
A horizontal force of 10 N is necessary to just hold a block stationary against a wall. The coefficient of friction between the block and the wall is 0.2. Find out the weight of the block.
${\text{A}}{\text{.}}$ 100 N
${\text{B}}{\text{.}}$ 2 N
${\text{C}}{\text{.}}$ 20 N
${\text{D}}{\text{.}}$ 50 N
Answer
619.2k+ views
Hint- Here, we will proceed by drawing the free body diagram of the block showing all the forces acting on the given block. Then, we will apply the concept of equilibrium in order to find the weight of the block.
Complete step-by-step solution -
Used Formulas- ${\text{F}} = \mu {\text{N}}$ and Weight = mg.
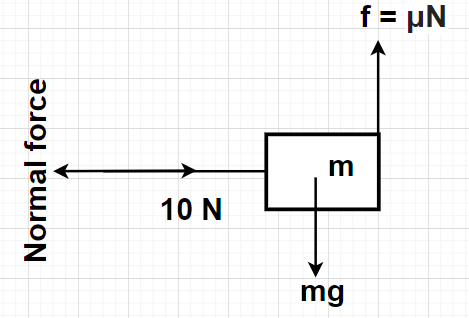
As shown in the figure, a force of 10 Newton is applied on the block just to hold it stationary against a wall. The forces which will be acting on the block are also shown in the other diagram. Normal force is acting on the block in a direction perpendicular to the surface of contact between the block and the surface (horizontal force). Since, the block has a tendency to fall downwards, so the friction force on the block will act opposite to it (i.e., friction force will be acting in the upward direction as shown in the figure).
Given, Applied force on the block = 10 N
Coefficient of friction between the block and the wall $\mu = 0.2$
As we know that, Force of friction is given by ${\text{F}} = \mu {\text{N}}$ where $\mu $ is the coefficient of friction between the two surfaces in contact and N is the normal force acting on the body
For equilibrium on the block, the horizontal forces acting to the left will be equal to the horizontal forces acting to the right and the vertical forces acting upwards will be equal to the vertical forces acting downwards.
According to the above concept, we can write
Normal Force on the block = Applied force to the block
$ \Rightarrow $ Normal Force on the block N = 10 Newton
Also, Force of friction on the block = mg
$
\Rightarrow \mu {\text{N}} = {\text{mg}} \\
\Rightarrow \left( {0.2} \right)\left( {10} \right) = {\text{mg}} \\
\Rightarrow {\text{mg}} = 2 \\
$
Since, weight of the block with mass m = mg = 2
Therefore, the weight of the block is 2 Newton (N).
Hence, option B is correct.
Note- In this particular problem, it was very important to determine the direction of the frictional force acting on the block. Since, the force of friction is acting upwards on the block so the force of friction will be acting downwards on the wall according to Newton’s third law of motion (i.e., To every action there is equal and opposite reaction).
Complete step-by-step solution -


Used Formulas- ${\text{F}} = \mu {\text{N}}$ and Weight = mg.
As shown in the figure, a force of 10 Newton is applied on the block just to hold it stationary against a wall. The forces which will be acting on the block are also shown in the other diagram. Normal force is acting on the block in a direction perpendicular to the surface of contact between the block and the surface (horizontal force). Since, the block has a tendency to fall downwards, so the friction force on the block will act opposite to it (i.e., friction force will be acting in the upward direction as shown in the figure).
Given, Applied force on the block = 10 N
Coefficient of friction between the block and the wall $\mu = 0.2$
As we know that, Force of friction is given by ${\text{F}} = \mu {\text{N}}$ where $\mu $ is the coefficient of friction between the two surfaces in contact and N is the normal force acting on the body
For equilibrium on the block, the horizontal forces acting to the left will be equal to the horizontal forces acting to the right and the vertical forces acting upwards will be equal to the vertical forces acting downwards.
According to the above concept, we can write
Normal Force on the block = Applied force to the block
$ \Rightarrow $ Normal Force on the block N = 10 Newton
Also, Force of friction on the block = mg
$
\Rightarrow \mu {\text{N}} = {\text{mg}} \\
\Rightarrow \left( {0.2} \right)\left( {10} \right) = {\text{mg}} \\
\Rightarrow {\text{mg}} = 2 \\
$
Since, weight of the block with mass m = mg = 2
Therefore, the weight of the block is 2 Newton (N).
Hence, option B is correct.
Note- In this particular problem, it was very important to determine the direction of the frictional force acting on the block. Since, the force of friction is acting upwards on the block so the force of friction will be acting downwards on the wall according to Newton’s third law of motion (i.e., To every action there is equal and opposite reaction).
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

Name the part of the brain responsible for the precision class 11 biology CBSE

The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to AEffect class 11 biology CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE




