
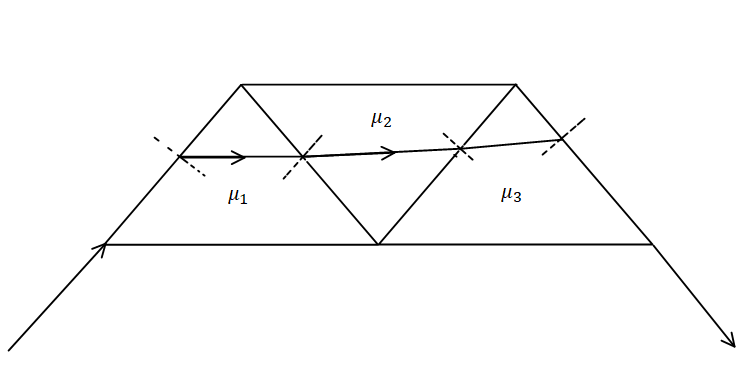
A ray of light enters at grazing angle of incidence into an assembly of three isosceles right-angled prisms having refractive indices ${\mu _1} = \sqrt 2 $,${\mu _2} = \sqrt x $ and ${\mu _3} = \sqrt 3 $. If finally an emergent light ray also emerges at gazing angle then calculate x.
A) 5
B) 3
C) 2
D) 1

Answer
587.4k+ views
Hint: The speed of light is different in different mediums and due to which the when a ray of light enters from one medium into another medium then the ray of light bends from the normal to the medium also speed of light of the medium depends upon the refractive index of the respective medium.
Complete step by step answer:
The Snell’s law is given by,$\dfrac{{\sin {i_1}}}{{\sin {r_1}}} = {\mu _1}$
As the angle of incidence is$90^\circ $ as the refractive index of the air is 1.
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{\sin {i_1}}}{{\sin {r_1}}} = {\mu _1}$
\[ \Rightarrow \sin {r_1} = \dfrac{{\sin {i_1}}}{{{\mu _1}}}\]
\[ \Rightarrow \sin {r_1} = \dfrac{{\sin 90^\circ }}{{\sqrt 2 }}\](as the value of the ${i_1} = 90^\circ $)
\[ \Rightarrow \sin {r_1} = \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 2 }}\](Since the value of \[\sin 90^\circ \]is equal to 1)
\[ \Rightarrow {r_1} = {\sin ^{ - 1}}\dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 2 }}\]
\[ \Rightarrow {r_1} = 45^\circ \](as the angle of $\sin 45^\circ $ is equal to $\dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 2 }}$)
Applying the Snell’s law for the second surface,
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{\sin {i_2}}}{{\sin {r_2}}} = \dfrac{{{\mu _2}}}{{{\mu _1}}}$
Since $\sin {i_2} = \cos {r_1}$
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{\cos {r_1}}}{{\sin {r_2}}} = \dfrac{{{\mu _2}}}{{\sqrt 2 }}$(as the value of ${\mu _3} = \sqrt 2 $)
$ \Rightarrow \sqrt 2 \cos {r_1} = {\mu _2}\sin {r_2}$
$ \Rightarrow \sin {r_2} = \dfrac{{\sqrt 2 }}{{{\mu _2}}} \cdot \left( {\cos 45^\circ } \right)$ (as the value of \[{r_1} = 45^\circ \])
$ \Rightarrow \sin {r_2} = \dfrac{1}{{{\mu _2}}}$………eq. (1)
Snell’s law for the third surface.
