
A nephridium of an earthworm drains materials directly from the
A. Gut
B. Coelom
C. Lymph
D. Blood
Answer
599.7k+ views
Hint: The nephridia of earthworm are typically tubular in shape.
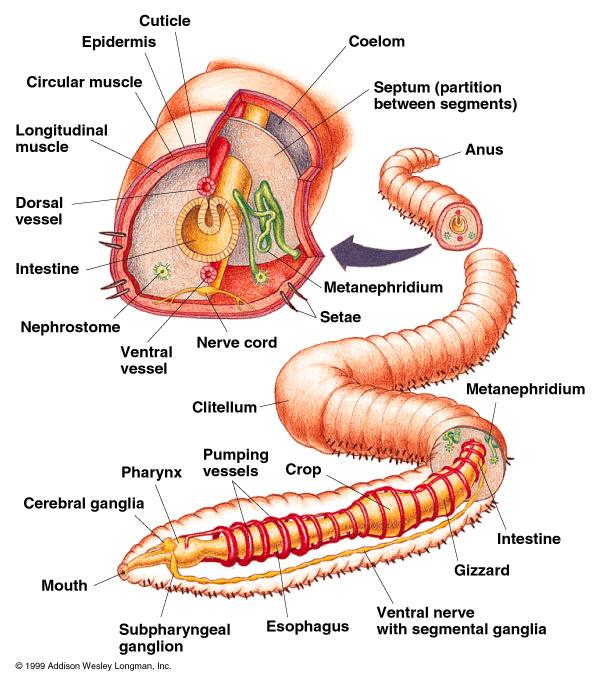
Each nephridium opens into the outer surface of the body by nephridiopore and the waste materials are discarded outside the body directly via these pores thus, they are also known as exonephric nephridia.
Complete answer: The earthworm is a tubular-shaped worm with a segmented body and it belongs to the phylum Annelida.
In this organism, most of the cells are not in direct contact with the surrounding environment. This is the reason for the requirement of a special excretory structure.
The excretory organs of the earthworm are called nephridia.
Nephridia are tubular structured and coiled tubes, which discards the nitrogenous wastes outside the body of the earthworm.
These structures are suspended within the body cavity (coelom).
Earthworms have two nephridia present nearly in each segment.
These nephridia play a crucial role in collecting the nitrogenous waste materials from each segment and transport it directly through the coelom to the soil through the anus.
Additional information: Earthworms and their relatives found anywhere there is moist soil and dead plant material.
Earthworms are more abundant in rain forest areas but can be found in many habitats on land and in freshwater.
All earthworm species require moist soil conditions to survive.
So, the correct answer is option B. Coelom.
Note: Except for the first two segments the nephridia are essentially present in all the remaining segments of the earthworm’s body wall. There is a total of two nephridia present in one segment.
Each nephridium opens into the outer surface of the body by nephridiopore and the waste materials are discarded outside the body directly via these pores thus, they are also known as exonephric nephridia.
Complete answer: The earthworm is a tubular-shaped worm with a segmented body and it belongs to the phylum Annelida.
In this organism, most of the cells are not in direct contact with the surrounding environment. This is the reason for the requirement of a special excretory structure.
The excretory organs of the earthworm are called nephridia.
Nephridia are tubular structured and coiled tubes, which discards the nitrogenous wastes outside the body of the earthworm.
These structures are suspended within the body cavity (coelom).
Earthworms have two nephridia present nearly in each segment.
These nephridia play a crucial role in collecting the nitrogenous waste materials from each segment and transport it directly through the coelom to the soil through the anus.
Additional information: Earthworms and their relatives found anywhere there is moist soil and dead plant material.
Earthworms are more abundant in rain forest areas but can be found in many habitats on land and in freshwater.
All earthworm species require moist soil conditions to survive.
So, the correct answer is option B. Coelom.
Note: Except for the first two segments the nephridia are essentially present in all the remaining segments of the earthworm’s body wall. There is a total of two nephridia present in one segment.

Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers

Give simple chemical tests to distinguish between the class 12 chemistry CBSE

Define Vant Hoff factor How is it related to the degree class 12 chemistry CBSE




