
What is a primary, secondary and tertiary halide?
Answer
515.4k+ views
Hint: Halogens are electronegative in nature and include fluorine, chlorine, bromine and iodine. Alkyl halides are those compounds in which one of the hydrogen atoms of the alkane is replaced with halide. Negative part of the compound is called halide.
Complete answer:
Alkyl halides are those compounds in which one of the hydrogen atoms of the alkane is replaced with halide. The general formula for alkyl halides is \[{{C}_{n}}{{H}_{2n+1}}X\]. Where \[n\] is a natural number. When \[n=1\], then the formula becomes \[C{{H}_{3}}X\] which is called methyl halide. Halides can be fluorides, chlorides, bromide and iodides. In order to form other members of primary halides, one of the hydrogen of methyl halide is replaced with a carbon atom. This is illustrated in the following diagram.
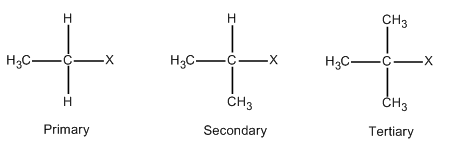
In case of secondary halides, two of the hydrogen of methyl halide is replaced with carbon atoms as described in the above diagram. On the similar lines, three of the hydrogen of methyl halide is replaced with carbon atoms in case of tertiary halides which is also described in the above diagram.
Additional Information: Due to electronegativity difference between halogen and carbon, \[C-X\]bond is polar in nature where \[X\]carries a \[\delta -\] negative charge while alkyl moiety carries a \[\delta +\]charge.
Note:
It is important to note that methyl halide is the simplest primary halide. In order to form other members of primary halides, one of the hydrogen of methyl halide is replaced with a carbon atom. In case of secondary and tertiary halides, two and three of the hydrogen of methyl halides are replaced with carbon atoms, respectively.
Complete answer:
Alkyl halides are those compounds in which one of the hydrogen atoms of the alkane is replaced with halide. The general formula for alkyl halides is \[{{C}_{n}}{{H}_{2n+1}}X\]. Where \[n\] is a natural number. When \[n=1\], then the formula becomes \[C{{H}_{3}}X\] which is called methyl halide. Halides can be fluorides, chlorides, bromide and iodides. In order to form other members of primary halides, one of the hydrogen of methyl halide is replaced with a carbon atom. This is illustrated in the following diagram.

In case of secondary halides, two of the hydrogen of methyl halide is replaced with carbon atoms as described in the above diagram. On the similar lines, three of the hydrogen of methyl halide is replaced with carbon atoms in case of tertiary halides which is also described in the above diagram.
Additional Information: Due to electronegativity difference between halogen and carbon, \[C-X\]bond is polar in nature where \[X\]carries a \[\delta -\] negative charge while alkyl moiety carries a \[\delta +\]charge.
Note:
It is important to note that methyl halide is the simplest primary halide. In order to form other members of primary halides, one of the hydrogen of methyl halide is replaced with a carbon atom. In case of secondary and tertiary halides, two and three of the hydrogen of methyl halides are replaced with carbon atoms, respectively.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

Name the part of the brain responsible for the precision class 11 biology CBSE

The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to AEffect class 11 biology CBSE

A solution of a substance X is used for white washing class 11 chemistry CBSE