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{\sin {i_3}}}{{\sin {r_3}}} = \dfrac{{{\mu _3}}}{{{\mu _2}}}$
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{\sin {i_3}}}{{\sin {r_3}}} = \dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{{{\mu _2}}}$(as the value of ${\mu _3} = \sqrt 3 $)
Since$\sin {i_3} = \cos {r_2}$, therefore we get
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{\cos {r_2}}}{{\sin {r_3}}} = \dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{{{\mu _2}}}$
$ \Rightarrow \sin {r_3} = \dfrac{{{\mu _2}\sqrt {1 - \sin {r_2}^2} }}{{{\mu _3}}}$ (Since $\cos {r_2} = \sqrt {1 - {{\sin }^2}{r_2}} $)
$ \Rightarrow \sin {r_3} = \dfrac{{{\mu _2}\sqrt {1 - {{\left( {\dfrac{1}{{{\mu _2}}}} \right)}^2}} }}{{\sqrt 3 }}$(replacing the value of $\sin {r_2}$from equation (1))
$ \Rightarrow \sin {r_3} = \dfrac{{{\mu _2}\sqrt {\dfrac{{{\mu _2}^2 - 1}}{{{\mu _2}^2}}} }}{{\sqrt 3 }}$(Taking L.C.M)
$ \Rightarrow \sin {r_3} = \dfrac{{\sqrt {{\mu _2}^2 - 1} }}{{\sqrt 3 }}$………eq. (2)
For the fourth interface, Snell’s law would be,
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{\sin {i_4}}}{{\sin {r_4}}} = \dfrac{{{\mu _4}}}{{{\mu _3}}}\]
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{\sin {i_4}}}{{\sin 90^\circ }} = \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 3 }}\](As the value of ${r_4} = 90^\circ $ also the value of${\mu _3} = \sqrt 3 $)
\[ \Rightarrow \sin {i_4} = \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 3 }}\]
Also,$\sin {i_4} = \cos {r_3}$,
\[ \Rightarrow \cos {r_3} = \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 3 }}\]………eq. (3)
We know that,
$ \Rightarrow {\sin ^2}{r_3} + {\cos ^2}{r_3} = 1$
Replace the value of $\sin {r_3}$ and $\cos {r_3}$ from equation (2) and equation (3) in above equation.
$ \Rightarrow {\sin ^2}{r_3} + {\cos ^2}{r_3} = 1$
$ \Rightarrow {\left[ {\dfrac{{\sqrt {{\mu _2}^2 - 1} }}{{\sqrt 3 }}} \right]^2} + {\left( {\dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 3 }}} \right)^2} = 1$
On simplification,
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{\mu _2}^2 - 1}}{3} + \dfrac{1}{3} = 1$
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{\mu _2}^2 - 1 + 1}}{3} = 1$
On further simplification,
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{\mu _2}^2}}{3} = 1$
$ \Rightarrow {\mu _2} = \sqrt 3 $
Therefore, the value of x=3. So the correct is option B.
Note:
It is advisable for the students to remember Snell’s law as it is a very important topic in ray optics and also the problems like this have to be solved using Snell’s law only. The refractive index of the air is equal to 1.
Complete step by step answer:
The Snell’s law is given by,$\dfrac{{\sin {i_1}}}{{\sin {r_1}}} = {\mu _1}$
As the angle of incidence is$90^\circ $ as the refractive index of the air is 1.
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{\sin {i_1}}}{{\sin {r_1}}} = {\mu _1}$
\[ \Rightarrow \sin {r_1} = \dfrac{{\sin {i_1}}}{{{\mu _1}}}\]
\[ \Rightarrow \sin {r_1} = \dfrac{{\sin 90^\circ }}{{\sqrt 2 }}\](as the value of the ${i_1} = 90^\circ $)
\[ \Rightarrow \sin {r_1} = \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 2 }}\](Since the value of \[\sin 90^\circ \]is equal to 1)
\[ \Rightarrow {r_1} = {\sin ^{ - 1}}\dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 2 }}\]
\[ \Rightarrow {r_1} = 45^\circ \](as the angle of $\sin 45^\circ $ is equal to $\dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 2 }}$)
Applying the Snell’s law for the second surface,
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{\sin {i_2}}}{{\sin {r_2}}} = \dfrac{{{\mu _2}}}{{{\mu _1}}}$
Since $\sin {i_2} = \cos {r_1}$
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{\cos {r_1}}}{{\sin {r_2}}} = \dfrac{{{\mu _2}}}{{\sqrt 2 }}$(as the value of ${\mu _3} = \sqrt 2 $)
$ \Rightarrow \sqrt 2 \cos {r_1} = {\mu _2}\sin {r_2}$
$ \Rightarrow \sin {r_2} = \dfrac{{\sqrt 2 }}{{{\mu _2}}} \cdot \left( {\cos 45^\circ } \right)$ (as the value of \[{r_1} = 45^\circ \])
$ \Rightarrow \sin {r_2} = \dfrac{1}{{{\mu _2}}}$………eq. (1)
Snell’s law for the third surface.
