
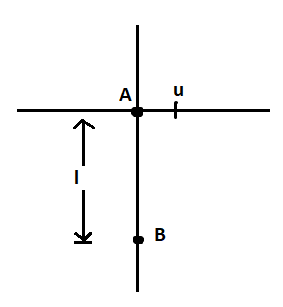
A moves with constant velocity u along the x-axis. B always has velocity towards A. After how much time will B meet A if B Moves with constant speed V? What distance will be traveled by A and B?

Answer
590.4k+ views
Hint: The question talks about the motion of two bodies or objects A and B in a rectilinear or straight line manner, where the velocity of A started and remains especially in the x axis or direction and B acting opposite to it with a uniform velocity.
Complete step by step answer:
Using the equation of motion which involves initial velocity, final velocity, acceleration and distance travelled or covered.
Appling $V = U + at$
Where V is the uniform velocity of impact from B
U is the uniform velocity of impact from A and a is the acceleration and t is the time taken
For us to calculate t we need to make t subject of the formula or equation by dividing both sides by a, it then become
$
V - U = at \\
\to \dfrac{{V - U}}{a} = \dfrac{{at}}{a} \\
\to t = \dfrac{{V - U}}{a} \\
$
To get the distance travelled by either the objects or bodies in other for them to meet we have to use the second equation of motion, the equation becomes
$S = velocity \times t + \dfrac{1}{2}a{t^2}$, where S is the distance travelled or covered but the acceleration is zero as the velocity is uniform
$S = velocity \times t$
The velocity in the above equation will be the average of velocities of A and B
$S = \dfrac{{U + V}}{2} \times t$
Therefore the distance between A and B will be $S = \dfrac{{\left( {U + V} \right)t}}{2}$
Note:The same kind of motion is seen in cars travelling along a straight path where average speed or velocity, time taken to cover some distances, acceleration along the part of impact as well as other relevant parameters that makes up the motion equation.
Complete step by step answer:
Using the equation of motion which involves initial velocity, final velocity, acceleration and distance travelled or covered.
Appling $V = U + at$
Where V is the uniform velocity of impact from B
U is the uniform velocity of impact from A and a is the acceleration and t is the time taken
For us to calculate t we need to make t subject of the formula or equation by dividing both sides by a, it then become
$
V - U = at \\
\to \dfrac{{V - U}}{a} = \dfrac{{at}}{a} \\
\to t = \dfrac{{V - U}}{a} \\
$
To get the distance travelled by either the objects or bodies in other for them to meet we have to use the second equation of motion, the equation becomes
$S = velocity \times t + \dfrac{1}{2}a{t^2}$, where S is the distance travelled or covered but the acceleration is zero as the velocity is uniform
$S = velocity \times t$
The velocity in the above equation will be the average of velocities of A and B
$S = \dfrac{{U + V}}{2} \times t$
Therefore the distance between A and B will be $S = \dfrac{{\left( {U + V} \right)t}}{2}$
Note:The same kind of motion is seen in cars travelling along a straight path where average speed or velocity, time taken to cover some distances, acceleration along the part of impact as well as other relevant parameters that makes up the motion equation.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

The largest wind power cluster is located in the state class 11 social science CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

State and prove Bernoullis theorem class 11 physics CBSE

What steps did the French revolutionaries take to create class 11 social science CBSE

Which among the following are examples of coming together class 11 social science CBSE




