
A ladder $ 15 $ meters long reaches a window which is $ 9 $ meters above the ground on one side of the street. Keeping its foot at the very same point, the ladder is turned to the other side of the street to reach a window $ 12 $ meters high. The width of the street is:
(A) $ 19 $ meters
(B) $ 20 $ meters
(C) $ 21 $ meters
(D) $ 22 $ meters
Answer
525k+ views
Hint: The given question involves the concepts of heights and distances and Pythagoras theorem. The ladder forms two right angled triangles on the two sides of the street and we have to solve both the right angled triangles in order to find the length of the street. We are provided with lengths of two of the sides of both triangles and are required to find the length of the third sides of both triangles. This can be done easily using the Pythagoras theorem. However, we first need to know the position of the right angle in the right angled triangle before applying the Pythagoras theorem.
Complete step by step solution:
So, the length of the ladder $ = 15m $
Height reached by ladder on one side of the street $ = 9m $
Height reached on other side of the street $ = 12m $
Now, we represent the situation in the figure below.
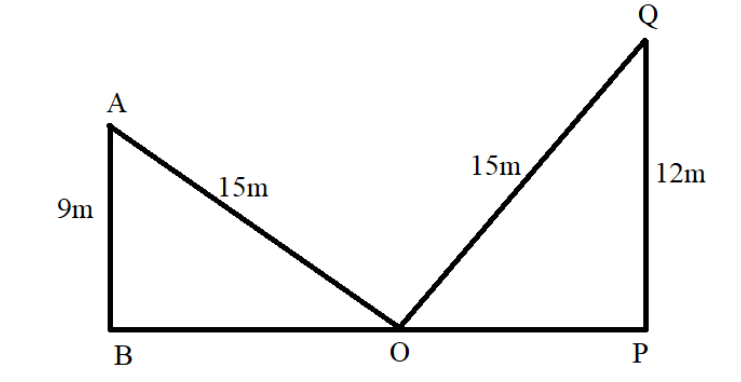
Now, we have two right angle triangles with us.
In triangle AOB,
$ \angle ABO = {90^ \circ } $
$ AO = 15m $ and $ AB = 9m $
Following the Pythagoras theorem, we have \[{\left( {Hypotenuse} \right)^2} = {\left( {Base} \right)^2} + {\left( {Altitude} \right)^2}\].
So, applying the Pythagoras theorem in the given triangle ABC, we get,
$ \Rightarrow A{O^2} = A{B^2} + B{O^2} $
$ \Rightarrow {\left( {15m} \right)^2} = {\left( {9m} \right)^2} + B{O^2} $
Evaluating the squares of the terms, we get,
$ \Rightarrow 225{m^2} = 81{m^2} + B{O^2} $
$ \Rightarrow B{O^2} = \left( {225 - 81} \right){m^2} $
Simplifying the calculations and taking square root on both sides of the equation, we get,
\[ \Rightarrow BO = \sqrt {144} m\]
Now, we know that the square root of $ 144 $ is $ 12 $ . So, we get,
\[ \Rightarrow BO = 12m\]
So, the length of BO is \[12m\].
Now, in triangle POQ,
$ \angle QPO = {90^ \circ } $
$ PO = 15m $ and $ PQ = 12m $
Following the Pythagoras theorem, we have \[{\left( {Hypotenuse} \right)^2} = {\left( {Base} \right)^2} + {\left( {Altitude} \right)^2}\].
So, applying the Pythagoras theorem in the given triangle ABC, we get,
$ \Rightarrow P{O^2} = P{Q^2} + Q{O^2} $
$ \Rightarrow {\left( {15m} \right)^2} = {\left( {12m} \right)^2} + Q{O^2} $
Evaluating the squares of the terms, we get,
$ \Rightarrow 225{m^2} = 144{m^2} + Q{O^2} $
$ \Rightarrow Q{O^2} = \left( {225 - 144} \right){m^2} $
Simplifying the calculations and taking square root on both sides of the equation, we get,
\[ \Rightarrow QO = \sqrt {81} m\]
Now, we know that the square root of $ 81 $ is $ 9 $ . So, we get,
\[ \Rightarrow QO = 9m\]
So, the length of QO is \[9m\].
Now, we know that the length of the street is the sum of the lengths of QO and BO. So, we get,
Length of street $ = 12m + 9m = 21m $
Hence, the length of the street is $ 21m $ .
Therefore, Option (C) is the correct answer.
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Note: For solving such type of question, where we need to find the third side of a triangle using the Pythagoras theorem, we need to know the position of right angle in the triangle beforehand since we need to know which of the three sides is the hypotenuse of the right angled triangle and then apply the Pythagoras theorem \[{\left( {Hypotenuse} \right)^2} = {\left( {Base} \right)^2} + {\left( {Altitude} \right)^2}\]. We can also find the given problem by the concepts of trigonometric ratios by calculating the trigonometric ratios first and using them to find the missing sides of the triangles.
Complete step by step solution:
So, the length of the ladder $ = 15m $
Height reached by ladder on one side of the street $ = 9m $
Height reached on other side of the street $ = 12m $
Now, we represent the situation in the figure below.

