
A plane area of $100c{m^2}$ is placed in a uniform electric field of 100 N/C such that the angle between area vector and an electric field is ${60^ \circ }$. The electric flux over the surface is
A. $0 \cdot 5Wb$
B. $5Wb$
C. $1Wb$
D. $0$
Answer
579.3k+ views
Hint: This question can be solved by the direct application of the definition of the term electric flux.
Electric flux is the measure of the electric field through a given surface, though an electric field cannot flow on itself. It is a way of describing the electric field strength at any distance from the charge causing the field.
The electric flux is defined as the product of the electric field and the area.
Electric flux, $\phi = \overrightarrow E. \overrightarrow S $
where $E$ is the electric field and S is the surface area vector.
Complete step by step answer:
When there is a charge in space, it has a sphere of influence around it by which it exerts a force on another similar positive charge. This is known as the electric field. This field is represented by the lines along which the force is applied, known as Gauss lines or “lines of flux”.
The distribution of these Gauss lines of flux in a region is represented by the quantity called as electric flux.
This quantity is scalar in nature which represents the number of lines per unit area.
The electric flux is equal to the product of the electric field and the area.
$\phi = E \times S$
Here, E is the electric field and S is the surface area.
However, the electric field and surface area quantities are vectors. So, they cannot be directly multiplied since the electric flux quantity is scalar.
In order to solve this, we have to consider the type of vector product known as the dot product.
The dot product of two vectors is defined as the product of the magnitude of the two vectors and cosine of the angle between the two vectors.
If $\overrightarrow a $ and $\overrightarrow b $ are two vectors and $\theta $ is the angle between these vectors.
Dot product, $D = \overrightarrow a. \overrightarrow b = \overrightarrow {\left| a \right|} \overrightarrow {\left| b \right|} \cos \theta $
Applying the dot product here,
$\phi = \overrightarrow E. \overrightarrow S$
$\Rightarrow \phi = ES\cos \theta $
Given, the magnitudes of
Electric field, $E = 100N{C^{ - 1}}$
Surface area, $S = 100c{m^2} = 100 \times {10^{ - 4}}{m^2}$
Angle between the vectors, $\theta = {60^ \circ }$
Substituting,
$\Rightarrow \phi = 100 \times 100 \times {10^{ - 4}} \times \cos {60^ \circ }$
$\Rightarrow \phi = 100 \times 100 \times {10^{ - 4}} \times \cos {60^ \circ } = {10^4} \times {10^{ - 4}} \times \dfrac{1}{2} = \dfrac{1}{2} = 0\cdot 5Wb$
The flux over the surface, $\phi =0\cdot 5Wb$. Hence, the correct option is Option A.
Note:
Area vector:
Students are often confused as to how the area, the 2-D space, be considered as a vector. Here is how.
The area vector is a vector quantity that has the magnitude of the area and the direction is along a unit vector perpendicular to the area.
Consider the random figure of area A as shown:
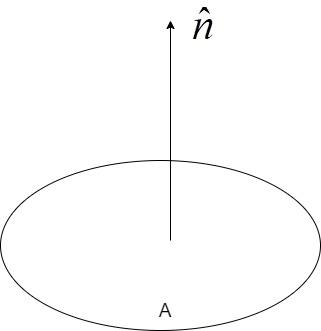
where $\hat n$ is a unit vector along the direction perpendicular to the area A.
Area vector, $\overrightarrow A = A\hat n$
Electric flux is the measure of the electric field through a given surface, though an electric field cannot flow on itself. It is a way of describing the electric field strength at any distance from the charge causing the field.
The electric flux is defined as the product of the electric field and the area.
Electric flux, $\phi = \overrightarrow E. \overrightarrow S $
where $E$ is the electric field and S is the surface area vector.
Complete step by step answer:
When there is a charge in space, it has a sphere of influence around it by which it exerts a force on another similar positive charge. This is known as the electric field. This field is represented by the lines along which the force is applied, known as Gauss lines or “lines of flux”.
The distribution of these Gauss lines of flux in a region is represented by the quantity called as electric flux.
This quantity is scalar in nature which represents the number of lines per unit area.
The electric flux is equal to the product of the electric field and the area.
$\phi = E \times S$
Here, E is the electric field and S is the surface area.
However, the electric field and surface area quantities are vectors. So, they cannot be directly multiplied since the electric flux quantity is scalar.
In order to solve this, we have to consider the type of vector product known as the dot product.
The dot product of two vectors is defined as the product of the magnitude of the two vectors and cosine of the angle between the two vectors.
If $\overrightarrow a $ and $\overrightarrow b $ are two vectors and $\theta $ is the angle between these vectors.
Dot product, $D = \overrightarrow a. \overrightarrow b = \overrightarrow {\left| a \right|} \overrightarrow {\left| b \right|} \cos \theta $
Applying the dot product here,
$\phi = \overrightarrow E. \overrightarrow S$
$\Rightarrow \phi = ES\cos \theta $
Given, the magnitudes of
Electric field, $E = 100N{C^{ - 1}}$
Surface area, $S = 100c{m^2} = 100 \times {10^{ - 4}}{m^2}$
Angle between the vectors, $\theta = {60^ \circ }$
Substituting,
$\Rightarrow \phi = 100 \times 100 \times {10^{ - 4}} \times \cos {60^ \circ }$
$\Rightarrow \phi = 100 \times 100 \times {10^{ - 4}} \times \cos {60^ \circ } = {10^4} \times {10^{ - 4}} \times \dfrac{1}{2} = \dfrac{1}{2} = 0\cdot 5Wb$
The flux over the surface, $\phi =0\cdot 5Wb$. Hence, the correct option is Option A.
Note:
Area vector:
Students are often confused as to how the area, the 2-D space, be considered as a vector. Here is how.
The area vector is a vector quantity that has the magnitude of the area and the direction is along a unit vector perpendicular to the area.
Consider the random figure of area A as shown:

where $\hat n$ is a unit vector along the direction perpendicular to the area A.
Area vector, $\overrightarrow A = A\hat n$
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

State and prove converse of BPT Basic Proportionality class 10 maths CBSE




