
A hemispherical bowl is made of brass, 0.25 cm thickness. The inner radius of the bowl is 5 cm. Find the ratio of the outer surface area to the inner surface area.
Answer
622.8k+ views
Hint: First of all, find the outer radius of the bowl by adding the inner radius and thickness of the bowl. Now, find the surface area of the bowl by using \[2\pi {{r}^{2}}\] and substitute ‘r’ as the outer radius and inner radius to find the outer area and inner area and take the ratio of it.
Complete step-by-step solution -
Here, we are given a hemispherical bowl made of brass having 0.25 cm thickness. Its inner radius is 5 cm. We have to find the ratio of its outer surface area to the inner surface area. Let us, first of all, draw the side and front view of the hemispherical bowl made of brass to visualize the question.
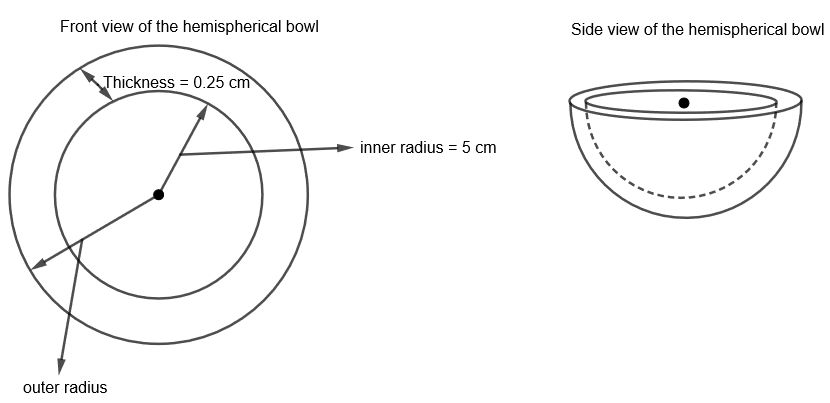
Here, we are given that the inner radius of the hemispherical bowl, \[\left( {{r}_{1}} \right)=5\text{ }cm\]
The thickness of hemispherical bowl = 0.25 cm
So, we get the outer radius of the hemispherical bowl, \[\left( {{r}_{2}} \right)=\] Inner radius of the hemispherical bowl + Thickness of the hemispherical bowl.
= 5 cm + 0.25 cm
\[{{r}_{2}}=5.25\text{ }cm\]
Now, we know that the surface area of the hemispherical bowl \[=2\pi {{r}^{2}}\] where ‘r’ is the radius of the bowl. So, we get the inner surface area of the hemispherical bowl,
\[{{H}_{i}}=2\pi {{\left( {{r}_{1}} \right)}^{2}}\]
By substituting the value of \[{{r}_{1}}=5\text{ }cm\] in the above equation, we get,
\[\begin{align}
& {{H}_{i}}=2\pi {{\left( 5 \right)}^{2}}\text{ c}{{\text{m}}^{2}} \\
& =2\pi \times 25\text{ c}{{\text{m}}^{2}} \\
& {{H}_{i}}=50\pi \text{ c}{{\text{m}}^{2}}......\left( i \right) \\
\end{align}\]
Also, we get the outer surface area of the hemispherical bowl,
\[{{H}_{o}}=2\pi {{\left( {{r}_{2}} \right)}^{2}}\]
By substituting the value of \[{{r}_{2}}=5.25\text{ }cm\] in the above equation, we get,
\[\begin{align}
& {{H}_{o}}=2\pi {{\left( 5.25 \right)}^{2}}\text{ c}{{\text{m}}^{2}} \\
& =2\pi \times \left( 27.5625 \right)\text{ c}{{\text{m}}^{2}} \\
& {{H}_{o}}=55.125\pi \text{ c}{{\text{m}}^{2}}......\left( ii \right) \\
\end{align}\]
So, we get the ratio of the outer surface area of the bowl to the inner surface area of the bowl as,
\[\dfrac{\text{Outer Surface area of the hemispherical bowl}}{\text{Inner surface area of the hemispherical bowl}}=\dfrac{{{H}_{o}}}{{{H}_{i}}}\]
By substituting the value of \[{{H}_{o}}\] and \[{{H}_{i}}\] from equation (ii) and (i) respectively, we get,
\[\dfrac{\text{Outer Surface area of the hemispherical bowl}}{\text{Inner surface area of the hemispherical bowl}}=\dfrac{55.125\pi \text{ c}{{\text{m}}^{2}}}{50\pi \text{ c}{{\text{m}}^{2}}}\]
Hence, we get the ratio of the outer surface area of the bowl to the inner surface area of the bowl as 1.1025.
Note: By looking at the hemisphere and surface area, some students make this mistake of writing the surface area as \[3\pi {{r}^{2}}\] in this wrong question. Students must note that the bowl is an open hemispherical container. So, we use the formula for the surface area as \[2\pi {{r}^{2}}\] where ‘r’ is the radius of the hemisphere. Also, note that the ratio of the same quantity is a dimensionless quantity. So here, we get the final answer without any dimensions because the quantities at numerator and denominator are the same and that is the surface area.
Complete step-by-step solution -
Here, we are given a hemispherical bowl made of brass having 0.25 cm thickness. Its inner radius is 5 cm. We have to find the ratio of its outer surface area to the inner surface area. Let us, first of all, draw the side and front view of the hemispherical bowl made of brass to visualize the question.

