
A position dependent force F acting on a particle and its force-position curve is shown in figure. Work done on the particle when its displacement 0 to 5 m is:
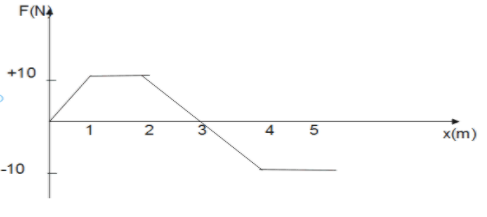
1) 35 J
2) 25 J
3) 45 J
4) 5 J

Answer
584.1k+ views
Hint: Work done on an object depends on the amount of force F causing the work, the displacement d experienced by the object. Also, work done is given by the area under the F-x curve. S.I unit of work is Joule (J).
Total area under the given curve can be calculated by dividing the curve in small areas and adding them.
Formula used:
Work done= area under F-x curve.
Area of triangle${A_T} = \dfrac{1}{2} \times base \times height$
Area of rectangle${A_R} = length \times breadth$
Complete answer:
We know that, Work done on an object depends on the amount of force F causing the work, the displacement d experienced by the object.
Work done = area under F-x curve.
Or, W= Area
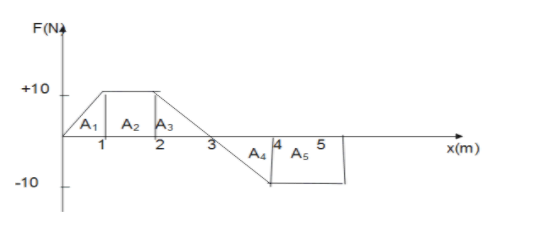
From above figure:
$\eqalign{
& W = {A_1} + {A_2} + {A_3} - ({A_4} + {A_5}) \cr
& \Rightarrow W = \left[ {\dfrac{1}{2} \times 1 \times 10} \right] + [1 \times 10] + \left[ {\dfrac{1}{2} \times 1 \times 10} \right] - \left[ {\dfrac{1}{2} \times 1 \times 10 + 10 \times 1} \right] \cr
& \Rightarrow W = 5 + 10 + 5 - (5 + 10) \cr
& \therefore W = 5J \cr} $
Therefore, option 4) is correct i.e., work done on the particle, when the displacement is 0 to 5 m is 5 Joule.
Additional information:
Work done can also be given by $W = Fd\cos \theta $, here $\theta $ is the angle between the force vector F and the displacement vector d.
If the angle between the force vector and the displacement d is zero, then the work done is maximum.
If the angle between the force vector and displacement d is ${90^ \circ }$, the work done is zero.
Force is push or pull upon an object’s interaction with another object. From Newton’s second law force F is given by the product of mass m and acceleration a. Acceleration is the rate of change of the velocity of an object with respect to time. Acceleration is a vector quantity.
Deceleration is when the speed or velocity decreases. It can also be defined as the acceleration which is opposite to the velocity.
Note:
Work done on an object depends on the amount of force F causing the work, the displacement d experienced by the object. So, if there is no displacement then the work done upon the object is zero. Also, in work when the force and the displacement are perpendicular to each other we do not have to do any work.
Total area under the given curve can be calculated by dividing the curve in small areas and adding them.
Formula used:
Work done= area under F-x curve.
Area of triangle${A_T} = \dfrac{1}{2} \times base \times height$
Area of rectangle${A_R} = length \times breadth$
Complete answer:
We know that, Work done on an object depends on the amount of force F causing the work, the displacement d experienced by the object.
Work done = area under F-x curve.
Or, W= Area

From above figure:
$\eqalign{
& W = {A_1} + {A_2} + {A_3} - ({A_4} + {A_5}) \cr
& \Rightarrow W = \left[ {\dfrac{1}{2} \times 1 \times 10} \right] + [1 \times 10] + \left[ {\dfrac{1}{2} \times 1 \times 10} \right] - \left[ {\dfrac{1}{2} \times 1 \times 10 + 10 \times 1} \right] \cr
& \Rightarrow W = 5 + 10 + 5 - (5 + 10) \cr
& \therefore W = 5J \cr} $
Therefore, option 4) is correct i.e., work done on the particle, when the displacement is 0 to 5 m is 5 Joule.
Additional information:
Work done can also be given by $W = Fd\cos \theta $, here $\theta $ is the angle between the force vector F and the displacement vector d.
If the angle between the force vector and the displacement d is zero, then the work done is maximum.
If the angle between the force vector and displacement d is ${90^ \circ }$, the work done is zero.
Force is push or pull upon an object’s interaction with another object. From Newton’s second law force F is given by the product of mass m and acceleration a. Acceleration is the rate of change of the velocity of an object with respect to time. Acceleration is a vector quantity.
Deceleration is when the speed or velocity decreases. It can also be defined as the acceleration which is opposite to the velocity.
Note:
Work done on an object depends on the amount of force F causing the work, the displacement d experienced by the object. So, if there is no displacement then the work done upon the object is zero. Also, in work when the force and the displacement are perpendicular to each other we do not have to do any work.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

Name the part of the brain responsible for the precision class 11 biology CBSE

The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to AEffect class 11 biology CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE




