
A Nicol prism is based on the principle of.
A. Refraction
B. Scattering
C. Dichroism
D. Double refraction
Answer
596.7k+ views
Hint:
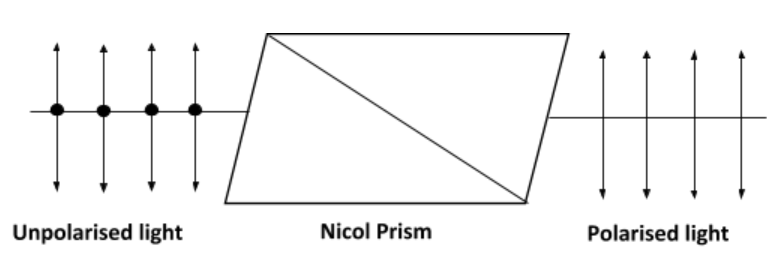
Nicol prism is an optical instrument that converts unpolarized light into polarised light. Nicol prism is made up of calcite crystal (CaCO$_3$) and is fabricated with Canada Balson whose refractive index (µ) =1.55.
Complete step by step solution:
1. A beam of unpolarized light falls on a surface of the prism and gets divided into two refracted rays i.e. ordinary ray and extraordinary ray.
2. These refracted rays are plane and polarized in nature, vibrations form right angles with each other.
3. For an extraordinary ray of light (µ=1.48), Canada Balsam (µ=1.55) acts as an optically denser medium.
4. For ordinary rays of light (µ=1.65), Canada Balsam (µ=1.55) acts as an optically rarer medium.
5. When ordinary ray falls on the Nicol prism and passes through this particular layer (Canada Balsam), it is a transition from a denser medium to a rarer medium, also its incident at a critical angle on Canada Balsam layer and thus a total internal reflection takes place.
6. When an extraordinary ray falls on the Nicol prism and passes through this particular layer (Canada Balsam), it is a transition from a rarer medium to a denser medium, and thus passes through prism after refraction which is totally plane polarised.
Hence, the correct option is: D (double refraction)
Note:
Nicol prism was the first type of polarising prism invented in 1828 by William Nicol (1770-1851) of Edinburgh, it consists of a rhombohedral crystal made up of calcite and has been cut at an angle of 68˚ with respect to the crystal axis, cut again diagonally and then re-joined with the help of a Canada Balsam as a glue.

Complete step by step solution:
1. A beam of unpolarized light falls on a surface of the prism and gets divided into two refracted rays i.e. ordinary ray and extraordinary ray.
2. These refracted rays are plane and polarized in nature, vibrations form right angles with each other.
3. For an extraordinary ray of light (µ=1.48), Canada Balsam (µ=1.55) acts as an optically denser medium.
4. For ordinary rays of light (µ=1.65), Canada Balsam (µ=1.55) acts as an optically rarer medium.
5. When ordinary ray falls on the Nicol prism and passes through this particular layer (Canada Balsam), it is a transition from a denser medium to a rarer medium, also its incident at a critical angle on Canada Balsam layer and thus a total internal reflection takes place.
6. When an extraordinary ray falls on the Nicol prism and passes through this particular layer (Canada Balsam), it is a transition from a rarer medium to a denser medium, and thus passes through prism after refraction which is totally plane polarised.
Hence, the correct option is: D (double refraction)
Note:
Nicol prism was the first type of polarising prism invented in 1828 by William Nicol (1770-1851) of Edinburgh, it consists of a rhombohedral crystal made up of calcite and has been cut at an angle of 68˚ with respect to the crystal axis, cut again diagonally and then re-joined with the help of a Canada Balsam as a glue.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

A moving boat is observed from the top of a 150 m high class 10 maths CBSE




