
A man standing on a level plane observes the angle of elevation of the top of the pole to be ‘a’. He walks a distance equal to double the height of pole towards it and finds that the angle of elevation increases to ‘2a’ then the value of ‘a’ is
A. $\dfrac{\pi }{{12}}$
B. $\dfrac{\pi }{4}$
C. $\dfrac{\pi }{6}$
D. $\dfrac{\pi }{3}$
Answer
598.5k+ views
Hint: Here, first we will draw a figure based on the statements given in the question. Find the trigonometric ratio tan a and tan 2a from the two triangles formed, and then relate the values of tan a and tan 2a obtained from the two triangles to get the unknown value.
Complete step by step answer:
Let AB be the pole of height h units and D and C be the initial and final positions of the man walking towards the pole, and BC = x units.
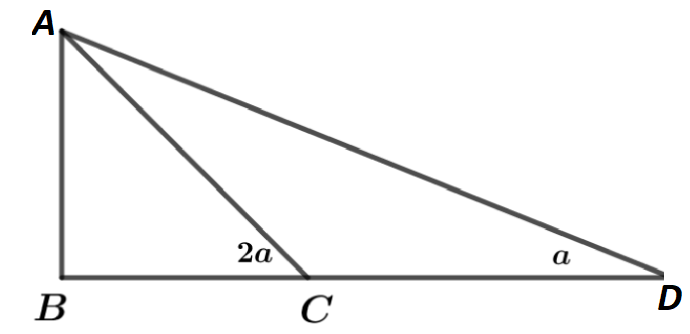
According to the question, distance travelled by man towards the pole is 2 times the height of the pole, i.e. $CD = 2AB$
That is $CD = 2h$and $BD = \left( {x + 2h} \right)$units
In $\vartriangle ABC$
$\tan 2a = \dfrac{{AB}}{{BC}}$
$\tan 2a = \dfrac{h}{x}$ …(i)
Also, In $\vartriangle ABD$
$\tan a = \dfrac{{AB}}{{BD}}$
$\tan a = \dfrac{h}{{x + 2h}}$ …(ii)
We have trigonometric identity, $\tan 2a = \dfrac{{2\tan a}}{{1 - {{\tan }^2}a}}$ …(iii)
Putting values of $\tan 2a$and $\tan a$ from equations (i) and (ii) in equation (iii), we have
$\dfrac{h}{x} = \dfrac{{2\left( {\dfrac{h}{{x + 2h}}} \right)}}{{1 - {{\left( {\dfrac{h}{{x + 2h}}} \right)}^2}}}$
On simplifying the equation, we have
$\dfrac{h}{x} = \dfrac{{\left( {\dfrac{{2h}}{{x + 2h}}} \right)}}{{\dfrac{{{{\left( {x + 2h} \right)}^2} - {h^2}}}{{{{\left( {x + 2h} \right)}^2}}}}}$
Using the identity $a^2-b^2=(a+b)(a-b)$, we get
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{h}{x} = \dfrac{{2h}}{{\dfrac{{\left( {x + 3h} \right)\left( {x + h} \right)}}{{\left( {x + 2h} \right)}}}}$
On cancelling h from both sides, we have
$\dfrac{1}{x} = \dfrac{{2\left( {x + 2h} \right)}}{{\left( {x + 3h} \right)\left( {x + h} \right)}}$
Cross-multiplying
${x^2} + 4hx + 3{h^2} = 2{x^2} + 4hx$
On cancelling 4hx of both sides we get
$3{h^2} = {x^2}$
On taking square root of both sides, we get
$\sqrt 3 h = x$
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{h}{x} = \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 3 }}$
From equation (i), we have
$\tan 2a = \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 3 }}$
Also we have,$\tan \dfrac{\pi }{6} = \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 3 }}$
On comparing, $2a = \dfrac{\pi }{6}$
$a = \dfrac{\pi }{{12}}$
Therefore, the value of a is $\dfrac{\pi }{{12}}$.
Therefore, option A is the correct answer.
Note:
In these types of questions, first draw the clear figure based on the given statements in question to understand the situation geometrically. Always keep in mind the situation while drawing figures as both angles of elevations are on the same side of pole or different sides of pole, sometimes this makes more confusion. Always use trigonometric facts and formulae to solve to get the result in an easy way.
Complete step by step answer:
Let AB be the pole of height h units and D and C be the initial and final positions of the man walking towards the pole, and BC = x units.

According to the question, distance travelled by man towards the pole is 2 times the height of the pole, i.e. $CD = 2AB$
That is $CD = 2h$and $BD = \left( {x + 2h} \right)$units
In $\vartriangle ABC$
$\tan 2a = \dfrac{{AB}}{{BC}}$
$\tan 2a = \dfrac{h}{x}$ …(i)
Also, In $\vartriangle ABD$
$\tan a = \dfrac{{AB}}{{BD}}$
$\tan a = \dfrac{h}{{x + 2h}}$ …(ii)
We have trigonometric identity, $\tan 2a = \dfrac{{2\tan a}}{{1 - {{\tan }^2}a}}$ …(iii)
Putting values of $\tan 2a$and $\tan a$ from equations (i) and (ii) in equation (iii), we have
$\dfrac{h}{x} = \dfrac{{2\left( {\dfrac{h}{{x + 2h}}} \right)}}{{1 - {{\left( {\dfrac{h}{{x + 2h}}} \right)}^2}}}$
On simplifying the equation, we have
$\dfrac{h}{x} = \dfrac{{\left( {\dfrac{{2h}}{{x + 2h}}} \right)}}{{\dfrac{{{{\left( {x + 2h} \right)}^2} - {h^2}}}{{{{\left( {x + 2h} \right)}^2}}}}}$
Using the identity $a^2-b^2=(a+b)(a-b)$, we get
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{h}{x} = \dfrac{{2h}}{{\dfrac{{\left( {x + 3h} \right)\left( {x + h} \right)}}{{\left( {x + 2h} \right)}}}}$
On cancelling h from both sides, we have
$\dfrac{1}{x} = \dfrac{{2\left( {x + 2h} \right)}}{{\left( {x + 3h} \right)\left( {x + h} \right)}}$
Cross-multiplying
${x^2} + 4hx + 3{h^2} = 2{x^2} + 4hx$
On cancelling 4hx of both sides we get
$3{h^2} = {x^2}$
On taking square root of both sides, we get
$\sqrt 3 h = x$
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{h}{x} = \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 3 }}$
From equation (i), we have
$\tan 2a = \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 3 }}$
Also we have,$\tan \dfrac{\pi }{6} = \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 3 }}$
On comparing, $2a = \dfrac{\pi }{6}$
$a = \dfrac{\pi }{{12}}$
Therefore, the value of a is $\dfrac{\pi }{{12}}$.
Therefore, option A is the correct answer.
Note:
In these types of questions, first draw the clear figure based on the given statements in question to understand the situation geometrically. Always keep in mind the situation while drawing figures as both angles of elevations are on the same side of pole or different sides of pole, sometimes this makes more confusion. Always use trigonometric facts and formulae to solve to get the result in an easy way.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

State and prove converse of BPT Basic Proportionality class 10 maths CBSE




