
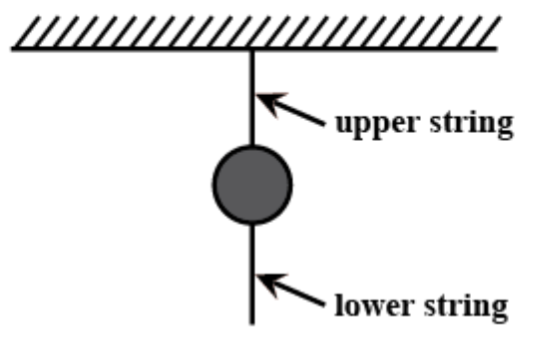
A heavy ball is suspended as shown. A quick jerk on the lower string will break that string but a slow pull on the lower string will break the upper string. The first result occurs because :
A). The force is too small to move the ball
B). Action and reaction are operating
C). The ball has inertia
D). Air friction holds the ball back

Answer
599.1k+ views
Hint: The phenomena of the ‘inertia ball experiment’ are often explained in terms of Newton’s three laws of motion. The 3rd law of motion states that whenever object A exerts a force on another object B, object B will simultaneously exert a force on object A with an equivalent magnitude within the other way.
Complete step-by-step solution:
Hence, when a force is applied to the lower string, the force is transferred along the string and exerts a force on the heavy ball. Assuming that the heavy ball may be a stationary point, it'll exert an equal and opposite force on the string.
These two forces, exerted by the physical tug and exerted by the heavy ball on the string causes tension within the string (as illustrated within the diagram). Similarly, the upper string experiences the tug at the lower string, but since the upper string has got to carry the load of the heavy ball, the strain within the upper string is bigger than the lower string by the mass of the heavy ball multiplied by the acceleration of gravity. However, different rates of forces can influence the speed of tension within the upper and lower string.
So, the correct answer is option C- the ball has inertia.
Additional Information:
Newton’s second law of motion states that the acceleration of an object is proportional to net forces applied and inversely proportional to the mass of the thing. Therefore, because the string has less inertia than the heavy ball, the lower string accelerates. As a result, the upper string doesn't experience the maximum amount stretch because the lower string and therefore the tension doesn't increase the maximum amount.
Note: The force applied on the ball is too small to move the ball and then the air friction holds the ball back. The heavy ball may be a stationary point, it'll exert an equal and opposite force on the string. It is the case of action and reaction and due to this we can conclude that the ball has inertia.
Complete step-by-step solution:
Hence, when a force is applied to the lower string, the force is transferred along the string and exerts a force on the heavy ball. Assuming that the heavy ball may be a stationary point, it'll exert an equal and opposite force on the string.
These two forces, exerted by the physical tug and exerted by the heavy ball on the string causes tension within the string (as illustrated within the diagram). Similarly, the upper string experiences the tug at the lower string, but since the upper string has got to carry the load of the heavy ball, the strain within the upper string is bigger than the lower string by the mass of the heavy ball multiplied by the acceleration of gravity. However, different rates of forces can influence the speed of tension within the upper and lower string.
So, the correct answer is option C- the ball has inertia.
Additional Information:
Newton’s second law of motion states that the acceleration of an object is proportional to net forces applied and inversely proportional to the mass of the thing. Therefore, because the string has less inertia than the heavy ball, the lower string accelerates. As a result, the upper string doesn't experience the maximum amount stretch because the lower string and therefore the tension doesn't increase the maximum amount.
Note: The force applied on the ball is too small to move the ball and then the air friction holds the ball back. The heavy ball may be a stationary point, it'll exert an equal and opposite force on the string. It is the case of action and reaction and due to this we can conclude that the ball has inertia.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

The largest wind power cluster is located in the state class 11 social science CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

State and prove Bernoullis theorem class 11 physics CBSE

What steps did the French revolutionaries take to create class 11 social science CBSE

Which among the following are examples of coming together class 11 social science CBSE




