
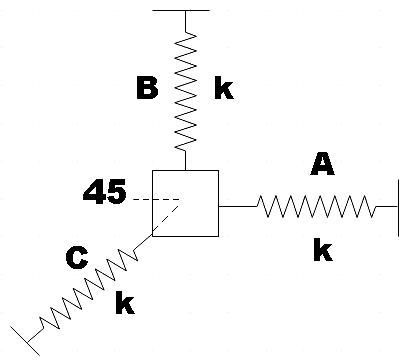
A particle of mass m is attached with three springs A, B and C of equal force constants k as shown in the figure. The particle is pushed slightly against the spring C and released, the time period of oscillation will be:
A.$2\pi \sqrt{\dfrac{m}{k}}$
B.$2\pi \sqrt{\dfrac{m}{2k}}$
C.$2\pi \sqrt{\dfrac{m}{3k}}$
D.$2\pi \sqrt{\dfrac{m}{5k}}$

Answer
579k+ views
Hint: Firstly, you could assign the restoring forces along each of the strings. Then, you could resolve these forces as per requirement and balance them. Thereby, you will be able to find the effective force constant of the system. You could substitute it in the expression for the time period of oscillation and thus get the answer.
Formula used:
Time period of oscillation,
$T=2\pi \sqrt{\dfrac{m}{{{k}_{eff}}}}$
Complete answer:
In the question, we are given a particle of mass m that is attached to three springs A, B and C and all three springs have the same force constant k. So, this particle is being pushed against C and then released. We are asked to find the time period of oscillation for the system.
In order to answer the given question, firstly, we have to find the net force acting on the system.
Let x be the distance at which the particle pushed against C and the resultant elongation (y) will be the same for all three strings. We could depict the situation in the following diagram,
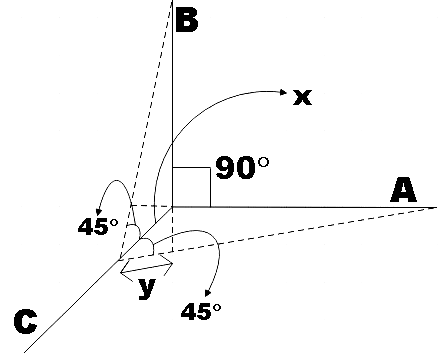
Now we have restoring forces in each string directed opposite to the elongation. And the restoring forces in strings A and B can be resolved into their horizontal and vertical components. Both their sine components get cancelled as they are directed opposite to each other.
From the figure, we see that,
$y=x\cos 45{}^\circ $ …………………………………… (1)
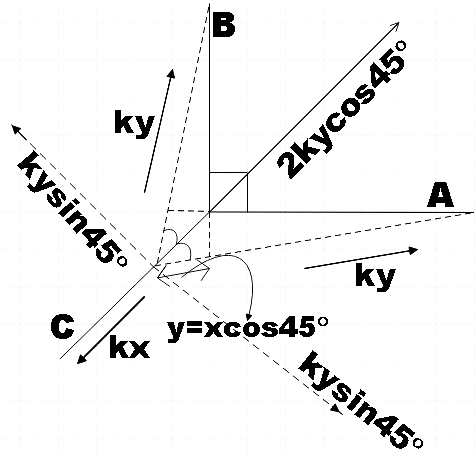
So the net force on the particle now will be,
${{F}_{net}}={{F}_{C}}-2ky\cos 45{}^\circ $
$\Rightarrow {{F}_{net}}=-kx-2ky\cos 45{}^\circ =-\left( kx+2ky\cos 45{}^\circ \right)$
Substituting (1), we get,
${{F}_{net}}=-\left( kx+2kx\cos 45{}^\circ .\cos 45{}^\circ \right)$
$\Rightarrow {{F}_{net}}=-kx\left( 1+\left( 2 \right)\times {{\left( \dfrac{1}{\sqrt{2}} \right)}^{2}} \right)$
$\therefore {{F}_{net}}=-2kx$
But we know that,
${{F}_{net}}=-{{K}_{eff}}x$
Comparing the two equations, we get the effective spring constant as,
${{K}_{eff}}=2k$ …………………………………. (2)
Now, we could recall the expression for the time period of oscillation which is given by,
$T=2\pi \sqrt{\dfrac{m}{{{k}_{eff}}}}$
Substituting (2) we get,
$T=2\pi \sqrt{\dfrac{m}{2k}}$
Therefore, we found the time period of oscillation of the system after the particle being pushed against string C as,
$T=2\pi \sqrt{\dfrac{m}{2k}}$
Hence, option B is found to be the right answer.
Note:
According to Hooke’s law, the restoring force is proportional to the displacement of the string, that is,
$F\propto x$
So,
$F=-kx$
Where, k is the force constant and the negative sign indicates that the force is directed in the direction opposite to the elongation caused. Knowledge of this law is the basic requirement for solving these kinds of problems.
Formula used:
Time period of oscillation,
$T=2\pi \sqrt{\dfrac{m}{{{k}_{eff}}}}$
Complete answer:
In the question, we are given a particle of mass m that is attached to three springs A, B and C and all three springs have the same force constant k. So, this particle is being pushed against C and then released. We are asked to find the time period of oscillation for the system.
In order to answer the given question, firstly, we have to find the net force acting on the system.
Let x be the distance at which the particle pushed against C and the resultant elongation (y) will be the same for all three strings. We could depict the situation in the following diagram,

Now we have restoring forces in each string directed opposite to the elongation. And the restoring forces in strings A and B can be resolved into their horizontal and vertical components. Both their sine components get cancelled as they are directed opposite to each other.
From the figure, we see that,
$y=x\cos 45{}^\circ $ …………………………………… (1)

So the net force on the particle now will be,
${{F}_{net}}={{F}_{C}}-2ky\cos 45{}^\circ $
$\Rightarrow {{F}_{net}}=-kx-2ky\cos 45{}^\circ =-\left( kx+2ky\cos 45{}^\circ \right)$
Substituting (1), we get,
${{F}_{net}}=-\left( kx+2kx\cos 45{}^\circ .\cos 45{}^\circ \right)$
$\Rightarrow {{F}_{net}}=-kx\left( 1+\left( 2 \right)\times {{\left( \dfrac{1}{\sqrt{2}} \right)}^{2}} \right)$
$\therefore {{F}_{net}}=-2kx$
But we know that,
${{F}_{net}}=-{{K}_{eff}}x$
Comparing the two equations, we get the effective spring constant as,
${{K}_{eff}}=2k$ …………………………………. (2)
Now, we could recall the expression for the time period of oscillation which is given by,
$T=2\pi \sqrt{\dfrac{m}{{{k}_{eff}}}}$
Substituting (2) we get,
$T=2\pi \sqrt{\dfrac{m}{2k}}$
Therefore, we found the time period of oscillation of the system after the particle being pushed against string C as,
$T=2\pi \sqrt{\dfrac{m}{2k}}$
Hence, option B is found to be the right answer.
Note:
According to Hooke’s law, the restoring force is proportional to the displacement of the string, that is,
$F\propto x$
So,
$F=-kx$
Where, k is the force constant and the negative sign indicates that the force is directed in the direction opposite to the elongation caused. Knowledge of this law is the basic requirement for solving these kinds of problems.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

The largest wind power cluster is located in the state class 11 social science CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

State and prove Bernoullis theorem class 11 physics CBSE

What steps did the French revolutionaries take to create class 11 social science CBSE

Which among the following are examples of coming together class 11 social science CBSE




