
A particle describes a horizontal circle in a conical funnel whose inner surface is smooth with speed of $ 0.5m{s^{ - 1}} $ . What is the height of the plane of the circle from the vertex of the funnel?
A. $ 0.25m $
B. $ 2cm $
C. $ 4cm $
D. $ 2.5cm $
Answer
525.3k+ views
Hint : The particle is moving in a circular path so centripetal force will act on it along with the gravitational pull. Equate both the components of force along the horizontal and vertical to find the height of the plane from the vertex of the funnel. The horizontal component of force will be, $ N\cos \theta = \dfrac{{m{v^2}}}{r} $ , the vertical component of force will be, $ N\sin \theta = mg $ . Where, $ m $ is the mass of the particle, $ N $ is the normal force acting on the particle, $ \dfrac{{m{v^2}}}{r} $ is the centripetal force, $ g $ is the gravitational acceleration.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
Here the particle is moving in a circle plane. So, the forces on the particle will be a centripetal force and the gravitational pull. Now, in equilibrium condition the net forces on the particle will be zero. Hence, we can equate all the components of the forces.
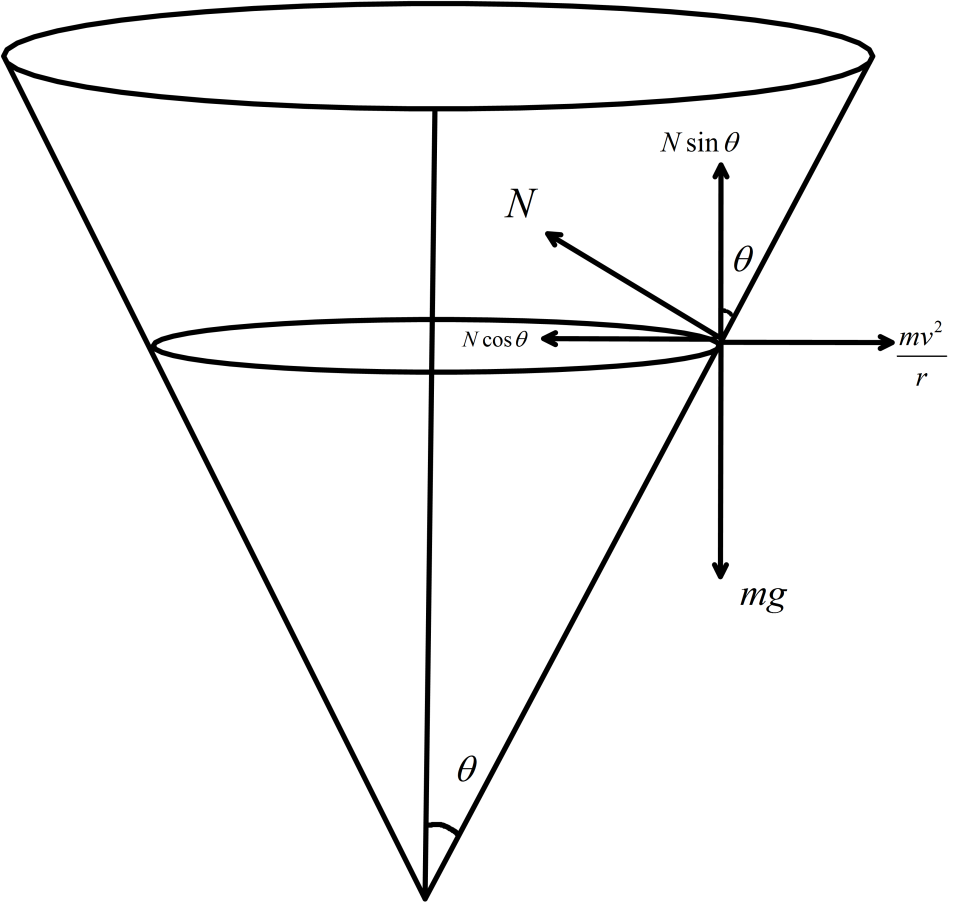
So, we can write for the horizontal component of force as, $ N\cos \theta = \dfrac{{m{v^2}}}{r} $ .…….(i)
Where, $ N $ is the normal force acting on the particle due to the plane of the cone, $ \dfrac{{m{v^2}}}{r} $ is the centripetal force acting on the particle. $ v $ is the speed of the force in the circular path and is the radius of the circular path.
And, the vertical component of force as, $ N\sin \theta = mg $ …….(ii)
Now, for a cone we can write, $ \dfrac{r}{h} = \tan \theta $ where $ h $ is the height of the plane from the vertex.
Now, from equation (i) and equation (ii) we can write,
$ \dfrac{{N\sin \theta }}{{N\cos \theta }} = \dfrac{{mg}}{{\dfrac{{m{v^2}}}{r}}} $
Up on simplifying we get,
$ \tan \theta = \dfrac{{gr}}{{{v^2}}} $
So, equating both the tangent we get,
$ \dfrac{r}{h} = \dfrac{{gr}}{{{v^2}}} $
Or, $ h = \dfrac{{{v^2}}}{g} $
Here, we have given the velocity of the particle, $ v = 0.5m{s^{ - 1}} $ and gravitational acceleration is $ g = 9.8m{s^{ - 2}} $ .
So, putting these values we get,
$ h = \dfrac{{{{0.5}^2}}}{{9.8}}m $
Or, $ h = 0.025m $
So, the height of the plane is $ h = 0.025m = 2.5cm $ .
So, option (D) is the correct answer.
Note :
The particle is kept on the circular path by the normal force of the plane. To keep a particle moving in a circular path some force like gravitation or tension must exist to cancel out the effect of the centripetal force.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
Here the particle is moving in a circle plane. So, the forces on the particle will be a centripetal force and the gravitational pull. Now, in equilibrium condition the net forces on the particle will be zero. Hence, we can equate all the components of the forces.

