
A mass is placed on a frictionless slope inclined at $30^\circ $ to the horizontal. The mass is then released. What is its acceleration down the slope?
A. $4.9\;{\rm{m}}{{\rm{s}}^{ - 2}}$
B. $5.7\;{\rm{m}}{{\rm{s}}^{ - 2}}$
C. $8.5\;{\rm{m}}{{\rm{s}}^{ - 2}}$
D. $9.8\;{\rm{m}}{{\rm{s}}^{ - 1}}$
Answer
576.6k+ views
Hint:First, we will draw a free body diagram showing all the forces acting on the mass. Then, we will balance the corresponding horizontal and vertical components of force to derive an equation for finding the acceleration.
Complete step by step answer:
Given: The angle of inclination of the frictionless slope, $\theta = 30^\circ $.
Let $m$ be the mass placed on the frictionless slope. Now, we draw a diagram showing the components of force acting on the mass as given below.
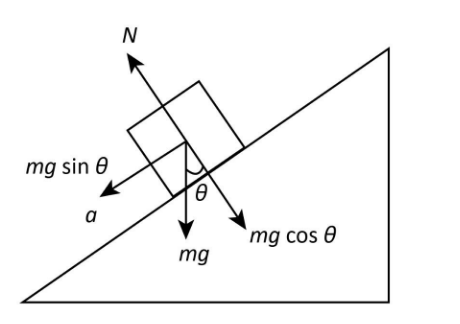
The force exerted on the mass by gravity can be written as,
$f = mg$
Here, $g$ is the acceleration due to gravity. The value of acceleration due to gravity is $9.8\;{\rm{m}}{{\rm{s}}^{ - 2}}$
The force due to gravity on the mass acts vertically downwards. We can split the vertical force of gravity into two components. A horizontal component $mg\sin \theta $ acting in a downward direction parallel to the slope and a vertical component $mg\cos \theta $ acting in a downward direction perpendicular to the plane of the slope as shown in the
diagram. From the diagram, the normal reaction force on the mass $m$ can be expressed as
$N = mg\cos \theta $
The mass moves downwards along the slope if it is released. Let $a$ be the acceleration of the mass when it is released. Therefore, we can express the force required to produce an acceleration $a$ as
$F = ma$
Since the slope is frictionless, we get the frictional force opposing the downward motion of the mass as zero. It implies that the force $F$ will equal the horizontal component of the force due to gravity. Equating the forces, we get
$
ma = mg\sin \theta \\
\Rightarrow a = g\sin \theta
$
Thus, we obtained an equation to find the acceleration of the mass.
Now, we substitute the values of $g$ and $\theta $ in the above equation to find acceleration.
$
a = 9.8\;{\rm{m}}{{\rm{s}}^{ - 2}} \times \sin 30^\circ \\
\Rightarrow a = 9.8\;{\rm{m}}{{\rm{s}}^{ - 2}} \times \dfrac{1}{2}\\
\therefore a = 4.9\;{\rm{m}}{{\rm{s}}^{ - 2}}
$
Therefore, we obtained the acceleration of the mass as $4.9\;{\rm{m}}{{\rm{s}}^{ - 2}}$.
Hence, option A is correct.
Note:In the question, only the value for the angle of inclination of the slope is given. So, we might tend to think that the acceleration cannot be found since no other quantities are given. Therefore, we should not assume anything and try to draw the free body diagram corresponding to the mass. In questions like this where the mass slips down along a frictionless slope, the acceleration will be always $g\sin \theta $, and hence, we can also calculate the answer directly without drawing the free body diagram.
Complete step by step answer:
Given: The angle of inclination of the frictionless slope, $\theta = 30^\circ $.
Let $m$ be the mass placed on the frictionless slope. Now, we draw a diagram showing the components of force acting on the mass as given below.

The force exerted on the mass by gravity can be written as,
$f = mg$
Here, $g$ is the acceleration due to gravity. The value of acceleration due to gravity is $9.8\;{\rm{m}}{{\rm{s}}^{ - 2}}$
The force due to gravity on the mass acts vertically downwards. We can split the vertical force of gravity into two components. A horizontal component $mg\sin \theta $ acting in a downward direction parallel to the slope and a vertical component $mg\cos \theta $ acting in a downward direction perpendicular to the plane of the slope as shown in the
diagram. From the diagram, the normal reaction force on the mass $m$ can be expressed as
$N = mg\cos \theta $
The mass moves downwards along the slope if it is released. Let $a$ be the acceleration of the mass when it is released. Therefore, we can express the force required to produce an acceleration $a$ as
$F = ma$
Since the slope is frictionless, we get the frictional force opposing the downward motion of the mass as zero. It implies that the force $F$ will equal the horizontal component of the force due to gravity. Equating the forces, we get
$
ma = mg\sin \theta \\
\Rightarrow a = g\sin \theta
$
Thus, we obtained an equation to find the acceleration of the mass.
Now, we substitute the values of $g$ and $\theta $ in the above equation to find acceleration.
$
a = 9.8\;{\rm{m}}{{\rm{s}}^{ - 2}} \times \sin 30^\circ \\
\Rightarrow a = 9.8\;{\rm{m}}{{\rm{s}}^{ - 2}} \times \dfrac{1}{2}\\
\therefore a = 4.9\;{\rm{m}}{{\rm{s}}^{ - 2}}
$
Therefore, we obtained the acceleration of the mass as $4.9\;{\rm{m}}{{\rm{s}}^{ - 2}}$.
Hence, option A is correct.
Note:In the question, only the value for the angle of inclination of the slope is given. So, we might tend to think that the acceleration cannot be found since no other quantities are given. Therefore, we should not assume anything and try to draw the free body diagram corresponding to the mass. In questions like this where the mass slips down along a frictionless slope, the acceleration will be always $g\sin \theta $, and hence, we can also calculate the answer directly without drawing the free body diagram.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

The largest wind power cluster is located in the state class 11 social science CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

State and prove Bernoullis theorem class 11 physics CBSE

What steps did the French revolutionaries take to create class 11 social science CBSE

Which among the following are examples of coming together class 11 social science CBSE




