
A right circular cone has a given curved surface A. Show that when it’s volume is maximum the ratio of the height to the base radius is $\sqrt{2}:1$ ?
Answer
558.9k+ views
Hint: Try to find the height ‘h’ of cone in terms of Area $A=\pi rl$(by putting $l=\sqrt{{{r}^{2}}+{{h}^{2}}}$). Put the value of ‘h’ in volume expression $V=\dfrac{1}{3}\pi {{r}^{2}}h$ and differentiate w.r.t ‘r’ equating to 0. Then simplify to obtain the required proof.
Complete step-by-step answer:
As we know, the formula for the curved surface area of a cone which does not include the area of the base is $A=\pi rl$, where ‘r’ is the radius of the base and ‘l’ is the lateral height (slant height)
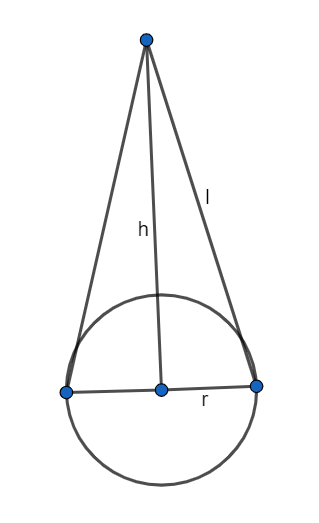
Pythagoras' theorem: If we have a right angle triangle with height ‘a’, base ‘b’ and hypotenuse ‘c’ then
$c=\sqrt{{{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}}$
Using Pythagoras' theorem for the above figure, we get
$l=\sqrt{{{r}^{2}}+{{h}^{2}}}$
Substituting the value of ‘l’ in $A=\pi rl$, we get
$\begin{align}
& A=\pi r\sqrt{{{r}^{2}}+{{h}^{2}}} \\
& \Rightarrow {{A}^{2}}={{\pi }^{2}}{{r}^{2}}\left( {{r}^{2}}+{{h}^{2}} \right) \\
& \Rightarrow {{A}^{2}}={{\pi }^{2}}{{r}^{4}}+{{\pi }^{2}}{{r}^{2}}{{h}^{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow {{\pi }^{2}}{{r}^{2}}{{h}^{2}}={{A}^{2}}-{{\pi }^{2}}{{r}^{4}} \\
& \Rightarrow {{h}^{2}}=\dfrac{{{A}^{2}}-{{\pi }^{2}}{{r}^{4}}}{{{\pi }^{2}}{{r}^{2}}} \\
& \Rightarrow h=\dfrac{\sqrt{{{A}^{2}}-{{\pi }^{2}}{{r}^{4}}}}{\pi r} \\
\end{align}$
Again we know the volume $V=\dfrac{1}{3}\pi {{r}^{2}}h$
Substituting the value of ‘h’, we get
$\begin{align}
& V=\dfrac{1}{3}\pi {{r}^{2}}\dfrac{\sqrt{{{A}^{2}}-{{\pi }^{2}}{{r}^{4}}}}{\pi r} \\
& \Rightarrow V=\dfrac{1}{3}r\sqrt{{{A}^{2}}-{{\pi }^{2}}{{r}^{4}}} \\
& \Rightarrow V=\dfrac{1}{3}r{{\left( {{A}^{2}}-{{\pi }^{2}}{{r}^{4}} \right)}^{\dfrac{1}{2}}} \\
\end{align}$
Taking derivative w.r.t ‘r’, we get
\[\begin{align}
& \dfrac{dV}{dr}=\dfrac{d}{dr}\left( \dfrac{1}{3}r{{\left( {{A}^{2}}-{{\pi }^{2}}{{r}^{4}} \right)}^{\dfrac{1}{2}}} \right) \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{dV}{dr}=\dfrac{1}{3}\left[ r\left( \dfrac{1}{2} \right){{\left( {{A}^{2}}-{{\pi }^{2}}{{r}^{4}} \right)}^{-\dfrac{1}{2}}}\left( -4{{\pi }^{2}}{{r}^{3}} \right)+{{\left( {{A}^{2}}-{{\pi }^{2}}{{r}^{4}} \right)}^{\dfrac{1}{2}}} \right] \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{dV}{dr}=\dfrac{1}{3}\left( \dfrac{-2{{\pi }^{2}}{{r}^{4}}}{\sqrt{{{A}^{2}}-{{\pi }^{2}}{{r}^{4}}}}+\sqrt{{{A}^{2}}-{{\pi }^{2}}{{r}^{4}}} \right) \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{dV}{dr}=\dfrac{-2{{\pi }^{2}}{{r}^{4}}+{{A}^{2}}-{{\pi }^{2}}{{r}^{4}}}{3\sqrt{{{A}^{2}}-{{\pi }^{2}}{{r}^{4}}}} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{dV}{dr}=\dfrac{-3{{\pi }^{2}}{{r}^{4}}+{{A}^{2}}}{3\sqrt{{{A}^{2}}-{{\pi }^{2}}{{r}^{4}}}} \\
\end{align}\]
For maximum volume,
\[\begin{align}
& \dfrac{dV}{dr}=0 \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{-3{{\pi }^{2}}{{r}^{4}}+{{A}^{2}}}{3\sqrt{{{A}^{2}}-{{\pi }^{2}}{{r}^{4}}}}=0 \\
& \Rightarrow -3{{\pi }^{2}}{{r}^{4}}+{{A}^{2}}=0 \\
& \Rightarrow {{A}^{2}}=3{{\pi }^{2}}{{r}^{4}} \\
\end{align}\]
Substituting the value of $A=\pi r\sqrt{{{r}^{2}}+{{h}^{2}}}$, we get
${{\pi }^{2}}{{r}^{2}}\left( {{r}^{2}}+{{h}^{2}} \right)=3{{\pi }^{2}}{{r}^{4}}$
Dividing both sides by ${{\pi }^{2}}{{r}^{2}}$, we get
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{\pi }^{2}}{{r}^{2}}\left( {{r}^{2}}+{{h}^{2}} \right)}{{{\pi }^{2}}{{r}^{2}}}=\dfrac{3{{\pi }^{2}}{{r}^{4}}}{{{\pi }^{2}}{{r}^{2}}} \\
& \Rightarrow {{r}^{2}}+{{h}^{2}}=3{{r}^{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow {{h}^{2}}=2{{r}^{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{h}^{2}}}{{{r}^{2}}}=2 \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{h}{r}=\dfrac{\sqrt{2}}{1} \\
\end{align}$
Hence Proved.
Note: Volume should be written in terms of ‘h’ which can be obtained from area. For maximum volume the first derivative of the volume function should be equal to 0 i.e. \[\dfrac{dV}{dr}=0\] and the second derivative of the volume function should be negative.
$\begin{align}
& \dfrac{{{\partial }^{2}}V}{\partial {{r}^{2}}} \\
& =\dfrac{d}{dr}\left( \dfrac{dV}{dr} \right) \\
& =\dfrac{d}{dr}\left( \dfrac{-3{{\pi }^{2}}{{r}^{4}}+{{A}^{2}}}{3\sqrt{{{A}^{2}}-{{\pi }^{2}}{{r}^{4}}}} \right) \\
\end{align}$
The derivative of the form $\dfrac{u}{v}=\dfrac{vdu-udv}{{{v}^{2}}}$
\[\begin{align}
& =\dfrac{\left( 3\sqrt{{{A}^{2}}-{{\pi }^{2}}{{r}^{4}}} \right)\dfrac{d}{dr}\left( -3{{\pi }^{2}}{{r}^{4}}+{{A}^{2}} \right)-\left( -3{{\pi }^{2}}{{r}^{4}}+{{A}^{2}} \right)\dfrac{d}{dr}\left( 3\sqrt{{{A}^{2}}-{{\pi }^{2}}{{r}^{4}}} \right)}{{{\left( 3\sqrt{{{A}^{2}}-{{\pi }^{2}}{{r}^{4}}} \right)}^{2}}} \\
& =\dfrac{\left( 3\sqrt{{{A}^{2}}-{{\pi }^{2}}{{r}^{4}}} \right)\left( -12{{\pi }^{2}}{{r}^{3}} \right)+\left( -3{{\pi }^{2}}{{r}^{4}}+{{A}^{2}} \right)\left( 12{{\pi }^{2}}{{r}^{3}}{{\left( \sqrt{{{A}^{2}}-{{\pi }^{2}}{{r}^{4}}} \right)}^{-\dfrac{1}{2}}} \right)}{{{\left( 3\sqrt{{{A}^{2}}-{{\pi }^{2}}{{r}^{4}}} \right)}^{2}}} \\
\end{align}\]
Since the numerator is the summation of two negative quantities and the denominator is a square term so we can conclude that $\dfrac{{{\partial }^{2}}V}{\partial {{r}^{2}}}$ is negative.
