
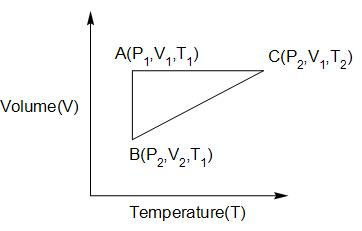
A reversible cyclic process for an ideal gas is shown. Here $P,V,T$ are pressure, volume and temperature, respectively. The thermodynamic parameters $q,w,H,U$ are heat, work, enthalpy and internal energy, respectively. The correct option(s) is?
A. ${q_{AC}} = \Delta {U_{BC}}$ and ${w_{AB}} = {P_2}\left( {{V_2} - {V_1}} \right)$
B.${q_{BC}} = \Delta {H_{AC}}$ and ${w_{BC}} = {P_2}\left( {{V_2} - {V_1}} \right)$
C. ${q_{AC}} = \Delta {U_{BC}}$ and $\Delta {H_{CA}} < \Delta {U_{CA}}$
D. ${q_{BC}} = \Delta {H_{AC}}$ and $\Delta {H_{CA}} > \Delta {U_{CA}}$

Answer
591k+ views
Hint: To answer this question, you need to recall the applications of first law of thermodynamics. The process AC is isochoric, process AB is isothermal and process BC is isobaric.
Formula used:
First law of thermodynamics: $\Delta U = q - w$
Where, $\Delta U$ is the internal energy of the system, $q$ is the heat change involved in the process, $w$ is the work done
Complete step by step answer:
Since the process is cyclic, we can say that $\Delta {H_{AC}} + \Delta {H_{CB}} + \Delta {H_{BA}} = 0$.
We know that, in an isochoric process, the change in volume during the process is zero hence work done will be zero across the process AC.
In an isothermal process, the temperature remains constant throughout and thus, the change in internal energy is zero. Also, the enthalpy change for an isothermal process is zero.
Thus, we can say that $\Delta {H_{AC}} = \Delta {H_{BC}}$
For an isobaric process, we have that ${q_p} = \Delta H$
$ \Rightarrow {q_{bc}} = \Delta {H_{BC}} = \Delta {H_{AC}}$
The work done in an isothermal process is given by, ${W_{AB}} = nRT\ln \left( {\dfrac{{{V_2}}}{{{V_1}}}} \right)$
Therefore, option A is incorrect.
Since ${q_{bc}} = \Delta {H_{AC}}$ and work done at constant pressure is $P({V_2} - {V_1})$, option B is correct.
We know that, $\Delta H \leqslant \Delta U$.
Thus, we can say that $\Delta {H_{CA}} < \Delta {U_{CA}}$.
Therefore, option C is correct and option D is incorrect.
Hence, the correct options are B and C.
Note:
The first law of thermodynamics is a version of the law of conservation of energy, modified for thermodynamic processes, distinguishing two types of transfer of energy, as heat transferred and thermodynamic work done, and relating them toInternal energy which is a function of a body's state. The law of conservation of energy states that the energy of any isolated system is always constant. In layman terms, energy can be transformed from one form to another, but can neither be created nor be destroyed.
Formula used:
First law of thermodynamics: $\Delta U = q - w$
Where, $\Delta U$ is the internal energy of the system, $q$ is the heat change involved in the process, $w$ is the work done
Complete step by step answer:
Since the process is cyclic, we can say that $\Delta {H_{AC}} + \Delta {H_{CB}} + \Delta {H_{BA}} = 0$.
We know that, in an isochoric process, the change in volume during the process is zero hence work done will be zero across the process AC.
In an isothermal process, the temperature remains constant throughout and thus, the change in internal energy is zero. Also, the enthalpy change for an isothermal process is zero.
Thus, we can say that $\Delta {H_{AC}} = \Delta {H_{BC}}$
For an isobaric process, we have that ${q_p} = \Delta H$
$ \Rightarrow {q_{bc}} = \Delta {H_{BC}} = \Delta {H_{AC}}$
The work done in an isothermal process is given by, ${W_{AB}} = nRT\ln \left( {\dfrac{{{V_2}}}{{{V_1}}}} \right)$
Therefore, option A is incorrect.
Since ${q_{bc}} = \Delta {H_{AC}}$ and work done at constant pressure is $P({V_2} - {V_1})$, option B is correct.
We know that, $\Delta H \leqslant \Delta U$.
Thus, we can say that $\Delta {H_{CA}} < \Delta {U_{CA}}$.
Therefore, option C is correct and option D is incorrect.
Hence, the correct options are B and C.
Note:
The first law of thermodynamics is a version of the law of conservation of energy, modified for thermodynamic processes, distinguishing two types of transfer of energy, as heat transferred and thermodynamic work done, and relating them toInternal energy which is a function of a body's state. The law of conservation of energy states that the energy of any isolated system is always constant. In layman terms, energy can be transformed from one form to another, but can neither be created nor be destroyed.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

The largest wind power cluster is located in the state class 11 social science CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

State and prove Bernoullis theorem class 11 physics CBSE

What steps did the French revolutionaries take to create class 11 social science CBSE

Which among the following are examples of coming together class 11 social science CBSE




