
A mirage occurs because
A. The refractive index of atmosphere increases with height
B. The refractive index of atmosphere decrease with height
C. The host ground acts like a mirror
D. Refractive index remains constant with height
Answer
585k+ views
Hint: The light rays coming from a distant object appear to be coming from the image of the object inside the ground and this is called a mirage. We know that light rays coming from a particular distance or distant object, all travel through nearly the same air layers. All are bent over about the same amount. The rays which are coming from the top of the object will arrive lower. Using these concepts, we can determine the reason behind the mirage occurrence.
Complete answer:
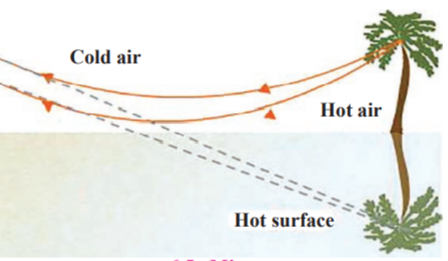
Have you seen a mirage which is an illusion of the appearance of water in a desert or on a hot road? Or have you seen that objects beyond and above a holy fire appear to be shaking? Why does this happen?
As hot air rises above, cold air descends, so as we move upward the refractive index also decreases.
Local atmospheric conditions affect the refraction of light to some extent. In both the examples above, the air near the hot road or desert surface and near the holy flames is hot and hence rarer than the air above it. The refractive index of air keeps increasing as we go to increasing heights. In the first case above, the direction of light rays, coming from a distance, keeps changing according to the laws of refraction.
The light rays coming from a distant object appear to be coming from the image of the object inside the ground as shown in the figure. This is called a mirage.
In the second example, the direction of light rays coming from objects beyond the holy fire changes due to changing refractive index above the fire. Thus, the objects appear to be moving.
Light rays coming from a particular distance or distant object, all travel through nearly the same air layers and all are bent over about the same amount by virtue of total internal reflection as the light is moving from a denser medium that is cold to a rarer medium that is hot air. Therefore, rays coming from the top of the object will arrive lower than those from the bottom or vice versa. The image usually is upside down by enhancing the illusion that the sky image seen in the distance is really an oil puddle of water acting as a mirror.
Hence a mirage occurs because the refractive index of the atmosphere increases with height.
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Note:
The real object in an inferior mirage is the sky (blue) or any distant (therefore bluish) object in that same direction. The mirage causes the observer to see a bright and bluish patch on the ground at some distance. The effect of atmospheric conditions on the refraction of light can be seen in the twinkling of the stars.
Complete answer:

Have you seen a mirage which is an illusion of the appearance of water in a desert or on a hot road? Or have you seen that objects beyond and above a holy fire appear to be shaking? Why does this happen?
As hot air rises above, cold air descends, so as we move upward the refractive index also decreases.
Local atmospheric conditions affect the refraction of light to some extent. In both the examples above, the air near the hot road or desert surface and near the holy flames is hot and hence rarer than the air above it. The refractive index of air keeps increasing as we go to increasing heights. In the first case above, the direction of light rays, coming from a distance, keeps changing according to the laws of refraction.
The light rays coming from a distant object appear to be coming from the image of the object inside the ground as shown in the figure. This is called a mirage.
In the second example, the direction of light rays coming from objects beyond the holy fire changes due to changing refractive index above the fire. Thus, the objects appear to be moving.
Light rays coming from a particular distance or distant object, all travel through nearly the same air layers and all are bent over about the same amount by virtue of total internal reflection as the light is moving from a denser medium that is cold to a rarer medium that is hot air. Therefore, rays coming from the top of the object will arrive lower than those from the bottom or vice versa. The image usually is upside down by enhancing the illusion that the sky image seen in the distance is really an oil puddle of water acting as a mirror.
Hence a mirage occurs because the refractive index of the atmosphere increases with height.
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Note:
The real object in an inferior mirage is the sky (blue) or any distant (therefore bluish) object in that same direction. The mirage causes the observer to see a bright and bluish patch on the ground at some distance. The effect of atmospheric conditions on the refraction of light can be seen in the twinkling of the stars.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

State and prove converse of BPT Basic Proportionality class 10 maths CBSE




