
A man of height $h$is walking away from a street lamp with a constant speed $v.$ The height of the street lamp is $3h.$ The rate at which length of the man’s shadow is increasing when he is at a distance $10h$ from the base of the street lamp is
Answer
588.3k+ views
Hint: $\dfrac{{dy}}{{dx}}$ represents the rate of change of $y$ with respect to $x.$ Assume the length of the man’s shadow to be $y$ and the distance from the street lamp at which he is standing to be $x.$ Then find the rate of change of $y$ with respect to $x.$
Complete step-by-step answer:
Let the horizontal distance of man from the street lamp be $x$
Let the length of the shadow of the man be $y$
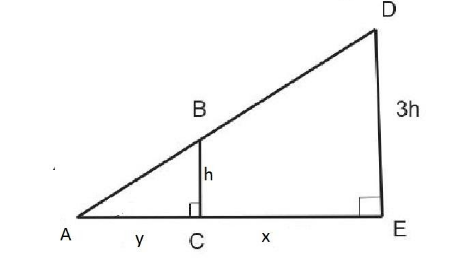
From the above figure we can say that
In $\Delta ACB$and $\Delta AED$
$\angle A = \angle A$(Common)
$\angle C = \angle E = {90^0}$ (Right angle)
$\angle B = \angle D$ (If two angles of two triangles are equal then the third angle must be equal as well)
Therefore, by AAA criteria of similarity of two triangles, we get
$\Delta ACB \approx \Delta AED$
Since, the ratio of the corresponding sides of similar triangles is equal, we can write
$\dfrac{{DE}}{{BC}} = \dfrac{{AE}}{{AC}}$
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{3h}}{h} = \dfrac{{x + y}}{y}\]
Cancelling the common terms, we get
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{x + y}}{y} = 3\]
By cross multiplying, we get
$x + y = 3y$
Re-arranging, we get
$ \Rightarrow 3y - y = x$
$ \Rightarrow 2y = x$
Different both the sides with respect to $x.$
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{2dy}}{{dx}} = 1$
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{dy}}{{dx}} = \dfrac{1}{2}$
Note: You need to find derivatives to find the rate of change. But to differentiate, you need to find a relation between the required variables. For that, you need to use some other properties like, similarity, trigonometric equations etc. So, just knowing differentiation is not enough.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Let the horizontal distance of man from the street lamp be $x$
Let the length of the shadow of the man be $y$

From the above figure we can say that
In $\Delta ACB$and $\Delta AED$
$\angle A = \angle A$(Common)
$\angle C = \angle E = {90^0}$ (Right angle)
$\angle B = \angle D$ (If two angles of two triangles are equal then the third angle must be equal as well)
Therefore, by AAA criteria of similarity of two triangles, we get
$\Delta ACB \approx \Delta AED$
Since, the ratio of the corresponding sides of similar triangles is equal, we can write
$\dfrac{{DE}}{{BC}} = \dfrac{{AE}}{{AC}}$
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{3h}}{h} = \dfrac{{x + y}}{y}\]
Cancelling the common terms, we get
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{x + y}}{y} = 3\]
By cross multiplying, we get
$x + y = 3y$
Re-arranging, we get
$ \Rightarrow 3y - y = x$
$ \Rightarrow 2y = x$
Different both the sides with respect to $x.$
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{2dy}}{{dx}} = 1$
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{dy}}{{dx}} = \dfrac{1}{2}$
Note: You need to find derivatives to find the rate of change. But to differentiate, you need to find a relation between the required variables. For that, you need to use some other properties like, similarity, trigonometric equations etc. So, just knowing differentiation is not enough.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Giving reasons state the signs positive or negative class 12 physics CBSE

Explain esterification reaction with the help of a class 12 chemistry CBSE

What is defined as a solenoid Depict a diagram with class 12 physics CBSE




