
A park, in the shape of a quadrilateral ABCD, has \[\angle C={{90}^{0}}\] ,
\[AB=9m,BC=12m,CD=5m,AD=8m\] , how much area does it occupy?


Answer
592.5k+ views
Hint: Here we find the area by adding the individual area of two triangles. For the right angled triangle we use formula as \[A=\dfrac{1}{2}\left( base \right)\left( height \right)\] while for the scalene triangle we use Heron’s formula. Heron’s formula states that if ‘a’, ‘b’, ‘c’ are sides of triangle we find area as
\[A=\sqrt{s\left( s-a \right)\left( s-b \right)\left( s-c \right)}\] where ‘s’ is called semi perimeter and \[s=\dfrac{a+b+c}{2}\] .
Complete step-by-step answer:
Let us consider the triangle \[\Delta BCD\] and by using the area formula by taking ‘BC’ as base and ‘CD’ as height we will get
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow {{A}_{1}}=\dfrac{1}{2}\left( base \right)\left( height \right) \\
& \Rightarrow {{A}_{1}}=\dfrac{1}{2}\times 12\times 5 \\
& \Rightarrow {{A}_{1}}=30{{m}^{2}} \\
\end{align}\]
Now for finding the side ‘BD’ we use Pythagoras theorem (hypotenuse square is equal to sum of squares of other two sides). That is for a triangle shown below the Pythagoras theorem can be applied as follows
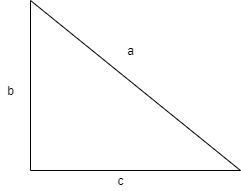
Applying Pythagoras theorem for above figure, \[{{a}^{2}}={{b}^{2}}+{{c}^{2}}\]
By applying the Pythagoras theorem we will get
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow B{{D}^{2}}=B{{C}^{2}}+C{{D}^{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow B{{D}^{2}}={{12}^{2}}+{{5}^{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow B{{D}^{2}}=144+25 \\
& \Rightarrow BD=\sqrt{169} \\
& \Rightarrow BD=13 \\
\end{align}\]
Let us consider the other triangle \[\Delta ABD\] and finding semi perimeter we get
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow s=\dfrac{AB+BD+DA}{2} \\
& \Rightarrow s=\dfrac{9+13+8}{2} \\
& \Rightarrow s=15 \\
\end{align}\]
Let us apply heron’s formula and by substituting the required values in the formula then we get
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow {{A}_{2}}=\sqrt{s\left( s-a \right)\left( s-b \right)\left( s-c \right)} \\
& \Rightarrow {{A}_{2}}=\sqrt{15\left( 15-9 \right)\left( 15-13 \right)\left( 15-8 \right)} \\
& \Rightarrow {{A}_{2}}=\sqrt{15\times 6\times 2\times 7} \\
& \Rightarrow {{A}_{2}}=6\sqrt{35} \\
\end{align}\]
Now by adding the two areas we will get total area as follows
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow A={{A}_{1}}+{{A}_{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow A=30+6\sqrt{35} \\
\end{align}\]
Therefore the total area of the park is \[30+6\sqrt{35}\] \[{{m}^{2}}\] .
Note: Some students will make mistakes in applying the Heron’s formula due to calculation mistakes. There is only one point where one can make mistakes. Remaining solution is just based on calculations only. Also the semi perimeter will have a formula as \[s=\dfrac{a+b+c}{2}\] .
But some students in a hurry will take \[s=\dfrac{a+b+c}{3}\] .This needs to be taken care of.
\[A=\sqrt{s\left( s-a \right)\left( s-b \right)\left( s-c \right)}\] where ‘s’ is called semi perimeter and \[s=\dfrac{a+b+c}{2}\] .
Complete step-by-step answer:
Let us consider the triangle \[\Delta BCD\] and by using the area formula by taking ‘BC’ as base and ‘CD’ as height we will get
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow {{A}_{1}}=\dfrac{1}{2}\left( base \right)\left( height \right) \\
& \Rightarrow {{A}_{1}}=\dfrac{1}{2}\times 12\times 5 \\
& \Rightarrow {{A}_{1}}=30{{m}^{2}} \\
\end{align}\]
Now for finding the side ‘BD’ we use Pythagoras theorem (hypotenuse square is equal to sum of squares of other two sides). That is for a triangle shown below the Pythagoras theorem can be applied as follows

Applying Pythagoras theorem for above figure, \[{{a}^{2}}={{b}^{2}}+{{c}^{2}}\]
By applying the Pythagoras theorem we will get
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow B{{D}^{2}}=B{{C}^{2}}+C{{D}^{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow B{{D}^{2}}={{12}^{2}}+{{5}^{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow B{{D}^{2}}=144+25 \\
& \Rightarrow BD=\sqrt{169} \\
& \Rightarrow BD=13 \\
\end{align}\]
Let us consider the other triangle \[\Delta ABD\] and finding semi perimeter we get
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow s=\dfrac{AB+BD+DA}{2} \\
& \Rightarrow s=\dfrac{9+13+8}{2} \\
& \Rightarrow s=15 \\
\end{align}\]
Let us apply heron’s formula and by substituting the required values in the formula then we get
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow {{A}_{2}}=\sqrt{s\left( s-a \right)\left( s-b \right)\left( s-c \right)} \\
& \Rightarrow {{A}_{2}}=\sqrt{15\left( 15-9 \right)\left( 15-13 \right)\left( 15-8 \right)} \\
& \Rightarrow {{A}_{2}}=\sqrt{15\times 6\times 2\times 7} \\
& \Rightarrow {{A}_{2}}=6\sqrt{35} \\
\end{align}\]
Now by adding the two areas we will get total area as follows
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow A={{A}_{1}}+{{A}_{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow A=30+6\sqrt{35} \\
\end{align}\]
Therefore the total area of the park is \[30+6\sqrt{35}\] \[{{m}^{2}}\] .
Note: Some students will make mistakes in applying the Heron’s formula due to calculation mistakes. There is only one point where one can make mistakes. Remaining solution is just based on calculations only. Also the semi perimeter will have a formula as \[s=\dfrac{a+b+c}{2}\] .
But some students in a hurry will take \[s=\dfrac{a+b+c}{3}\] .This needs to be taken care of.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 10 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which country won the ICC Men's ODI World Cup in 2023?

In cricket, how many legal balls are there in a standard over?

Explain the Treaty of Vienna of 1815 class 10 social science CBSE

A boat goes 24 km upstream and 28 km downstream in class 10 maths CBSE

What does "powerplay" mean in limited-overs cricket?

What is the "Powerplay" in T20 cricket?




