
A hiker stands on the edge of a cliff of 490m, above the ground and throws a stone horizontally with an initial speed of $15m{{s}^{-1}}.$ Neglecting air resistance, find the time taken by the stone to reach the ground, and the speed with which it hits the ground. (Take g=$9.8m{{s}^{-2}}$)
Answer
520.1k+ views
Hint: The question is based on two dimensional kinematics. Knowing how to break speed and acceleration into horizontal and vertical components will help in solving this problem. Additionally, if you know formulas of various quantities such as height, velocity, acceleration etc. for two dimensional kinematics, it is helpful.
Step by step solution:
Let’s start off by making a diagram of the problem. We have a cliff of height 490m, from where a ball is thrown horizontally with velocity $15m{{s}^{-1}}.$ The gravity (g=$9.8m{{s}^{-2}}$) acts vertically downwards. This leads to the ball making a trajectory instead of following the straight path. We will consider the positive x axis as it moves from left to right and for y axis, positive is from top towards the bottom. Hence, g is positive.
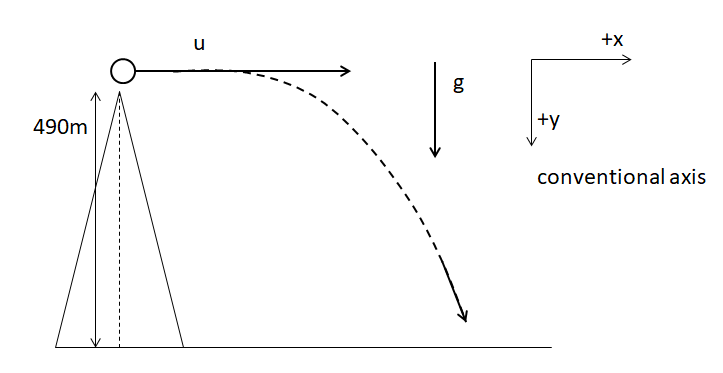
Hence, Vertical height$:h=y=490m.$ The initial velocity is only along the horizontal axis, hence, $u={{u}_{x}}=15m{{s}^{-1}}.$
Let’s use the formula for distance along the y axis, $y={{u}_{y}}t+\dfrac{1}{2}g{{t}^{2}}$.
Since, ${{u}_{y}}=0$ as no initial vertical velocity is given to the ball. Therefore, $490=0\times t+\dfrac{1}{2}(9.8){{t}^{2}}\Rightarrow 490=4.9{{t}^{2}}\Rightarrow 100={{t}^{2}}$
Therefore, $t=10\operatorname{s}.$
The final velocity of the particle along the y direction will be given by, $v_{y}^{2}-u_{y}^{2}=2gy$
Hence, $v_{y}^{2}-{{(0)}^{2}}=2(9.8)(490)\Rightarrow v_{y}^{2}={{98}^{2}}\Rightarrow {{v}_{y}}=98m{{s}^{-1}}$
The final velocity along the x axis (or) the horizontal direction is the same as the initial horizontal velocity as there is no acceleration along the x axis.
Therefore,${{v}_{x}}={{u}_{x}}=15m{{s}^{-1}}.$
Hence the final velocity will be $v=\sqrt{v_{x}^{2}+v_{y}^{2}}\Rightarrow v=\sqrt{{{98}^{2}}+{{15}^{2}}}=\sqrt{225+9604}=\sqrt{9829}\Rightarrow v=99.14m{{s}^{-1}}$
Hence, the ball will hit the ground with a velocity of $99.14m{{s}^{-1}}$ and the time of flight is 10s.
Note: An alternate way to find the final velocity along the vertical axis is using Newton's first law of motion. That is, $v=u+at$. This changes to ${{v}_{y}}={{u}_{y}}+{{a}_{y}}t$. Here initial velocity along vertical direction was already zero and hence, ${{v}_{y}}=0+9.8(10)\Rightarrow {{v}_{y}}=98m{{s}^{-1}}$ which is the same that we found earlier in the solution.
The time of flight will be the same that we found by using the y axis oriented variables as it would be, if we found out using the x axis oriented variables.
Step by step solution:
Let’s start off by making a diagram of the problem. We have a cliff of height 490m, from where a ball is thrown horizontally with velocity $15m{{s}^{-1}}.$ The gravity (g=$9.8m{{s}^{-2}}$) acts vertically downwards. This leads to the ball making a trajectory instead of following the straight path. We will consider the positive x axis as it moves from left to right and for y axis, positive is from top towards the bottom. Hence, g is positive.

Hence, Vertical height$:h=y=490m.$ The initial velocity is only along the horizontal axis, hence, $u={{u}_{x}}=15m{{s}^{-1}}.$
Let’s use the formula for distance along the y axis, $y={{u}_{y}}t+\dfrac{1}{2}g{{t}^{2}}$.
Since, ${{u}_{y}}=0$ as no initial vertical velocity is given to the ball. Therefore, $490=0\times t+\dfrac{1}{2}(9.8){{t}^{2}}\Rightarrow 490=4.9{{t}^{2}}\Rightarrow 100={{t}^{2}}$
Therefore, $t=10\operatorname{s}.$
The final velocity of the particle along the y direction will be given by, $v_{y}^{2}-u_{y}^{2}=2gy$
Hence, $v_{y}^{2}-{{(0)}^{2}}=2(9.8)(490)\Rightarrow v_{y}^{2}={{98}^{2}}\Rightarrow {{v}_{y}}=98m{{s}^{-1}}$
The final velocity along the x axis (or) the horizontal direction is the same as the initial horizontal velocity as there is no acceleration along the x axis.
Therefore,${{v}_{x}}={{u}_{x}}=15m{{s}^{-1}}.$
Hence the final velocity will be $v=\sqrt{v_{x}^{2}+v_{y}^{2}}\Rightarrow v=\sqrt{{{98}^{2}}+{{15}^{2}}}=\sqrt{225+9604}=\sqrt{9829}\Rightarrow v=99.14m{{s}^{-1}}$
Hence, the ball will hit the ground with a velocity of $99.14m{{s}^{-1}}$ and the time of flight is 10s.
Note: An alternate way to find the final velocity along the vertical axis is using Newton's first law of motion. That is, $v=u+at$. This changes to ${{v}_{y}}={{u}_{y}}+{{a}_{y}}t$. Here initial velocity along vertical direction was already zero and hence, ${{v}_{y}}=0+9.8(10)\Rightarrow {{v}_{y}}=98m{{s}^{-1}}$ which is the same that we found earlier in the solution.
The time of flight will be the same that we found by using the y axis oriented variables as it would be, if we found out using the x axis oriented variables.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




