
When a p-n-p transistor is operated in a saturation region, then its _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ .
A. Base-emitter junction is forward biased and base-collector junction is reverse biased.
B. Both base-emitter and base-collector junctions are reverse biased.
C. Both base-emitter and base-collector junctions are forward biased.
D. Base-emitter junction is reversed biased and base-collector junction is forward biased.
Answer
593.7k+ views
Hint: When a transistor is operated in a saturation region, the emitter and the collector terminals are at higher potential. When the anode terminal of a junction diode is at higher potential than that of the cathode, the junction diode is said to be forward biased.
Complete answer:
A transistor is a semiconductor device, which is formed by fusing two junction diodes. When the anodes of the two diodes are fused, the transistor is called an n-p-n transistor. When the cathodes of the two diodes are fused, the transistor is called a p-n-p transistor.
A transistor consists of three parts – a collector, an emitter and a base. The middle part is base.
Consider a p-n-p transistor. In a p-n-p transistor, the outer ends (terminal) of the emitter and the collector are anodes (positive terminals). And the terminal of the base is a cathode.
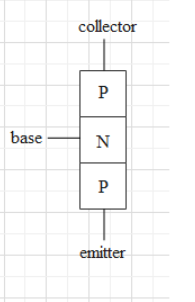
When a transistor is operated in a saturation region, the emitter and the collector terminals are at higher potential. When the anode terminal of a junction diode is at higher potential than that of the cathode, the junction diode is said to be forward biased.
Since in a p-n-p transistor the emitter and collector are the anodes, they are at higher potential. Hence, both base-emitter and base-collector junctions are forward biased.
This means that the correct option is C.
Note:
When the both junctions are forward biased, a high amount current will flow in the transistor. Therefore, the resistance of the circuit is very low.
In case of a n-p-n transition, in the saturation region, both junctions will be reverse biased. Hence, no current will flow and the resistance will be high.
Complete answer:
A transistor is a semiconductor device, which is formed by fusing two junction diodes. When the anodes of the two diodes are fused, the transistor is called an n-p-n transistor. When the cathodes of the two diodes are fused, the transistor is called a p-n-p transistor.
A transistor consists of three parts – a collector, an emitter and a base. The middle part is base.
Consider a p-n-p transistor. In a p-n-p transistor, the outer ends (terminal) of the emitter and the collector are anodes (positive terminals). And the terminal of the base is a cathode.

When a transistor is operated in a saturation region, the emitter and the collector terminals are at higher potential. When the anode terminal of a junction diode is at higher potential than that of the cathode, the junction diode is said to be forward biased.
Since in a p-n-p transistor the emitter and collector are the anodes, they are at higher potential. Hence, both base-emitter and base-collector junctions are forward biased.
This means that the correct option is C.
Note:
When the both junctions are forward biased, a high amount current will flow in the transistor. Therefore, the resistance of the circuit is very low.
In case of a n-p-n transition, in the saturation region, both junctions will be reverse biased. Hence, no current will flow and the resistance will be high.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Organisms of a higher trophic level which feed on several class 12 biology CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers

Give simple chemical tests to distinguish between the class 12 chemistry CBSE




