{V}_{1}}=\dfrac{1}{3}\pi {{r}^{2}}h\]
Now, on substituting the respective values in the above equation we get,
\[\Rightarrow {{V}_{1}}=\dfrac{1}{3}\pi \times {{\left( 12 \right)}^{2}}\times 9\]
Now, on further simplification we get,
\[\Rightarrow {{V}_{1}}=\dfrac{1}{3}\times \dfrac{22}{7}\times 144\times 9\]
Now, on cancelling out the common terms we get,
\[\therefore {{V}_{1}}=\dfrac{9504}{7}c{{m}^{3}}\]
Let us now calculate the surface area of this cone
\[\Rightarrow {{S}_{1}}=\pi r\left( l+r \right)\]
Now, on substituting the respective values we get,
\[\Rightarrow {{S}_{1}}=\pi \times 12\times \left( 12+15 \right)\]
Now, on further simplification we get,
\[\Rightarrow {{S}_{1}}=\dfrac{22}{7}\times 12\times 27\]
\[\therefore {{S}_{1}}=\dfrac{7128}{7}c{{m}^{2}}\]
Now, the volume and surface area of the second cone can be calculated as follows.
Let us compare the dimensions of the cone with the formulae.
\[\begin{align}
& h=25-x=16 \\
& r=y=12 \\
& l=20 \\
\end{align}\]
Now, let us calculate the volume of the cone
\[\Rightarrow {{V}_{2}}=\dfrac{1}{3}\pi {{r}^{2}}h\]
Now, on substituting the respective values in the above equation we get,
\[\Rightarrow {{V}_{2}}=\dfrac{1}{3}\pi \times {{\left( 12 \right)}^{2}}\times 16\]
Now, on further simplification we get,
\[\Rightarrow {{V}_{2}}=\dfrac{1}{3}\times \dfrac{22}{7}\times 144\times 16\]
Now, on cancelling out the common terms we get,
\[\therefore {{V}_{2}}=\dfrac{16896}{7}c{{m}^{3}}\]
Let us now calculate the surface area of this cone
\[\Rightarrow {{S}_{2}}=\pi r\left( l+r \right)\]
Now, on substituting the respective values we get,
\[\Rightarrow {{S}_{2}}=\pi \times 12\times \left( 12+20 \right)\]
Now, on further simplification we get,
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow {{S}_{2}}=\dfrac{22}{7}\times 12\times 32 \\
& \therefore {{S}_{2}}=\dfrac{8448}{7}c{{m}^{2}} \\
\end{align}\]
Now, the volume of the double cone is
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow {{V}_{1}}+{{V}_{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{9504}{7}+\dfrac{16896}{7} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{26400}{7}c{{m}^{3}} \\
\end{align}\]
Now, the surface area of the double cone is given by
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow {{S}_{1}}+{{S}_{2}}-\pi {{r}^{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{7128}{7}+\dfrac{8448}{7}-\dfrac{3168}{7} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{12408}{7}c{{m}^{2}} \\
\end{align}\]
Note:
Instead of finding the value of x and y in the beginning we can also find after substituting them in the volume of double cones. But, it would be a lengthy process to find the values according to the equation obtained.
It is important to note that while calculating the surface area we need to subtract the circular area because in the total surface area calculation we already added the circular area. Here, as the circular area is common for both the cones so when we add the total surface area we are including the circular area twice. So, we need to subtract one circular area.
While calculating and substituting we need to be careful because neglecting any of the term or substituting the incorrect value changes the result completely.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

State and prove converse of BPT Basic Proportionality class 10 maths CBSE




