
A large glass slab $(\mu = \dfrac53)$ thickness 8 cm is placed over a point source of light on a plane surface. It is seen that light emerges out of the top surface of the slab from a circular area of radius r cm. What is the value of r?
Answer
588.6k+ views
Hint: Critical angle – It is an angle on which if light is incident from denser to rarer medium, it won’t go outside the medium but will refract through $90^{\circ}$. After this angle, the light will come back in the same medium as if the mirror is placed in its path. This phenomenon is called total internal reflection, also known as TIR.
Formula used:
$critical\ angle (c) = sin^{-1} \left[ \dfrac{1}{\mu} \right]$
As shown in the figure, ‘c’ represents the critical angle, the refraction angle of whose ray is $90^{\circ}$.
Complete answer:
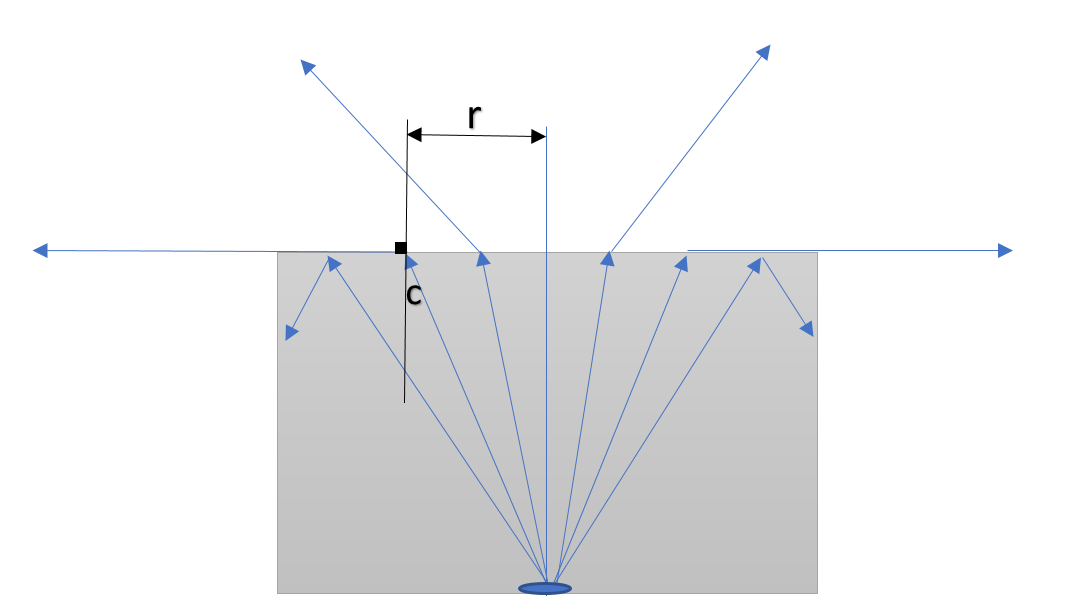
Only that object could be seen by the human eye from which light after reflection or by any other means falls on the human eye. Here, in the question, we are given that only the area of radius ‘r’ can be seen. That means all the rays after ‘r’, are definitely not going out. This must be the point of critical angle.
Now, $critical\ angle (c) = sin^{-1} \left[ \dfrac{1}{\mu} \right]$
$\implies c = sin^{-1} (\dfrac35) = 37^{\circ}$
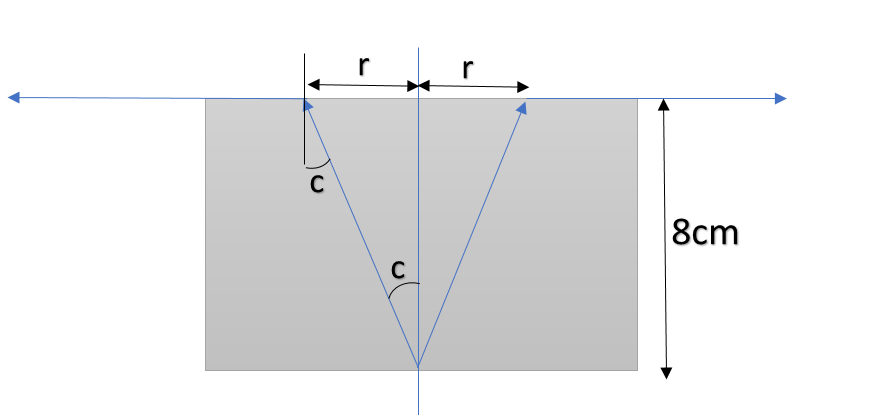
Now, from the figure, we have;
$tan(c) = \dfrac{r}{8}$
$\implies tan 37^{\circ} = \dfrac{r}{8}$
$\implies r = 8\times \dfrac{3}{4} = 6 cm$
Hence r = 6 cm.
Note:
The speed of light changes if it enters from one medium to another. Refractive index is a property of the medium which is the measure of how slow the speed of light gets on entering a medium. The refractive index is a unique property of a medium which can be constant or variable. Certain physical quantities like temperature govern the change of refractive index of a material. These concepts of total internal reflection (TIR) and critical angle are very important in understanding different natural phenomena like the formation of the rainbow is based on the concept of total internal reflection.
Formula used:
$critical\ angle (c) = sin^{-1} \left[ \dfrac{1}{\mu} \right]$
As shown in the figure, ‘c’ represents the critical angle, the refraction angle of whose ray is $90^{\circ}$.
Complete answer:

Only that object could be seen by the human eye from which light after reflection or by any other means falls on the human eye. Here, in the question, we are given that only the area of radius ‘r’ can be seen. That means all the rays after ‘r’, are definitely not going out. This must be the point of critical angle.
Now, $critical\ angle (c) = sin^{-1} \left[ \dfrac{1}{\mu} \right]$
$\implies c = sin^{-1} (\dfrac35) = 37^{\circ}$

Now, from the figure, we have;
$tan(c) = \dfrac{r}{8}$
$\implies tan 37^{\circ} = \dfrac{r}{8}$
$\implies r = 8\times \dfrac{3}{4} = 6 cm$
Hence r = 6 cm.
Note:
The speed of light changes if it enters from one medium to another. Refractive index is a property of the medium which is the measure of how slow the speed of light gets on entering a medium. The refractive index is a unique property of a medium which can be constant or variable. Certain physical quantities like temperature govern the change of refractive index of a material. These concepts of total internal reflection (TIR) and critical angle are very important in understanding different natural phenomena like the formation of the rainbow is based on the concept of total internal reflection.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers

Give simple chemical tests to distinguish between the class 12 chemistry CBSE

Define Vant Hoff factor How is it related to the degree class 12 chemistry CBSE