Hence, the maxima exists.
Now we can move forward for \[\dfrac{dV}{dr}=0\] which is already done earlier in the solution part.
Complete step-by-step answer:
As we know, the formula for the curved surface area of a cone which does not include the area of the base is $A=\pi rl$, where ‘r’ is the radius of the base and ‘l’ is the lateral height (slant height)

Pythagoras' theorem: If we have a right angle triangle with height ‘a’, base ‘b’ and hypotenuse ‘c’ then
$c=\sqrt{{{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}}$
Using Pythagoras' theorem for the above figure, we get
$l=\sqrt{{{r}^{2}}+{{h}^{2}}}$
Substituting the value of ‘l’ in $A=\pi rl$, we get
$\begin{align}
& A=\pi r\sqrt{{{r}^{2}}+{{h}^{2}}} \\
& \Rightarrow {{A}^{2}}={{\pi }^{2}}{{r}^{2}}\left( {{r}^{2}}+{{h}^{2}} \right) \\
& \Rightarrow {{A}^{2}}={{\pi }^{2}}{{r}^{4}}+{{\pi }^{2}}{{r}^{2}}{{h}^{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow {{\pi }^{2}}{{r}^{2}}{{h}^{2}}={{A}^{2}}-{{\pi }^{2}}{{r}^{4}} \\
& \Rightarrow {{h}^{2}}=\dfrac{{{A}^{2}}-{{\pi }^{2}}{{r}^{4}}}{{{\pi }^{2}}{{r}^{2}}} \\
& \Rightarrow h=\dfrac{\sqrt{{{A}^{2}}-{{\pi }^{2}}{{r}^{4}}}}{\pi r} \\
\end{align}$
Again we know the volume $V=\dfrac{1}{3}\pi {{r}^{2}}h$
Substituting the value of ‘h’, we get
$\begin{align}
& V=\dfrac{1}{3}\pi {{r}^{2}}\dfrac{\sqrt{{{A}^{2}}-{{\pi }^{2}}{{r}^{4}}}}{\pi r} \\
& \Rightarrow V=\dfrac{1}{3}r\sqrt{{{A}^{2}}-{{\pi }^{2}}{{r}^{4}}} \\
& \Rightarrow V=\dfrac{1}{3}r{{\left( {{A}^{2}}-{{\pi }^{2}}{{r}^{4}} \right)}^{\dfrac{1}{2}}} \\
\end{align}$
Taking derivative w.r.t ‘r’, we get
\[\begin{align}
& \dfrac{dV}{dr}=\dfrac{d}{dr}\left( \dfrac{1}{3}r{{\left( {{A}^{2}}-{{\pi }^{2}}{{r}^{4}} \right)}^{\dfrac{1}{2}}} \right) \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{dV}{dr}=\dfrac{1}{3}\left[ r\left( \dfrac{1}{2} \right){{\left( {{A}^{2}}-{{\pi }^{2}}{{r}^{4}} \right)}^{-\dfrac{1}{2}}}\left( -4{{\pi }^{2}}{{r}^{3}} \right)+{{\left( {{A}^{2}}-{{\pi }^{2}}{{r}^{4}} \right)}^{\dfrac{1}{2}}} \right] \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{dV}{dr}=\dfrac{1}{3}\left( \dfrac{-2{{\pi }^{2}}{{r}^{4}}}{\sqrt{{{A}^{2}}-{{\pi }^{2}}{{r}^{4}}}}+\sqrt{{{A}^{2}}-{{\pi }^{2}}{{r}^{4}}} \right) \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{dV}{dr}=\dfrac{-2{{\pi }^{2}}{{r}^{4}}+{{A}^{2}}-{{\pi }^{2}}{{r}^{4}}}{3\sqrt{{{A}^{2}}-{{\pi }^{2}}{{r}^{4}}}} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{dV}{dr}=\dfrac{-3{{\pi }^{2}}{{r}^{4}}+{{A}^{2}}}{3\sqrt{{{A}^{2}}-{{\pi }^{2}}{{r}^{4}}}} \\
\end{align}\]
For maximum volume,
\[\begin{align}
