
A glass capillary tube is of the shape of truncated cone with an apex angle $\alpha $ so that its two ends have cross sections of different radii. When dipped in water vertically, water rises in it to a height h, where the radius of its cross section if b. if the surface tension of water is S, its density is $\rho $, and its contact angle with glass is $\theta $, the value of h will be (g is the acceleration due to gravity)
A. $\dfrac{2S}{bg\rho }\cos (\theta -\alpha )$
B. $\dfrac{2S}{bg\rho }\cos (\theta +\alpha )$
C. $\dfrac{2S}{bg\rho }\cos (\theta -\dfrac{\alpha }{2})$
D. $\dfrac{2S}{bg\rho }\cos (\theta +\dfrac{\alpha }{2})$
Answer
606.9k+ views
Hint: Use the concept of capillary action and angle of contact. Surface tension for liquid makes liquid to have a minimum possible area. Draw geometry over capillary. Use triangle property and rearrange or adjust the equation to get the result.
Complete step by step solution:
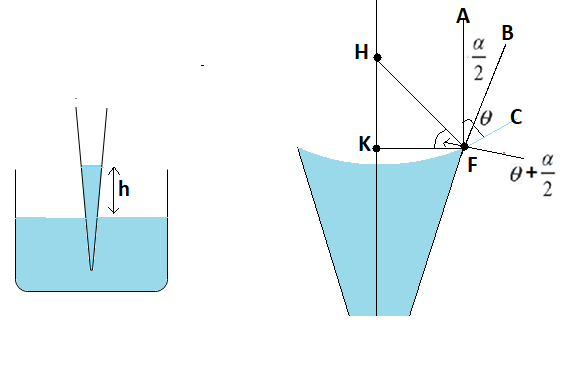
FA= extension of curved portion of capillary
FB= extension of edges of capillary tube
FA= perpendicular drawn
FH= line joining the point F with capillary axis at point H
FK= line joining the point F with capillary axis at point K
$\angle KFH=\theta +\dfrac{\alpha }{2}$
$\angle CFB=\theta $
$\angle AFB=\dfrac{\alpha }{2}$
When a glass of fine bore is dipped in a liquid, the liquid rises immediately to a certain height due to surface tension. The liquid column exerts a force by S per unit length of a line of contact at an inclination $\theta $ with the vertical and R is the radius of a capillary tube.
$\begin{align}
& In\Delta FKH \\
& \cos (\theta +\dfrac{\alpha }{2})=\dfrac{b}{R} \\
\end{align}$
Applying surface tension to capillary, we get
$\begin{align}
& {{P}_{0}}-\dfrac{2S}{R}+hg\rho ={{P}_{0}} \\
& hg\rho =\dfrac{2S}{R} \\
\end{align}$
Where, R=radius of capillary tube
$h=\dfrac{2S}{Rg\rho }$
Put value of R, then
$h=\dfrac{2S}{gb\rho }\cos (\theta +\dfrac{\alpha }{2})$
So the correct option is D.
Additional information:
Angle of contact $\theta $ is the angle made by tangent at the point of contact of the liquid surface with solid surface inside the liquid. The angle of contact is acute i.e. less than 90 for Water and angle of contact is obtuse i.e. more than 90 for mercury.
Note: Concept of capillary action is the same of all kinds of shape whether it is cone square or anything. You just need to take care of the cross-section of the capillary tube, a radius of it and water rise at a certain height. Don’t get confused about the shape of capillary tubes.
Complete step by step solution:

FA= extension of curved portion of capillary
FB= extension of edges of capillary tube
FA= perpendicular drawn
FH= line joining the point F with capillary axis at point H
FK= line joining the point F with capillary axis at point K
$\angle KFH=\theta +\dfrac{\alpha }{2}$
$\angle CFB=\theta $
$\angle AFB=\dfrac{\alpha }{2}$
When a glass of fine bore is dipped in a liquid, the liquid rises immediately to a certain height due to surface tension. The liquid column exerts a force by S per unit length of a line of contact at an inclination $\theta $ with the vertical and R is the radius of a capillary tube.
$\begin{align}
& In\Delta FKH \\
& \cos (\theta +\dfrac{\alpha }{2})=\dfrac{b}{R} \\
\end{align}$
Applying surface tension to capillary, we get
$\begin{align}
& {{P}_{0}}-\dfrac{2S}{R}+hg\rho ={{P}_{0}} \\
& hg\rho =\dfrac{2S}{R} \\
\end{align}$
Where, R=radius of capillary tube
$h=\dfrac{2S}{Rg\rho }$
Put value of R, then
$h=\dfrac{2S}{gb\rho }\cos (\theta +\dfrac{\alpha }{2})$
So the correct option is D.
Additional information:
Angle of contact $\theta $ is the angle made by tangent at the point of contact of the liquid surface with solid surface inside the liquid. The angle of contact is acute i.e. less than 90 for Water and angle of contact is obtuse i.e. more than 90 for mercury.
Note: Concept of capillary action is the same of all kinds of shape whether it is cone square or anything. You just need to take care of the cross-section of the capillary tube, a radius of it and water rise at a certain height. Don’t get confused about the shape of capillary tubes.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

Name the part of the brain responsible for the precision class 11 biology CBSE

The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to AEffect class 11 biology CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE




