
A particle moving on a straight line ultimately comes to rest. What is the angle between its
initial velocity and acceleration?
A) Zero
B) 45°
C) 90°
D) 180°
Answer
591.6k+ views
Hint: We can assume a moving body and then observe the variations of velocities according to the question graphically so as to calculate the required angle.
Relationship between acceleration and velocity is given as:
$a = \dfrac{{du}}{{dt}}$
Rate of change of velocity is defined as acceleration and its units are $m/{s^2}$
Complete step by step answer:Let a particle move with an initial velocity u and acceleration a.
The object finally comes to rest, this means its final velocity (v) will be zero
$ \Rightarrow $ v = 0
If we plot a velocity – time graph it will be:
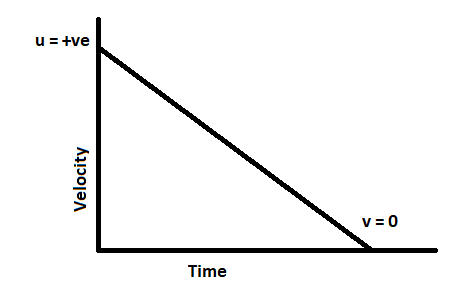
Here,
u has any positive value which finally decreases and becomes zero with respect to time.
Now, the slope (S) of any graph is the change in quantity on y – axis with respect to the x-axis:
$S = \dfrac{{dy}}{{dx}}$
In this case the slope will be $\dfrac{{du}}{{dt}}$; rate of change of velocity
And,
Acceleration is defined as the rate of change of velocity:
$a = \dfrac{{du}}{{dt}}$
Thus, the slope of this graph represents acceleration.
We can see that the slope is degrading and hence have a negative value
$ \Rightarrow $ a = -ve
For positive initial velocity, the acceleration of a body is negative:
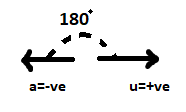
As both are in opposite directions, the angle formed between them is 180°
Therefore, the angle between the initial velocity and acceleration of the given particle is 180° and the correct option is D)
Note:‘Rate’ is always measured with respect to the time.
The derivatives show the change in respective quantities. E.g.
If x = ${x_1} - {x_2}$; then this will also be equal to dx.
The graph basically shows variation of one quantity with respect to the other
Relationship between acceleration and velocity is given as:
$a = \dfrac{{du}}{{dt}}$
Rate of change of velocity is defined as acceleration and its units are $m/{s^2}$
Complete step by step answer:Let a particle move with an initial velocity u and acceleration a.
The object finally comes to rest, this means its final velocity (v) will be zero
$ \Rightarrow $ v = 0
If we plot a velocity – time graph it will be:

Here,
u has any positive value which finally decreases and becomes zero with respect to time.
Now, the slope (S) of any graph is the change in quantity on y – axis with respect to the x-axis:
$S = \dfrac{{dy}}{{dx}}$
In this case the slope will be $\dfrac{{du}}{{dt}}$; rate of change of velocity
And,
Acceleration is defined as the rate of change of velocity:
$a = \dfrac{{du}}{{dt}}$
Thus, the slope of this graph represents acceleration.
We can see that the slope is degrading and hence have a negative value
$ \Rightarrow $ a = -ve
For positive initial velocity, the acceleration of a body is negative:

As both are in opposite directions, the angle formed between them is 180°
Therefore, the angle between the initial velocity and acceleration of the given particle is 180° and the correct option is D)
Note:‘Rate’ is always measured with respect to the time.
The derivatives show the change in respective quantities. E.g.
If x = ${x_1} - {x_2}$; then this will also be equal to dx.
The graph basically shows variation of one quantity with respect to the other
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

The largest wind power cluster is located in the state class 11 social science CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

State and prove Bernoullis theorem class 11 physics CBSE

What steps did the French revolutionaries take to create class 11 social science CBSE

Which among the following are examples of coming together class 11 social science CBSE