So, we can write for the horizontal component of force as, $ N\cos \theta = \dfrac{{m{v^2}}}{r} $ .…….(i)
Where, $ N $ is the normal force acting on the particle due to the plane of the cone, $ \dfrac{{m{v^2}}}{r} $ is the centripetal force acting on the particle. $ v $ is the speed of the force in the circular path and is the radius of the circular path.
And, the vertical component of force as, $ N\sin \theta = mg $ …….(ii)
Now, for a cone we can write, $ \dfrac{r}{h} = \tan \theta $ where $ h $ is the height of the plane from the vertex.
Now, from equation (i) and equation (ii) we can write,
$ \dfrac{{N\sin \theta }}{{N\cos \theta }} = \dfrac{{mg}}{{\dfrac{{m{v^2}}}{r}}} $
Up on simplifying we get,
$ \tan \theta = \dfrac{{gr}}{{{v^2}}} $
So, equating both the tangent we get,
$ \dfrac{r}{h} = \dfrac{{gr}}{{{v^2}}} $
Or, $ h = \dfrac{{{v^2}}}{g} $
Here, we have given the velocity of the particle, $ v = 0.5m{s^{ - 1}} $ and gravitational acceleration is $ g = 9.8m{s^{ - 2}} $ .
So, putting these values we get,
$ h = \dfrac{{{{0.5}^2}}}{{9.8}}m $
Or, $ h = 0.025m $
So, the height of the plane is $ h = 0.025m = 2.5cm $ .
So, option (D) is the correct answer.
Note :
The particle is kept on the circular path by the normal force of the plane. To keep a particle moving in a circular path some force like gravitation or tension must exist to cancel out the effect of the centripetal force.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Name the part of the brain responsible for the precision class 11 biology CBSE

The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to AEffect class 11 biology CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

State and prove Bernoullis theorem class 11 physics CBSE

Actinoid contraction is more than lanthanoid contraction class 11 chemistry CBSE

Which out of the following hydrocarbons undergo addition class 11 chemistry CBSE