& \dfrac{dV}{dr}=0 \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{-3{{\pi }^{2}}{{r}^{4}}+{{A}^{2}}}{3\sqrt{{{A}^{2}}-{{\pi }^{2}}{{r}^{4}}}}=0 \\
& \Rightarrow -3{{\pi }^{2}}{{r}^{4}}+{{A}^{2}}=0 \\
& \Rightarrow {{A}^{2}}=3{{\pi }^{2}}{{r}^{4}} \\
\end{align}\]
Substituting the value of $A=\pi r\sqrt{{{r}^{2}}+{{h}^{2}}}$, we get
${{\pi }^{2}}{{r}^{2}}\left( {{r}^{2}}+{{h}^{2}} \right)=3{{\pi }^{2}}{{r}^{4}}$
Dividing both sides by ${{\pi }^{2}}{{r}^{2}}$, we get
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{\pi }^{2}}{{r}^{2}}\left( {{r}^{2}}+{{h}^{2}} \right)}{{{\pi }^{2}}{{r}^{2}}}=\dfrac{3{{\pi }^{2}}{{r}^{4}}}{{{\pi }^{2}}{{r}^{2}}} \\
& \Rightarrow {{r}^{2}}+{{h}^{2}}=3{{r}^{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow {{h}^{2}}=2{{r}^{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{h}^{2}}}{{{r}^{2}}}=2 \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{h}{r}=\dfrac{\sqrt{2}}{1} \\
\end{align}$
Hence Proved.
Note: Volume should be written in terms of ‘h’ which can be obtained from area. For maximum volume the first derivative of the volume function should be equal to 0 i.e. \[\dfrac{dV}{dr}=0\] and the second derivative of the volume function should be negative.
$\begin{align}
& \dfrac{{{\partial }^{2}}V}{\partial {{r}^{2}}} \\
& =\dfrac{d}{dr}\left( \dfrac{dV}{dr} \right) \\
& =\dfrac{d}{dr}\left( \dfrac{-3{{\pi }^{2}}{{r}^{4}}+{{A}^{2}}}{3\sqrt{{{A}^{2}}-{{\pi }^{2}}{{r}^{4}}}} \right) \\
\end{align}$
The derivative of the form $\dfrac{u}{v}=\dfrac{vdu-udv}{{{v}^{2}}}$
\[\begin{align}
& =\dfrac{\left( 3\sqrt{{{A}^{2}}-{{\pi }^{2}}{{r}^{4}}} \right)\dfrac{d}{dr}\left( -3{{\pi }^{2}}{{r}^{4}}+{{A}^{2}} \right)-\left( -3{{\pi }^{2}}{{r}^{4}}+{{A}^{2}} \right)\dfrac{d}{dr}\left( 3\sqrt{{{A}^{2}}-{{\pi }^{2}}{{r}^{4}}} \right)}{{{\left( 3\sqrt{{{A}^{2}}-{{\pi }^{2}}{{r}^{4}}} \right)}^{2}}} \\
& =\dfrac{\left( 3\sqrt{{{A}^{2}}-{{\pi }^{2}}{{r}^{4}}} \right)\left( -12{{\pi }^{2}}{{r}^{3}} \right)+\left( -3{{\pi }^{2}}{{r}^{4}}+{{A}^{2}} \right)\left( 12{{\pi }^{2}}{{r}^{3}}{{\left( \sqrt{{{A}^{2}}-{{\pi }^{2}}{{r}^{4}}} \right)}^{-\dfrac{1}{2}}} \right)}{{{\left( 3\sqrt{{{A}^{2}}-{{\pi }^{2}}{{r}^{4}}} \right)}^{2}}} \\
\end{align}\]
Since the numerator is the summation of two negative quantities and the denominator is a square term so we can conclude that $\dfrac{{{\partial }^{2}}V}{\partial {{r}^{2}}}$ is negative.
Hence, the maxima exists.
Now we can move forward for \[\dfrac{dV}{dr}=0\] which is already done earlier in the solution part.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

State and prove converse of BPT Basic Proportionality class 10 maths CBSE