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{\sin {i_3}}}{{\sin {r_3}}} = \dfrac{{{\mu _3}}}{{{\mu _2}}}$
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{\sin {i_3}}}{{\sin {r_3}}} = \dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{{{\mu _2}}}$(as the value of ${\mu _3} = \sqrt 3 $)
Since$\sin {i_3} = \cos {r_2}$, therefore we get
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{\cos {r_2}}}{{\sin {r_3}}} = \dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{{{\mu _2}}}$
$ \Rightarrow \sin {r_3} = \dfrac{{{\mu _2}\sqrt {1 - \sin {r_2}^2} }}{{{\mu _3}}}$ (Since $\cos {r_2} = \sqrt {1 - {{\sin }^2}{r_2}} $)
$ \Rightarrow \sin {r_3} = \dfrac{{{\mu _2}\sqrt {1 - {{\left( {\dfrac{1}{{{\mu _2}}}} \right)}^2}} }}{{\sqrt 3 }}$(replacing the value of $\sin {r_2}$from equation (1))
$ \Rightarrow \sin {r_3} = \dfrac{{{\mu _2}\sqrt {\dfrac{{{\mu _2}^2 - 1}}{{{\mu _2}^2}}} }}{{\sqrt 3 }}$(Taking L.C.M)
$ \Rightarrow \sin {r_3} = \dfrac{{\sqrt {{\mu _2}^2 - 1} }}{{\sqrt 3 }}$………eq. (2)
For the fourth interface, Snell’s law would be,
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{\sin {i_4}}}{{\sin {r_4}}} = \dfrac{{{\mu _4}}}{{{\mu _3}}}\]
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{\sin {i_4}}}{{\sin 90^\circ }} = \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 3 }}\](As the value of ${r_4} = 90^\circ $ also the value of${\mu _3} = \sqrt 3 $)
\[ \Rightarrow \sin {i_4} = \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 3 }}\]
Also,$\sin {i_4} = \cos {r_3}$,
\[ \Rightarrow \cos {r_3} = \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 3 }}\]………eq. (3)
We know that,
$ \Rightarrow {\sin ^2}{r_3} + {\cos ^2}{r_3} = 1$
Replace the value of $\sin {r_3}$ and $\cos {r_3}$ from equation (2) and equation (3) in above equation.
$ \Rightarrow {\sin ^2}{r_3} + {\cos ^2}{r_3} = 1$
$ \Rightarrow {\left[ {\dfrac{{\sqrt {{\mu _2}^2 - 1} }}{{\sqrt 3 }}} \right]^2} + {\left( {\dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 3 }}} \right)^2} = 1$
On simplification,
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{\mu _2}^2 - 1}}{3} + \dfrac{1}{3} = 1$
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{\mu _2}^2 - 1 + 1}}{3} = 1$
On further simplification,
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{\mu _2}^2}}{3} = 1$
$ \Rightarrow {\mu _2} = \sqrt 3 $
Therefore, the value of x=3. So the correct is option B.
Note:
It is advisable for the students to remember Snell’s law as it is a very important topic in ray optics and also the problems like this have to be solved using Snell’s law only. The refractive index of the air is equal to 1.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Giving reasons state the signs positive or negative class 12 physics CBSE

Explain esterification reaction with the help of a class 12 chemistry CBSE

What is defined as a solenoid Depict a diagram with class 12 physics CBSE




