
A lotus is $20cm$ above the water surface in a pond and its stem is partly below the water surface. As the wind blew, the stem was pushed aside so that the lotus touched the water $40cm$ away from the original position of the stem. How much of the stem was below the water surface originally?
Answer
613.8k+ views
Hint:To find the length of the stem was below the water originally we need to draw the diagram according to the question carefully, and then with the help of Pythagoras theorem i.e. ${{(hypotenuse)}^{2}}={{(opposite)}^{2}}+{{(adjacent)}^{2}}$ find the answer.
Complete step-by-step answer:
To solve this question let us draw a diagram with the help of data given in the question as to understand clearly.
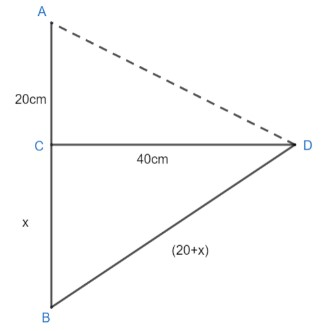
Here, A is the Lotus; AB is the stem of Lotus. When the wind blows the lotus from point A touches the surface of the water at point D, Thus, $AB=BD$. AC is the part of the stem which is above the surface of the water and BC is the part of the stem which is below the water.
As shown in the figure, the lotus was straight and it was 20 cm above the water surface of the pound at $'A'$ .
$\therefore AC=20cm$.
Let us say that the stem which is partly below the water surface is $'x'$ .
i.e. $BC=x$ .
Then the total length of the stem should be $AB=20+x$ .
Now, when the wind blew the stem is pushed aside so, that the lotus from point A touched water 40cm away from the original position at D i.e. $CD=40cm$ and $BD=\left( 20+x \right)$
Now, in \[\Delta BCD\]
$B{{D}^{2}}=B{{C}^{2}}+C{{D}^{2}}$ (By Pythagoras theorem ${{\left( 20+x \right)}^{2}}={{x}^{2}}+{{\left( 40 \right)}^{2}}$ .
We know that ${{\left( a+b \right)}^{2}}={{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}+2ab$
$\left( {{\left( 20 \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( x \right)}^{2}}+2\times 20\times x \right)={{x}^{2}}+1600$ .
$400+{{x}^{2}}+40x={{x}^{2}}+1600$ .
Subtract $'400'$ on both side we get –
${{x}^{2}}+40x={{x}^{2}}+1200$ .
Subtract $'{{x}^{2}}'$ from both side we get –
$40x=1200$ .
Divide $'40'$ on both side, we get –
$x=30$ .
Hence, the stem below the water surface originally is 30 cm.
Note: Students might get confused by this type of tricky question and can be mistaken while taking the values of hypotenuse, opposite and adjacent sides of a triangle. They should be very clear that the side opposite side of the right angle is hypotenuse, the perpendicular of the angle is opposite and the base of the triangle is adjacent. Thus the square of the length of the hypotenuse of the right triangle equals the sum of squares of the lengths of the other two sides. i.e. ${{(hypotenuse)}^{2}}={{(opposite)}^{2}}+{{(adjacent)}^{2}}$.
Complete step-by-step answer:
To solve this question let us draw a diagram with the help of data given in the question as to understand clearly.

Here, A is the Lotus; AB is the stem of Lotus. When the wind blows the lotus from point A touches the surface of the water at point D, Thus, $AB=BD$. AC is the part of the stem which is above the surface of the water and BC is the part of the stem which is below the water.
As shown in the figure, the lotus was straight and it was 20 cm above the water surface of the pound at $'A'$ .
$\therefore AC=20cm$.
Let us say that the stem which is partly below the water surface is $'x'$ .
i.e. $BC=x$ .
Then the total length of the stem should be $AB=20+x$ .
Now, when the wind blew the stem is pushed aside so, that the lotus from point A touched water 40cm away from the original position at D i.e. $CD=40cm$ and $BD=\left( 20+x \right)$
Now, in \[\Delta BCD\]
$B{{D}^{2}}=B{{C}^{2}}+C{{D}^{2}}$ (By Pythagoras theorem ${{\left( 20+x \right)}^{2}}={{x}^{2}}+{{\left( 40 \right)}^{2}}$ .
We know that ${{\left( a+b \right)}^{2}}={{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}+2ab$
$\left( {{\left( 20 \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( x \right)}^{2}}+2\times 20\times x \right)={{x}^{2}}+1600$ .
$400+{{x}^{2}}+40x={{x}^{2}}+1600$ .
Subtract $'400'$ on both side we get –
${{x}^{2}}+40x={{x}^{2}}+1200$ .
Subtract $'{{x}^{2}}'$ from both side we get –
$40x=1200$ .
Divide $'40'$ on both side, we get –
$x=30$ .
Hence, the stem below the water surface originally is 30 cm.
Note: Students might get confused by this type of tricky question and can be mistaken while taking the values of hypotenuse, opposite and adjacent sides of a triangle. They should be very clear that the side opposite side of the right angle is hypotenuse, the perpendicular of the angle is opposite and the base of the triangle is adjacent. Thus the square of the length of the hypotenuse of the right triangle equals the sum of squares of the lengths of the other two sides. i.e. ${{(hypotenuse)}^{2}}={{(opposite)}^{2}}+{{(adjacent)}^{2}}$.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

Name the part of the brain responsible for the precision class 11 biology CBSE

The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to AEffect class 11 biology CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE




