
A nucleotide is made up of
(a)A carboxyl, a sugar, and a phosphate
(b)A phosphate, an amino acid, and a carboxyl
(c)An amino acid, a carboxyl, and a phosphate
(d) A sugar, a phosphate, and a nitrogenous base
(e)A nitrogenous base, an amino acid, and a sugar
Answer
588.3k+ views
Hint: It is the structural unit or building block of DNA or RNA in which bases combine with the sugar to make nucleoside. The nucleotide is termed “nucleoside monophosphate”. It depends on the no. of phosphate attached to make up the phosphate group.
Complete answer:
A nucleotide is made up of three individual chemical subunits: a five-carbon sugar, a nitrogenous base, and one phosphate group. The nitrogenous base together with a five-carbon sugar is called nucleoside. There are two types of nitrogenous bases:
Purine: Adenine (A) and Guanine (G)
Pyrimidine: Cytosine (C), Thymine (T) and Uracil (U)
Nitrogenous bases are linked to the pentose sugar through an N-glycosidic linkage to form a nucleoside. The phosphate group is linked to nucleoside at 5' -OH end through a phosphodiester linkage that forms nucleotides. Two nucleotides are linked by the help of 3'-5' phosphodiester linkage to form a dinucleotide. A number of nucleotides joined together in the same manner to form a polynucleotide chain.
Sugar and phosphates together form the backbone of a polynucleotide chain. The nitrogenous bases are linked to the sugar moiety project from the backbone. In two DNA strands, the nitrogenous bases are paired through hydrogen bonds (H-bonds) resulting in the formation of base pairs. Adenine paired with thymine by forming two hydrogen bonds. Similarly, Guanine forms three hydrogen bonds with Cytosine.
So, the correct answer is ‘a sugar, a phosphate, and a nitrogenous base’.
Note: -Hydrogen bonds provide stability to the helical structure.
-In RNA, the uracil is present at the place of thymine.
-RNA has an additional –OH group present at 2' -position in the ribose, in each nucleotide residue.
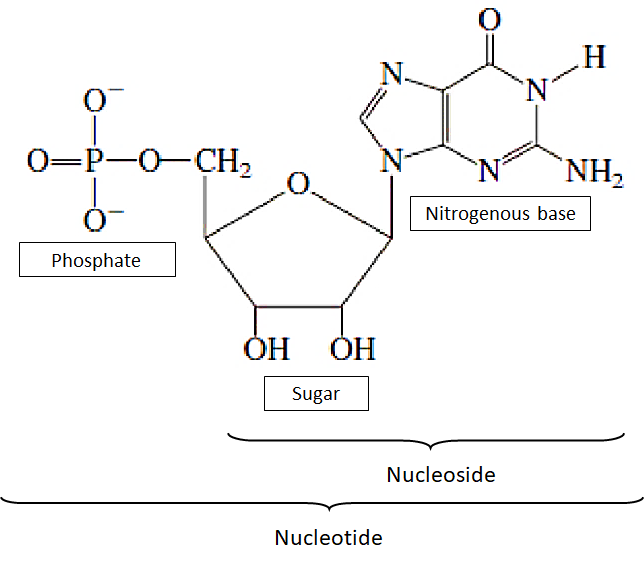
Complete answer:
A nucleotide is made up of three individual chemical subunits: a five-carbon sugar, a nitrogenous base, and one phosphate group. The nitrogenous base together with a five-carbon sugar is called nucleoside. There are two types of nitrogenous bases:
Purine: Adenine (A) and Guanine (G)
Pyrimidine: Cytosine (C), Thymine (T) and Uracil (U)
Nitrogenous bases are linked to the pentose sugar through an N-glycosidic linkage to form a nucleoside. The phosphate group is linked to nucleoside at 5' -OH end through a phosphodiester linkage that forms nucleotides. Two nucleotides are linked by the help of 3'-5' phosphodiester linkage to form a dinucleotide. A number of nucleotides joined together in the same manner to form a polynucleotide chain.
Sugar and phosphates together form the backbone of a polynucleotide chain. The nitrogenous bases are linked to the sugar moiety project from the backbone. In two DNA strands, the nitrogenous bases are paired through hydrogen bonds (H-bonds) resulting in the formation of base pairs. Adenine paired with thymine by forming two hydrogen bonds. Similarly, Guanine forms three hydrogen bonds with Cytosine.
So, the correct answer is ‘a sugar, a phosphate, and a nitrogenous base’.
Note: -Hydrogen bonds provide stability to the helical structure.
-In RNA, the uracil is present at the place of thymine.
-RNA has an additional –OH group present at 2' -position in the ribose, in each nucleotide residue.

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




