
A is named as:
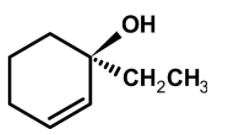
A) $\text{ }\left[ \text{R} \right]-1-\text{ethylcyclohex}-2-\text{enol }$
B) $\text{ }\left[ \text{S} \right]-1-\text{ethylcyclohex}-2-\text{enol }$
C) $\text{ S}-3-\text{ethylcyclohex}-3-\text{en}-3-\text{ol }$
D) None of these

Answer
591.3k+ views
Hint: The compound can be named based on IUPAC rules. The general presentation of the organic compound is as follows:
\[\text{ Substituents + Word root + primary suffix + secondary suffix }\]
If the compound contains the chiral carbon atoms, then the stereochemistry at the chiral carbon atom is expressed as R or S configuration. It depends on the properties assigned to the substituents.
Complete answer:
We are interested in determining the name of the organic compound. We will follow the two-step to determine the name of the compound
1) IUPAC nomenclature
2) Stereochemistry or the configuration at the chiral centre
Step 1) IUPAC nomenclature:
The compound is given as follows:
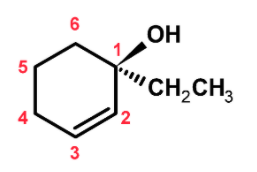
The compound has a six-membered ring. The word root would be hexane. Since it is a ring we add the ‘cyclo’ before the hexane word root.
The ring has a substituent such as a hydroxyl group $\text{ }-\text{OH }$ and an ethyl group$\text{ }-\text{C}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\text{C}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}\text{ }$. The $\text{ }-\text{OH }$group is treated as the primary functional group and written as a secondary suffix. The secondary suffix is added to the work root. Thus we add ‘-ol’ as the secondary suffix. The compound contains the double bond at the 2 number position. It is treated as a primary suffix. The ethyl group is treated as a substituent. The IUPAC name of the compound is,
$\text{ Substituents +Cyclo + Word root + primary suffix + secondary suffix }$
The name is,
$\text{ 1}-\text{Ethyl}-\text{cyclohex}-2-\text{enol }$
Step 2) now will find out the configuration at the chiral centre. The compound $\text{ 1}-\text{Ethyl}-\text{cyclohex}-2-\text{enol }$has a chiral centre at the $\text{ }{{\text{C}}_{\text{1}}}\text{ }$ carbon position. The $\text{ }{{\text{C}}_{\text{1}}}\text{ }$carbon atom is bonded to the$\text{ }-\text{OH }$, $\text{ }-\text{C}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\text{C}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}\text{ }$and two carbon atom on either side of it.
To determine the configuration,
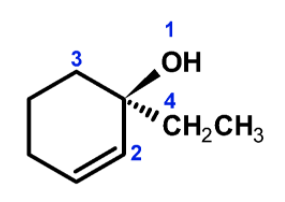
1) First assign the properties to the groups on the chiral carbon atom. The priorities are assigned based on the atomic number of the directly bonded atom. The oxygen of the hydroxyl group has a higher atomic number than the other groups. Thus the $\text{ }-\text{OH }$has given the (1) propriety .the other priorities are as shown in the following figure,
Now, draw an arrow starting from the highest priority group to the lowest priority group.
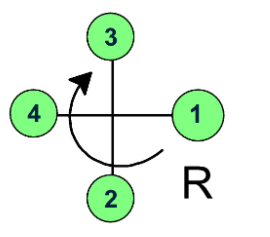
Here, the arrow goes through the clockwise direction, the chiral carbon has the R configuration.
Thus the name of the compound A is [R]-1-methylcyclohex-2-enol.
Hence, (A) is the correct option.
Note: The R and S, when the lowest priority group is towards the observer (wedge) then the configuration obtained is changes form $\text{ R}\to \text{ S }$ or$\text{S}\to \text{ R}$. If the lowest priority group is away from the observer (dashed), then the configuration remains as it is. Here, the lowest priority group is away from the observer thus no change in the configuration.
\[\text{ Substituents + Word root + primary suffix + secondary suffix }\]
If the compound contains the chiral carbon atoms, then the stereochemistry at the chiral carbon atom is expressed as R or S configuration. It depends on the properties assigned to the substituents.
Complete answer:
We are interested in determining the name of the organic compound. We will follow the two-step to determine the name of the compound
1) IUPAC nomenclature
2) Stereochemistry or the configuration at the chiral centre
Step 1) IUPAC nomenclature:
The compound is given as follows:

The compound has a six-membered ring. The word root would be hexane. Since it is a ring we add the ‘cyclo’ before the hexane word root.
The ring has a substituent such as a hydroxyl group $\text{ }-\text{OH }$ and an ethyl group$\text{ }-\text{C}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\text{C}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}\text{ }$. The $\text{ }-\text{OH }$group is treated as the primary functional group and written as a secondary suffix. The secondary suffix is added to the work root. Thus we add ‘-ol’ as the secondary suffix. The compound contains the double bond at the 2 number position. It is treated as a primary suffix. The ethyl group is treated as a substituent. The IUPAC name of the compound is,
$\text{ Substituents +Cyclo + Word root + primary suffix + secondary suffix }$
The name is,
$\text{ 1}-\text{Ethyl}-\text{cyclohex}-2-\text{enol }$
Step 2) now will find out the configuration at the chiral centre. The compound $\text{ 1}-\text{Ethyl}-\text{cyclohex}-2-\text{enol }$has a chiral centre at the $\text{ }{{\text{C}}_{\text{1}}}\text{ }$ carbon position. The $\text{ }{{\text{C}}_{\text{1}}}\text{ }$carbon atom is bonded to the$\text{ }-\text{OH }$, $\text{ }-\text{C}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\text{C}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}\text{ }$and two carbon atom on either side of it.
To determine the configuration,
1) First assign the properties to the groups on the chiral carbon atom. The priorities are assigned based on the atomic number of the directly bonded atom. The oxygen of the hydroxyl group has a higher atomic number than the other groups. Thus the $\text{ }-\text{OH }$has given the (1) propriety .the other priorities are as shown in the following figure,

Now, draw an arrow starting from the highest priority group to the lowest priority group.

Here, the arrow goes through the clockwise direction, the chiral carbon has the R configuration.
Thus the name of the compound A is [R]-1-methylcyclohex-2-enol.
Hence, (A) is the correct option.
Note: The R and S, when the lowest priority group is towards the observer (wedge) then the configuration obtained is changes form $\text{ R}\to \text{ S }$ or$\text{S}\to \text{ R}$. If the lowest priority group is away from the observer (dashed), then the configuration remains as it is. Here, the lowest priority group is away from the observer thus no change in the configuration.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers

Give simple chemical tests to distinguish between the class 12 chemistry CBSE

Define Vant Hoff factor How is it related to the degree class 12 chemistry CBSE




