
A refrigerator has a coefficient of performance $1 \cdot 6$ . Find the work to be supplied to this refrigerator so that it rejects $1000{\text{kJ}}$ of heat.
A) ${\text{385kJ}}$
B) ${\text{627kJ}}$
C) ${\text{836kJ}}$
D) $1000{\text{kJ}}$
Answer
592.8k+ views
Hint:In a refrigerator, the working substance supplies work to extract some heat from the cold reservoir and then rejects heat to the hot reservoir. The coefficient of performance of a refrigerator is the ratio of the useful heat obtained from the cold reservoir to the work supplied to reject the heat. The first law of thermodynamics gives the heat rejected to the surroundings as the sum of the external work done and the heat extracted from the cold reservoir.
Formulas used:
-The heat rejected to the surroundings is given by, ${Q_1} = W + {Q_2}$ where ${Q_2}$ is the heat absorbed from the cold reservoir and $W$ is the external work done or supplied to reject the heat ${Q_1}$ .
-The coefficient of performance of a refrigerator is given by, $\alpha = \dfrac{{{Q_2}}}{W}$ where ${Q_2}$ is the heat absorbed from the cold reservoir and $W$ is the external work done or supplied to the refrigerator.
Complete step by step answer.
Step 1: Sketch a schematic representation of the working of the refrigerator and list the given parameters.
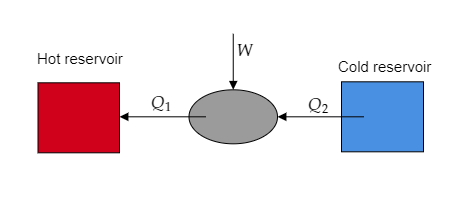
Here heat ${Q_2}$ is absorbed from the refrigerator by the external agency and $W$ is the amount of work supplied to the refrigerator to reject the heat ${Q_1}$ .
The amount of heat rejected to the surroundings is given to be ${Q_1} = 1000{\text{kJ}}$.
The coefficient of performance of the refrigerator is given to be $\alpha = 1 \cdot 6$ .
Step 2: Express the heat rejected to the surroundings based on the first law of thermodynamics and express the relation for the coefficient of performance of the refrigerator.
According to the first law of thermodynamics, we have ${Q_1} = W + {Q_2}$ -------- (1)
Now the coefficient of performance of the refrigerator can be expressed as $\alpha = \dfrac{{{Q_2}}}{W}$ -------- (2)
$ \Rightarrow {Q_2} = \alpha W$ -------- (3)
Substituting equation (3) in (1) we get, ${Q_1} = W + \alpha W$
$ \Rightarrow W = \dfrac{{{Q_1}}}{{1 + \alpha }}$
Thus the work to be supplied is given as $W = \dfrac{{{Q_1}}}{{1 + \alpha }}$ --------- (4)
Step 3: Substitute the values for the rejected heat ${Q_1}$ and the coefficient of performance $\alpha $ to find $W$ .
Equation (4) gives the work supplied to the refrigerator as $W = \dfrac{{{Q_1}}}{{1 + \alpha }}$ .
Substituting for ${Q_1} = 1000{\text{kJ}}$ and $\alpha = 1 \cdot 6$ in equation (4) we get, $W = \dfrac{{1000}}{{1 + 1 \cdot 6}} = \dfrac{{1000}}{{2 \cdot 6}} = 384 \cdot 6{\text{kJ}}$
Thus the work supplied to the refrigerator is $W \approx 385{\text{kJ}}$ .
So the correct option is A.
Note:In a refrigerator, the cold reservoir refers to the inside of a refrigerator and the work is done by the compressor. The hot reservoir refers to the surroundings of a refrigerator. It is a known fact that heat flows from a hotter body to a colder body. But in a refrigerator whose sole purpose is to keep its content at a low temperature, the reverse of the above-mentioned fact happens. This is only because of an external agency continuously supplying work to keep the temperature of the refrigerator colder than its surroundings. This implies that heat will not flow by itself from a colder body to a hotter one.
Formulas used:
-The heat rejected to the surroundings is given by, ${Q_1} = W + {Q_2}$ where ${Q_2}$ is the heat absorbed from the cold reservoir and $W$ is the external work done or supplied to reject the heat ${Q_1}$ .
-The coefficient of performance of a refrigerator is given by, $\alpha = \dfrac{{{Q_2}}}{W}$ where ${Q_2}$ is the heat absorbed from the cold reservoir and $W$ is the external work done or supplied to the refrigerator.
Complete step by step answer.
Step 1: Sketch a schematic representation of the working of the refrigerator and list the given parameters.

Here heat ${Q_2}$ is absorbed from the refrigerator by the external agency and $W$ is the amount of work supplied to the refrigerator to reject the heat ${Q_1}$ .
The amount of heat rejected to the surroundings is given to be ${Q_1} = 1000{\text{kJ}}$.
The coefficient of performance of the refrigerator is given to be $\alpha = 1 \cdot 6$ .
Step 2: Express the heat rejected to the surroundings based on the first law of thermodynamics and express the relation for the coefficient of performance of the refrigerator.
According to the first law of thermodynamics, we have ${Q_1} = W + {Q_2}$ -------- (1)
Now the coefficient of performance of the refrigerator can be expressed as $\alpha = \dfrac{{{Q_2}}}{W}$ -------- (2)
$ \Rightarrow {Q_2} = \alpha W$ -------- (3)
Substituting equation (3) in (1) we get, ${Q_1} = W + \alpha W$
$ \Rightarrow W = \dfrac{{{Q_1}}}{{1 + \alpha }}$
Thus the work to be supplied is given as $W = \dfrac{{{Q_1}}}{{1 + \alpha }}$ --------- (4)
Step 3: Substitute the values for the rejected heat ${Q_1}$ and the coefficient of performance $\alpha $ to find $W$ .
Equation (4) gives the work supplied to the refrigerator as $W = \dfrac{{{Q_1}}}{{1 + \alpha }}$ .
Substituting for ${Q_1} = 1000{\text{kJ}}$ and $\alpha = 1 \cdot 6$ in equation (4) we get, $W = \dfrac{{1000}}{{1 + 1 \cdot 6}} = \dfrac{{1000}}{{2 \cdot 6}} = 384 \cdot 6{\text{kJ}}$
Thus the work supplied to the refrigerator is $W \approx 385{\text{kJ}}$ .
So the correct option is A.
Note:In a refrigerator, the cold reservoir refers to the inside of a refrigerator and the work is done by the compressor. The hot reservoir refers to the surroundings of a refrigerator. It is a known fact that heat flows from a hotter body to a colder body. But in a refrigerator whose sole purpose is to keep its content at a low temperature, the reverse of the above-mentioned fact happens. This is only because of an external agency continuously supplying work to keep the temperature of the refrigerator colder than its surroundings. This implies that heat will not flow by itself from a colder body to a hotter one.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

The largest wind power cluster is located in the state class 11 social science CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

State and prove Bernoullis theorem class 11 physics CBSE

What steps did the French revolutionaries take to create class 11 social science CBSE

Which among the following are examples of coming together class 11 social science CBSE