Now, we have two right angle triangles with us.
In triangle AOB,
$ \angle ABO = {90^ \circ } $
$ AO = 15m $ and $ AB = 9m $
Following the Pythagoras theorem, we have \[{\left( {Hypotenuse} \right)^2} = {\left( {Base} \right)^2} + {\left( {Altitude} \right)^2}\].
So, applying the Pythagoras theorem in the given triangle ABC, we get,
$ \Rightarrow A{O^2} = A{B^2} + B{O^2} $
$ \Rightarrow {\left( {15m} \right)^2} = {\left( {9m} \right)^2} + B{O^2} $
Evaluating the squares of the terms, we get,
$ \Rightarrow 225{m^2} = 81{m^2} + B{O^2} $
$ \Rightarrow B{O^2} = \left( {225 - 81} \right){m^2} $
Simplifying the calculations and taking square root on both sides of the equation, we get,
\[ \Rightarrow BO = \sqrt {144} m\]
Now, we know that the square root of $ 144 $ is $ 12 $ . So, we get,
\[ \Rightarrow BO = 12m\]
So, the length of BO is \[12m\].
Now, in triangle POQ,
$ \angle QPO = {90^ \circ } $
$ PO = 15m $ and $ PQ = 12m $
Following the Pythagoras theorem, we have \[{\left( {Hypotenuse} \right)^2} = {\left( {Base} \right)^2} + {\left( {Altitude} \right)^2}\].
So, applying the Pythagoras theorem in the given triangle ABC, we get,
$ \Rightarrow P{O^2} = P{Q^2} + Q{O^2} $
$ \Rightarrow {\left( {15m} \right)^2} = {\left( {12m} \right)^2} + Q{O^2} $
Evaluating the squares of the terms, we get,
$ \Rightarrow 225{m^2} = 144{m^2} + Q{O^2} $
$ \Rightarrow Q{O^2} = \left( {225 - 144} \right){m^2} $
Simplifying the calculations and taking square root on both sides of the equation, we get,
\[ \Rightarrow QO = \sqrt {81} m\]
Now, we know that the square root of $ 81 $ is $ 9 $ . So, we get,
\[ \Rightarrow QO = 9m\]
So, the length of QO is \[9m\].
Now, we know that the length of the street is the sum of the lengths of QO and BO. So, we get,
Length of street $ = 12m + 9m = 21m $
Hence, the length of the street is $ 21m $ .
Therefore, Option (C) is the correct answer.
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Note: For solving such type of question, where we need to find the third side of a triangle using the Pythagoras theorem, we need to know the position of right angle in the triangle beforehand since we need to know which of the three sides is the hypotenuse of the right angled triangle and then apply the Pythagoras theorem \[{\left( {Hypotenuse} \right)^2} = {\left( {Base} \right)^2} + {\left( {Altitude} \right)^2}\]. We can also find the given problem by the concepts of trigonometric ratios by calculating the trigonometric ratios first and using them to find the missing sides of the triangles.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 9 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 9 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Trending doubts
Find the sum of series 1 + 2 + 3 + 4 + 5 + + 100 class 9 maths CBSE

Distinguish between Conventional and nonconventional class 9 social science CBSE

Find the mode and median of the data 13 16 12 14 1-class-9-maths-CBSE

Describe the 4 stages of the Unification of German class 9 social science CBSE

What is the role of Mahatma Gandhi in national movement

What was the Treaty of Constantinople of 1832 class 9 social science CBSE