Here, we are given that the inner radius of the hemispherical bowl, \[\left( {{r}_{1}} \right)=5\text{ }cm\]
The thickness of hemispherical bowl = 0.25 cm
So, we get the outer radius of the hemispherical bowl, \[\left( {{r}_{2}} \right)=\] Inner radius of the hemispherical bowl + Thickness of the hemispherical bowl.
= 5 cm + 0.25 cm
\[{{r}_{2}}=5.25\text{ }cm\]
Now, we know that the surface area of the hemispherical bowl \[=2\pi {{r}^{2}}\] where ‘r’ is the radius of the bowl. So, we get the inner surface area of the hemispherical bowl,
\[{{H}_{i}}=2\pi {{\left( {{r}_{1}} \right)}^{2}}\]
By substituting the value of \[{{r}_{1}}=5\text{ }cm\] in the above equation, we get,
\[\begin{align}
& {{H}_{i}}=2\pi {{\left( 5 \right)}^{2}}\text{ c}{{\text{m}}^{2}} \\
& =2\pi \times 25\text{ c}{{\text{m}}^{2}} \\
& {{H}_{i}}=50\pi \text{ c}{{\text{m}}^{2}}......\left( i \right) \\
\end{align}\]
Also, we get the outer surface area of the hemispherical bowl,
\[{{H}_{o}}=2\pi {{\left( {{r}_{2}} \right)}^{2}}\]
By substituting the value of \[{{r}_{2}}=5.25\text{ }cm\] in the above equation, we get,
\[\begin{align}
& {{H}_{o}}=2\pi {{\left( 5.25 \right)}^{2}}\text{ c}{{\text{m}}^{2}} \\
& =2\pi \times \left( 27.5625 \right)\text{ c}{{\text{m}}^{2}} \\
& {{H}_{o}}=55.125\pi \text{ c}{{\text{m}}^{2}}......\left( ii \right) \\
\end{align}\]
So, we get the ratio of the outer surface area of the bowl to the inner surface area of the bowl as,
\[\dfrac{\text{Outer Surface area of the hemispherical bowl}}{\text{Inner surface area of the hemispherical bowl}}=\dfrac{{{H}_{o}}}{{{H}_{i}}}\]
By substituting the value of \[{{H}_{o}}\] and \[{{H}_{i}}\] from equation (ii) and (i) respectively, we get,
\[\dfrac{\text{Outer Surface area of the hemispherical bowl}}{\text{Inner surface area of the hemispherical bowl}}=\dfrac{55.125\pi \text{ c}{{\text{m}}^{2}}}{50\pi \text{ c}{{\text{m}}^{2}}}\]
Hence, we get the ratio of the outer surface area of the bowl to the inner surface area of the bowl as 1.1025.
Note: By looking at the hemisphere and surface area, some students make this mistake of writing the surface area as \[3\pi {{r}^{2}}\] in this wrong question. Students must note that the bowl is an open hemispherical container. So, we use the formula for the surface area as \[2\pi {{r}^{2}}\] where ‘r’ is the radius of the hemisphere. Also, note that the ratio of the same quantity is a dimensionless quantity. So here, we get the final answer without any dimensions because the quantities at numerator and denominator are the same and that is the surface area.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 10 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Who is known as the "Little Master" in Indian cricket history?

A boat goes 24 km upstream and 28 km downstream in class 10 maths CBSE

State and explain Ohms law class 10 physics CBSE

Distinguish between soap and detergent class 10 chemistry CBSE

a Why did Mendel choose pea plants for his experiments class 10 biology CBSE

Draw the diagram of the sectional view of the human class 10 biology CBSE




